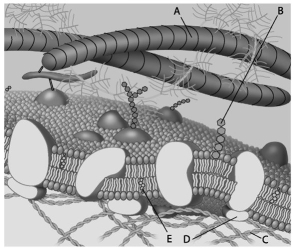
A) peripheral proteins.
B) phospholipids.
C) carbohydrates.
D) integral proteins.
E) cholesterol molecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease in humans in which the CFTR protein, which functions as a chloride ion channel, is missing or nonfunctional in cell membranes. -If the sodium ion concentration outside the cell increases, and the CFTR channel is open, in what direction will chloride ions and water move across the cell membrane?
A) Chloride ions will move out of the cell, and water will move into the cell.
B) Both chloride ions and water will move out of the cell.
C) Chloride ions will move into the cell, and water will move out of the cell.
D) Both chloride ions and water will move into the cell.
E) The movement of chloride ions and water molecules will not be affected by changes in sodium ion concentration outside the cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease in humans in which the CFTR protein, which functions as a chloride ion channel, is missing or nonfunctional in cell membranes. -The CFTR protein belongs to what category of membrane proteins?
A) gap junctions
B) aquaporins
C) electrogenic ion pumps
D) cotransporters
E) hydrophilic channels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of integral membrane proteins?
A) They lack tertiary structure.
B) They are loosely bound to the surface of the bilayer.
C) They are usually transmembrane proteins.
D) They are not mobile within the bilayer.
E) They serve only a structural role in membranes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a Paramecium, cell surface integral membrane proteins are synthesized
A) in the cytoplasm by free ribosomes.
B) by ribosomes in the nucleus.
C) by ribosomes bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
D) by ribosomes in the Golgi vesicles.
E) by ribosomes bound to the inner surface of the plasma membrane.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, match the labelled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description.
 -After the system reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed?
-After the system reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed?
A) The molarity of sucrose and glucose are equal on both sides.
B) The molarity of glucose is higher in side A than in side B.
C) The water level is higher in side A than in side B.
D) The water level is unchanged.
E) The water level is higher in side B than in side A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
Five dialysis bags, constructed from a semipermeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose, were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution. At 10-minute intervals, the bags were massed (weighed) and the percent change in mass of each bag was graphed.
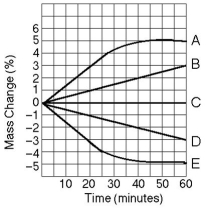 -Which line in the graph represents the bag that contained a solution isotonic to the 0.6 M solution at the beginning of the experiment?
-Which line in the graph represents the bag that contained a solution isotonic to the 0.6 M solution at the beginning of the experiment?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sodium-potassium pump in animal cells requires cytoplasmic ATP to pump ions across the plasma membrane. When the proteins of the pump are first synthesized in the rough ER, what side of the ER membrane will the ATP binding site be on?
A) It will be on the cytoplasmic side of the ER.
B) It will be on the side facing the interior of the ER.
C) It could be facing in either direction because proteins are properly reoriented in the Golgi apparatus.
D) It doesn't matter, because the pump is not active in the ER.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would likely move through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane most rapidly?
A) CO₂
B) an amino acid
C) glucose
D) K⁺
E) starch
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for a protein to be an integral membrane protein, it would have to be
A) hydrophilic.
B) hydrophobic.
C) amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region.
D) completely covered with phospholipids.
E) exposed on only one surface of the membrane.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure, proteins of the membrane are mostly
A) spread in a continuous layer over the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane.
B) confined to the hydrophobic interior of the membrane.
C) embedded in a lipid bilayer.
D) randomly oriented in the membrane, with no fixed inside-outside polarity.
E) free to depart from the fluid membrane and dissolve in the surrounding solution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The formulation of a model for a structure or for a process serves which of the following purposes?
A) It asks a scientific question.
B) It functions as a testable hypothesis.
C) It records observations.
D) It serves as a data point among results.
E) It can only be arrived at after years of experimentation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a reasonable explanation for why unsaturated fatty acids help keep any membrane more fluid at lower temperatures?
A) The double bonds form kinks in the fatty acid tails, preventing adjacent lipids from packing tightly.
B) Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content and therefore more cholesterol in membranes.
C) Unsaturated fatty acids are more polar than saturated fatty acids.
D) The double bonds block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids.
E) The double bonds result in shorter fatty acid tails and thinner membranes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects cells that have both CD4 and CCR5 cell surface molecules. The viral nucleic acid molecules are enclosed in a protein capsid, and the protein capsid is itself contained inside an envelope consisting of a lipid bilayer membrane and viral glycoproteins. One hypothesis for viral entry into cells is that binding of HIV membrane glycoproteins to CD4 and CCR5 initiates fusion of the HIV membrane with the plasma membrane, releasing the viral capsid into the cytoplasm. An alternative hypothesis is that HIV gains entry into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis, and membrane fusion occurs in the endocytotic vesicle. To test these alternative hypotheses for HIV entry, researchers labelled the lipids on the HIV membrane with a red fluorescent dye.
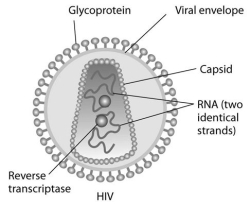 -Using live-cell fluorescence microscopy, researchers observed that a red fluorescent spot moved from the plasma membrane into the interior of target cells when red fluorescent dye-labelled HIV was added to the cells. What is the best conclusion from these observations?
-Using live-cell fluorescence microscopy, researchers observed that a red fluorescent spot moved from the plasma membrane into the interior of target cells when red fluorescent dye-labelled HIV was added to the cells. What is the best conclusion from these observations?
A) The hypothesis that HIV enters the cell via fusion with the target cell plasma membrane is proved.
B) The hypothesis that HIV enters the cell via fusion with the target cell plasma membrane is not supported.
C) The hypothesis that HIV enters the cell via endocytosis is proved.
D) The hypothesis that HIV enters the cell via endocytosis is not supported.
E) Neither hypothesis is supported by these results.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following membrane activities require energy from ATP hydrolysis?
A) facilitated diffusion of chloride ions across the membrane through a chloride channel
B) movement of water into a cell
C) Na⁺ ions moving out of a mammalian cell bathed in physiological saline
D) movement of glucose molecules into a bacterial cell from a medium containing a higher concentration of glucose than inside the cell
E) movement of carbon dioxide out of a paramecium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the years since the proposal of the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane, which of the following observations has been added to the model?
A) The membrane is only fluid across a very narrow temperature range.
B) Proteins rarely move, even though they possibly can do so.
C) Unsaturated lipids are excluded from the membranes.
D) The concentration of protein molecules is now known to be much higher.
E) The proteins are known to be made of only acidic amino acids.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects cells that have both CD4 and CCR5 cell surface molecules. The viral nucleic acid molecules are enclosed in a protein capsid, and the protein capsid is itself contained inside an envelope consisting of a lipid bilayer membrane and viral glycoproteins. One hypothesis for viral entry into cells is that binding of HIV membrane glycoproteins to CD4 and CCR5 initiates fusion of the HIV membrane with the plasma membrane, releasing the viral capsid into the cytoplasm. An alternative hypothesis is that HIV gains entry into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis, and membrane fusion occurs in the endocytotic vesicle. To test these alternative hypotheses for HIV entry, researchers labelled the lipids on the HIV membrane with a red fluorescent dye.
 -If HIV first enters the cell in an endocytotic vesicle, instead of directly fusing with the plasma membrane, then
-If HIV first enters the cell in an endocytotic vesicle, instead of directly fusing with the plasma membrane, then
A) HIV infection should be hindered by microtubule polymerization inhibitors such as nocodazole.
B) HIV infection should be more efficient at lower temperatures.
C) intact cortical actin microfilaments should interfere with HIV infection.
D) cells lacking integrins should be resistant to HIV infection.
E) addition of ligands for other cell-surface receptors to stimulate their endocytosis should increase the efficiency of HIV infection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phosphate transport system in bacteria imports phosphate into the cell even when the concentration of phosphate outside the cell is much lower than the cytoplasmic phosphate concentration. Phosphate import depends on a pH gradient across the membrane-more acidic outside the cell than inside the cell. Phosphate transport is an example of
A) passive diffusion.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) active transport.
D) osmosis.
E) cotransport.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the normal tonicity conditions for typical plant and animal cells?
A) The animal cell is in a hypotonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution.
B) The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypertonic solution.
C) The animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution.
D) The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution.
E) The animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, match the labelled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description.
 -Which component is a microfilament of the cytoskeleton?
-Which component is a microfilament of the cytoskeleton?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 78
Related Exams