A) anti-A
B) anti-D
C) anti-B
D) anti-Rh
E) anti-O
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mary is tested for the amount of hemoglobin in her blood. The test results indicate that her hemoglobinlevel is 16 g/dL of blood. This value indicates that
A) she is suffering from anemia.
B) she has fewer red blood cells than normal.
C) her hematocrit is probably lower than normal.
D) she may be suffering from a form of leukemia.
E) her hemoglobin level is normal.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ is a condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is reduced.
A) Polycythemia
B) Leukemia
C) Anemia
D) Leukopenia
E) Thrombocytopenia
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jane has Type A blood; therefore, she
A) has antibodies to B agglutinogens.
B) can give blood to other people with Type A blood only.
C) can receive blood from other people with Type A blood only.
D) makes anti-A without ever having been exposed to Type A blood.
E) has B antigen on her RBCs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not one of the formed elements of blood?
A) RBCs
B) platelets
C) antibodies
D) lymphocytes
E) basophils
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of lymphopoiesis occurs mainly in the
A) spleen.
B) kidneys.
C) lymph nodes.
D) red bone marrow.
E) thymus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All the circulating red blood cells in an adult originate in the
A) heart.
B) thymus.
C) spleen.
D) red bone marrow.
E) lymph tissue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Natural killer cells are one of the functional classes of
A) neutrophils.
B) lymphocytes.
C) thrombocytes.
D) eosinophils.
E) monocytes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed Elements
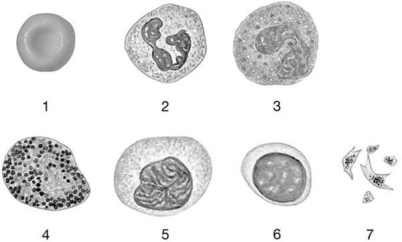 Use Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the cell labeled "4."
Use Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the cell labeled "4."
A) neutrophil
B) lymphocyte
C) platelet
D) basophil
E) monocyte
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have spent 24 hours traveling from the U.S to New Zealand, on quite a few airplanes with many stops.Because of the stress, changes in time zones, and short blocks of time between planes, you find yourself tired with a headache when you arrive. You are severely dehydrated. A hematocrit value of your blood would be ________ than normal because ________.
A) lower; more red blood cells are being made by the bone marrow
B) higher; you have less blood plasma volume
C) lower; the bone marrow is making fewer red blood cells due to the latitude of the airplanes
D) higher; more plasma proteins are made by the liver
E) lower; you have less blood plasma volume
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The combination of plasma and formed elements is called
A) serum.
B) lymph.
C) whole blood.
D) extracellular fluid.
E) packed blood.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most abundant proteins in blood plasma are
A) globulins.
B) transport proteins.
C) albumins.
D) lipoproteins.
E) fibrinogens.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalyzed by the enzyme
A) fibrinogen-converting enzyme.
B) plasmin.
C) factor VIII.
D) thrombin.
E) prothrombinase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hormone that stimulates platelet formation is
A) thymosin.
B) thrombopoietin.
C) erythropoietin.
D) colony-stimulating factor.
E) endothelin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Red blood cell production is regulated by the hormone
A) thymosin.
B) angiotensin.
C) erythropoietin.
D) thymopoietin.
E) renin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person's blood type is determined by the
A) size of the RBCs.
B) volume of the RBCs.
C) chemical composition of the hemoglobin.
D) presence of specific glycoproteins on the cell membrane.
E) shape of the RBCs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which plasma protein transports fatty acids and some hormones?
A) apolipoprotein
B) steroid-binding protein
C) hormone-binding protein
D) albumin
E) gamma globulin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small white blood cell with a large round nucleus would be a
A) neutrophil.
B) lymphocyte.
C) monocyte.
D) basophil.
E) eosinophil.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -Type A blood has what type of RBC surface antigen and what type of opposing antibodies? (Figure 19-6)
A) antigen A; anti-B antibodies
B) antigen B; anti-A antibodies
C) antigen A; anti-A antibodies
D) antigen B; anti-B antibodies
E) antigen A; both anti-A and anti-B antibodies
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these proteins functions to store or transport iron?
A) hemoglobin
B) ferritin
C) hemosiderin
D) transferrin
E) ferritin, hemosiderin, and transferrin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 162
Related Exams