A) 0.2°C
B) 1.0°C
C) 2.0°C
D) 10.0°C
E) 20.0°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of a 1 millimolar NaOH solution?
A) pH 3
B) pH 8
C) pH 9
D) pH 10
E) pH 11
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does evaporation of water from a surface cause cooling of the surface?
A) The breaking of bonds between water molecules absorbs heat.
B) The water molecules with the most heat energy evaporate more readily.
C) The solute molecules left behind absorb heat.
D) Water molecules absorb heat from the surface in order to acquire enough energy to evaporate.
E) The expansion of water vapor extracts heat from the surface.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You live in Atlantic Canada and you are Skyping a friend in Manitoba. You are both complaining about the weather as both regions are being subjected to the same arctic air mass. As you discuss it, however, it becomes clear that she is experiencing a bitter cold that you are not. You realize that you had pretty much the same conversation last summer when it was much hotter in Manitoba than at home. -Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydroxide ion concentration of the lake?
A) 10⁻¹⁰ M
B) 10⁻⁴ M
C) 10⁻⁷ M
D) 10⁻¹⁴ M
E) 10 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How would acidification of sea water affect marine organisms?
A) Acidification would increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
B) Acidification would decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
C) Acidification would increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
D) Acidification would decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
E) Acidification would increase dissolved bicarbonate concentrations, and cause increased calcification of corals and shellfish.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
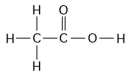 -How many grams would be equal to 1 mol of the compound shown in the figure above? (carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
-How many grams would be equal to 1 mol of the compound shown in the figure above? (carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You live in Atlantic Canada and you are Skyping a friend in Manitoba. You are both complaining about the weather as both regions are being subjected to the same arctic air mass. As you discuss it, however, it becomes clear that she is experiencing a bitter cold that you are not. You realize that you had pretty much the same conversation last summer when it was much hotter in Manitoba than at home. -Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of the lake?
A) 4.0 M
B) 10⁻¹⁰ M
C) 10⁻⁴ M
D) 10⁴ M
E) 4%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface tension of water?
A) Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures.
B) A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
C) Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D) Evaporation of sweat from the skin helps to keep people from overheating.
E) Water flows upward from the roots to the leaves in plants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
is 180 g/mol. Which of the following procedures should you carry out to make a 0.5 M solution of glucose?
A) Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of solution is 1 L.
B) Dissolve 90 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
C) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
D) Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
E) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 0.5 L of water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize?
A) ionic bonds
B) both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds
C) polar covalent bonds
D) hydrogen bonds
E) both polar covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slight negative charge at one end of one water molecule is attracted to the slight positive charge of another water molecule. What is this attraction called?
A) a covalent bond
B) a hydrogen bond
C) an ionic bond
D) a hydrophilic bond
E) a van der Waals interaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The only common substance on earth, which occurs naturally in all three physical states, is
A) oxygen.
B) carbon.
C) nitrogen.
D) sodium chloride.
E) water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these molecules would be soluble in water?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Buffers are substances that help resist shifts in pH by
A) releasing H⁺ to a solution when acids are added.
B) donating H⁺ to a solution when bases are added.
C) releasing OH⁻ to a solution when bases are added.
D) accepting H⁺ from a solution when acids are added.
E) both donating H⁺ to a solution when bases are added, and accepting H⁺ when acids are added.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Liquid water's high specific heat is mainly a consequence of the
A) small size of the water molecules.
B) high specific heat of oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
C) absorption and release of heat when hydrogen bonds break and form.
D) fact that water is a poor heat conductor.
E) higher density of liquid water than solid water (ice) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a freshly prepared 0.1 M solution of glucose in water. Each litre of this solution contains how many glucose molecules?
A) 6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D) 12.04 × 10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One litre of a solution of pH 9 has how many more hydroxyl ions (OH⁻) than 1 L of a solution of pH 4?
A) 5 times more
B) 32 times more
C) 50 000 times more
D) 10 000 times more
E) 100 000 times more
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Research indicates that acid precipitation can damage living organisms by
A) buffering aquatic systems such as lakes and streams.
B) decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and streams.
C) increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and streams.
D) washing away certain mineral ions that help buffer soil solution and are essential nutrients for plant growth.
E) both decreasing the H⁺ concentration of lakes and streams and increasing the OH⁻ concentration of lakes and streams.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following solutions would require the greatest amount of base to be added to bring the solution to neutral pH?
A) gastric juice at pH 2
B) vinegar at pH 3
C) tomato juice at pH 4
D) black coffee at pH 5
E) household bleach at pH 12
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Equal volumes (5 mL) of vinegar from a freshly opened bottle are added to each of the following solutions. After complete mixing, which of the mixtures will have the highest pH?
A) 100 mL of pure water
B) 100 mL of freshly brewed coffee
C) 100 mL of household cleanser containing 0.5 M ammonia
D) 100 mL of freshly squeezed orange juice
E) 100 mL of tomato juice
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 80
Related Exams