A) cardiac output
B) stroke volume
C) end-systolic volume
D) end-diastolic volume
E) ejection fraction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cardiac muscle cells and skeletal muscle cells differ in a few ways. Which of the following is not one of them?
A) Cardiac muscle cells are smaller in size.
B) Cardiac muscle cells have a single, centered nucleus.
C) Cardiac muscle cells branch.
D) Skeletal muscle cells lack intercalated discs.
E) Cardiac muscle cells lack transverse tubules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The AV node delay is beneficial because
A) it allows time for the atria to contract.
B) it allows time for the ventricles to contract.
C) it allows time to send feedback to the brain about heartrate.
D) it decreases neural stimulation of the heart.
E) it hyperpolarizes the ventricular cell membranes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bicuspid or mitral valve is located
A) in the opening of the aorta.
B) in the opening of the pulmonary trunk.
C) where the venae cavae join the right atrium.
D) between the right atrium and right ventricle.
E) between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The basic heartrate established by the SA node is called the
A) pacemaker potential.
B) action potential.
C) vagal tone.
D) sinus rhythm.
E) SA potential.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The first blood vessels to branch from the aorta are the ________ arteries.
A) pulmonary
B) coronary
C) circumflex
D) carotid
E) subclavian
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prominent muscular ridges in the anterior atrial wall and auricles are called
A) pectinate muscles.
B) conus arteriosus.
C) papillary muscles.
D) trabeculae carneae.
E) fossa ovalis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ is the difference between the resting and maximal cardiac output.
A) end-systolic volume
B) end-diastolic volume
C) cardiac reserve
D) stroke volume
E) ejection fraction
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 20-2 Cardiac Cycle
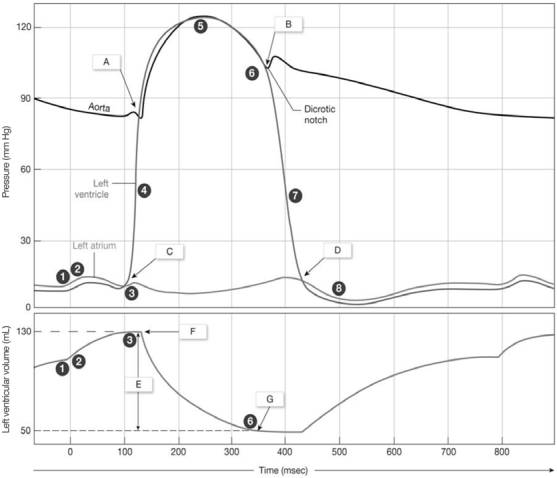 Use Figure 20-2 to answer the following questions:
-What occurs at "A" on the graph?
Use Figure 20-2 to answer the following questions:
-What occurs at "A" on the graph?
A) Semilunar valve opens.
B) Semilunar valve closes.
C) AV valve opens.
D) AV valve closes.
E) end systolic volume
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pulmonary veins carry blood to the
A) heart.
B) lungs.
C) brain.
D) intestines.
E) liver.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The earlike extension of the atrium is the
A) ventricle.
B) coronary sinus.
C) coronary sulcus.
D) auricle.
E) interatrial septum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term used to describe fluid collecting in the pericardial cavity that restricts the movement of the heart is known as
A) cardiac tamponade.
B) mitral valve prolapse.
C) pleural effusion.
D) cardiomyopathy.
E) pericarditis.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As blood leaves the right ventricle, it passes through the ________ and then into the pulmonary trunk.
A) pulmonary veins
B) conus arteriosus
C) aorta
D) inferior vena cava
E) superior vena cava
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cardiac output is increased by
A) sympathetic stimulation.
B) increased end systolic volume.
C) decreased end diastolic volume.
D) decreased venous return.
E) inhibiting the atrial reflex.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -Which ion's entry causes rapid depolarization? Which ion's entry causes the plateau? Which ion's exit causesrepolarization? (Figure 20-15)
A) sodium; calcium; potassium
B) potassium; calcium; sodium
C) calcium; sodium; potassium
D) sodium; potassium; calcium
E) sodium; iron; potassium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a result of the long refractory period in the cardiac action potential, cardiac muscle cannot exhibit
A) tonus.
B) treppe.
C) tetany.
D) recruitment.
E) fatigue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are ________ pulmonary veins.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 12
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The coronary sulcus is a groove that
A) marks the border between the atria and ventricles.
B) marks the boundary line between the right and left ventricles.
C) marks the boundary line between the right and left atria.
D) separates the atrioventricular valves from the atria.
E) separates the coronary arteries from the coronary veins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The circumflex branch and the anterior interventricular artery are branches of the
A) right coronary artery.
B) left coronary artery.
C) interventricular artery.
D) coronary sinus.
E) aorta.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ is an important ridge of muscle extending horizontally around the right ventricle from theinterventricular septum to the base of the anterior papillary muscle containing part of the conducting system.
A) auricle
B) pectinate muscle
C) trabeculae carneae
D) moderator band
E) conus arteriosus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 178
Related Exams