A) starch and cellulose.
B) triglycerides and steroids.
C) proteins and nucleic acids.
D) phospholipids and glycolipids.
E) fatty acids and glycerol.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An excretory system that is partly based on the filtration of fluid under high hydrostatic pressure is the
A) flame bulb system of flatworms.
B) protonephridia of rotifers.
C) metanephridia of earthworms.
D) Malpighian tubules of insects.
E) kidneys of vertebrates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After blood flow is artificially reduced at one kidney, you would expect that kidney to secrete more of the hormone known as
A) erythropoietin.
B) angiotensinogen.
C) renin.
D) antidiuretic hormone.
E) atrial natriuretic peptide.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Human urine is usually more acidic than most other body fluids because
A) hydrogen ions are actively moved into the filtrate.
B) the sodium transporter exchanges one hydrogen ion for each sodium ion.
C) excreted plasma proteins are nearly all acidic ions.
D) excreted amino acids are in abundance.
E) potassium and sodium exchange generates lots of acidity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Low selectivity of solute movement is a characteristic of
A) salt pumping to control osmolarity.
B) H⁺ pumping to control pH.
C) reabsorption mechanisms along the proximal tubule.
D) filtration from the glomerular capillaries.
E) secretion along the distal tubule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When stimulated by aldosterone, the reabsorption of Na⁺ is increased along
A) the loop of Henle.
B) the collecting duct.
C) Bowman's capsule.
D) the proximal tubule.
E) the distal tubule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The high osmolarity of the renal medulla is maintained by all of the following except
A) diffusion of salt from the thin segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
B) active transport of salt from the upper region of the ascending limb.
C) the spatial arrangement of juxtamedullary nephrons.
D) diffusion of urea from the collecting duct.
E) diffusion of salt from the descending limb of the loop of Henle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The porbeagle shark (Lamana nasus) , found on the continental shelf between Newfoundland and Labrador and Gulf of Maine, excretes ________ which is produced in the ________.
A) urea, gall bladder
B) ammonia, kidney
C) urea, kidney
D) ammonia, liver
E) urea, liver
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A primary reason that the kidneys have one of the highest metabolic rates of all body organs is that
A) it stores the body's excess fats.
B) it has membranes of varying permeability to water.
C) it operates an extensive set of active-transport ion pumps.
D) it is the body's only means of shedding excess nutrients.
E) it has an abundance of myogenic smooth muscle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The osmoregulatory/excretory system of an earthworm is based on the operation of
A) protonephridia.
B) metanephridia.
C) Malpighian tubules.
D) nephrons.
E) ananephredia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The osmoregulatory process called secretion refers to the
A) formation of filtrate at an excretory structure.
B) reabsorption of nutrients from a filtrate.
C) selective elimination of excess ions and toxins from body fluids.
D) formation of an osmotic gradient along an excretory structure.
E) expulsion of urine from the body.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Processing of filtrate in the proximal and distal tubules
A) achieves the sorting of plasma proteins according to size.
B) achieves the conversion of toxic ammonia to less toxic urea.
C) maintains homeostasis of pH in body fluids.
D) regulates the speed of blood flow through the nephrons.
E) reabsorbs urea to maintain osmotic balance.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Excretory structures known as protonephridia are present in
A) flatworms.
B) earthworms.
C) insects.
D) vertebrates.
E) cnidarians.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fluid with the highest osmolarity is
A) distilled water.
B) plasma in birds.
C) plasma in mammals.
D) sea water in a tidal pool.
E) estuarine water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Within a normally functioning kidney, blood can be found in
A) the vasa recta.
B) Bowman's capsule.
C) the loop of Henle.
D) the proximal tubule.
E) the collecting duct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a laboratory experiment with three groups of students, one group drinks pure water, a second group drinks an equal amount of beer, and a third group drinks an equal amount of concentrated salt solution, all during the same time period. Their urine production is monitored for several hours. Which groups are expected to have the greatest and least amounts of urine, respectively?
A) Beer drinkers have the most; salt solution drinkers have the least.
B) Salt solution drinkers have the most; water drinkers have the least.
C) Water drinkers have the most; beer drinkers have the least.
D) Beer drinkers have the most; water drinkers have the least.
E) There will be no significant difference between these groups.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following structural formulas to identify the following items.
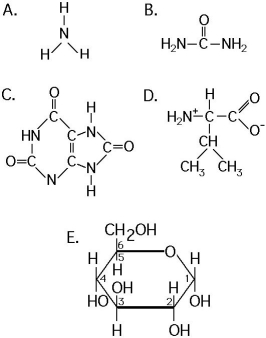 -Which of the following is synthesized by mammals, most amphibians, sharks, and some bony fishes, and has lower toxicity than its nitrogenous substrate?
-Which of the following is synthesized by mammals, most amphibians, sharks, and some bony fishes, and has lower toxicity than its nitrogenous substrate?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Excretory organs known as Malpighian tubules are present in
A) earthworms.
B) flatworms.
C) insects.
D) jellyfish.
E) sea stars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans, the transport epithelial cells in the ascending loop of Henle
A) are the largest epithelial cells in the body.
B) are not in contact with interstitial fluid.
C) have plasma membranes of low permeability to water.
D) have 50% of their cell mass made of smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
E) are not affected by high levels of nitrogenous wastes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A human who has no access to fresh water but is forced to drink sea water instead
A) will thrive under such conditions, as long as he has lived at the ocean most of his life.
B) will excrete more water molecules than taken in, because of the high load of ion ingestion.
C) will develop structural changes in the kidneys to accommodate the salt overload.
D) will find that drinking saltwater satiates his thirst.
E) will risk becoming overhydrated within 12 hours.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 79
Related Exams