A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and II
E) II and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In models of sigmoidal (logistic) population growth,
A) population growth rate slows dramatically as N approaches K.
B) new individuals are added to the population most rapidly at the beginning of the population's growth.
C) only density-dependent factors affect the rate of population growth.
D) only density-independent factors affect the rate of population growth.
E) carrying capacity is never reached.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carrying capacity is
A) seldom reached by marine producers and consumers because of the vast resources of the ocean.
B) the maximum population size that a particular environment can support.
C) fixed for most species over most of their range most of the time.
D) determined by density and dispersion data.
E) the term used to describe the stress a population undergoes due to limited resources.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
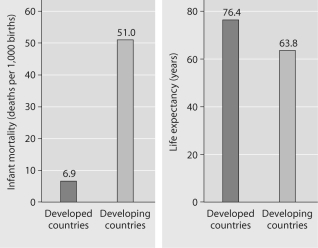 Infant mortality and life expectancy at birth in developed and developing countries. (Data as of 2005.) Figure 53.4
-What is a logical conclusion that can be drawn from the graphs above?
Infant mortality and life expectancy at birth in developed and developing countries. (Data as of 2005.) Figure 53.4
-What is a logical conclusion that can be drawn from the graphs above?
A) Developed countries have lower infant mortality rates and lower life expectancy than developing countries.
B) Developed countries have higher infant mortality rates and lower life expectancy than developing countries.
C) Developed countries have lower infant mortality rates and higher life expectancy than developing countries.
D) Developed countries have higher infant mortality rates and higher life expectancy than developing countries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following assumptions have to be made regarding the capture-recapture estimate of population size? I. Marked and unmarked individuals have the same probability of being trapped. II. The marked individuals have thoroughly mixed with population after being marked. III. No individuals have entered or left the population by immigration or emigration, and no individuals have been added by birth or eliminated by death during the course of the estimate.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) II and III only
E) I, II, and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the logistic growth equation dN/dt = rmaxN(K - N) /K,
A) the number of individuals added per unit time is greatest when N is close to zero.
B) the per capita growth rate (r) increases as N approaches K.
C) population growth is zero when N equals K.
D) the population grows exponentially when K is small.
E) the birth rate (b) approaches zero as N approaches K.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on current growth rates, Earth's human population in 2010 will be closest to
A) 2 million.
B) 3 billion.
C) 4 billion.
D) 7 billion.
E) 10 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to Figure 53.3, which depicts the age structure of three populations.
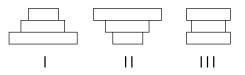 Figure 53.3
-Assuming these age-structure diagrams describe human populations, in which population is unemployment likely to be a societal issue in the future?
Figure 53.3
-Assuming these age-structure diagrams describe human populations, in which population is unemployment likely to be a societal issue in the future?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) No differences in the magnitude of future unemployment would be expected among these populations.
E) It is not possible to infer anything about future social conditions from age-structure diagrams.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Allee effect is used to describe a population that
A) has become so small that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing.
B) has become so large it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing.
C) approaches carrying capacity.
D) exceeds carrying capacity.
E) is in crash decline.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Logistic growth of a population is represented by dN/dt =
A)
B) rN
C) rN (K + N)
D) rN
E) rN
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Natural selection involves energetic trade-offs between
A) choosing how many offspring to produce over the course of a lifetime and how long to live.
B) producing large numbers of gametes when employing internal fertilization versus fewer numbers of gametes when employing external fertilization.
C) the emigration of individuals when they are no longer reproductively capable or committing suicide.
D) increasing the number of individuals produced during each reproductive episode with a corresponding decrease in parental care.
E) high survival rates of offspring and the cost of parental care.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the pattern of spacing for individuals within the boundaries of the population?
A) cohort
B) dispersion
C) Allee effect
D) iteroparous
E) semelparous
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the spring, you are studying the mice that live in a field near your home. There are lots of mice in this field, but you realize that you rarely observe any reproductive females. This most likely indicates
A) that there is selective predation on female mice.
B) that female mice die before reproducing.
C) that this habitat is a good place for mice to reproduce.
D) that you are observing immigrant mice.
E) that the breeding season is over
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Use the survivorship curves in Figure 53.1 to answer the following questions.
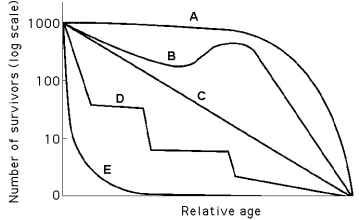 Figure 53.1
-Which curve best describes survivorship in marine mollusks?
Figure 53.1
-Which curve best describes survivorship in marine mollusks?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Use the survivorship curves in Figure 53.1 to answer the following questions.
 Figure 53.1
-Which curve best describes survivorship in elephants?
Figure 53.1
-Which curve best describes survivorship in elephants?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes having more than one reproductive episode during a lifetime?
A) cohort
B) dispersion
C) Allee effect
D) iteroparous
E) semelparous
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To measure the population density of monarch butterflies occupying a particular park, 100 butterflies are captured, marked with a small dot on a wing, and then released. The next day, another 100 butterflies are captured, including the recapture of 20 marked butterflies. One would estimate the population to be
A) 200.
B) 500.
C) 1,000.
D) 10,000.
E) 900,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a density-independent factor limiting human population growth?
A) social pressure for birth control
B) earthquakes
C) plagues
D) famines
E) pollution
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is territoriality an adaptive behavior for songbirds maintaining populations at or near their carrying capacity?
A) Songbirds expend a tremendous amount of energy defending territories so that they spend less time feeding their young and fledgling mortality increases.
B) Only the fittest males defend territories and they attract the fittest females so the best genes are conveyed to the next generation.
C) Songbird males defend territories commensurate with the size from which they can derive adequate resources for themselves, their mate, and their chicks.
D) Many individuals are killed in the ritualistic conflicts that go along with territorial defense.
E) Songbirds make improvements to the territories they inhabit so that they can all enjoy larger clutches and successfully fledged chicks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Natural selection has led to the evolution of diverse natural history strategies, which have in common
A) many offspring per reproductive episode.
B) limitation only by density-independent limiting factors.
C) adaptation to stable environments.
D) maximum lifetime reproductive success.
E) relatively large offspring.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 80
Related Exams