A) individuals enter the labor market and make the rounds of potential employers.
B) individuals with skills no longer valued in the domestic labor market cannot find employment.
C) individuals give up the search for employment.
D) a downturn in economic activity decreases employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person quits her job in order to spend time looking for a better paying job. This is an example of
A) frictional unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) seasonal unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The level of unemployment that is equal to the frictional and structural rate in the long run is sometimes referred to as
A) cyclical employment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the total rate of unemployment.
D) the zero unemployment rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about the seasonally adjusted unemployment rate?
A) The seasonally adjusted unemployment rate is the sum of the frictional unemployment rate, structural unemployment rate, and cyclical unemployment rate.
B) The seasonally adjusted unemployment rate shows how the unemployment rate fluctuates with the various seasons.
C) The seasonally adjusted unemployment rate is the same as the natural rate of unemployment.
D) The seasonally adjusted unemployment rate is the rate computed for Fall, Spring, Summer and Winter.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the rate of inflation is 4 percent and the real interest rate is 3 percent, the nominal interest rate should be
A) 1 percent.
B) 4 percent.
C) 7 percent.
D) 11 percent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
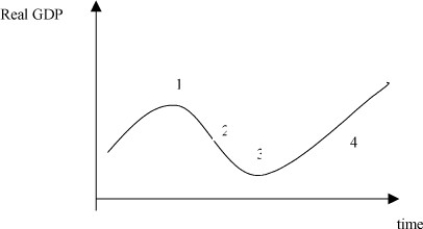 -Refer to the above figure. Stage "3" of the economy is called
-Refer to the above figure. Stage "3" of the economy is called
A) a development.
B) a pit.
C) a trough.
D) a hole.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to business activity charts for the last 100 years, the point of the highest business activity in the United States occurred
A) during the 1920s bull market boom.
B) during World War II.
C) during the Vietnam War.
D) during the Clinton administration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price index that measures the changes in prices of ALL goods and services produced by the economy is the
A) CPI.
B) PPI.
C) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) deflator.
D) Personal Consumption Expenditure Index.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of a cyclically unemployed individual is
A) Charles, who lost his job as a real estate salesperson when the housing market went soft.
B) Alice, who quit her job to enter college.
C) Mary, who lost her job in the textile industry following a decrease in the tariff on textiles.
D) Bob, who has just graduated from college and is entering the labor market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The unemployment rate can increase when
A) the number of job finders increases.
B) the size of the military increases.
C) the proportion of 18-22 year olds that go to college increases.
D) the number of unemployed workers increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes an economy with full employment?
A) "Everyone who is looking for a job will have one."
B) "No person is unemployed for whatever reason."
C) "Full employment occurs only when the economy has a zero percent unemployment rate."
D) "The level of unemployment that corresponds to the normal friction in the labor market."
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To be considered officially unemployed, a person must be at least 16 years old
A) and not working.
B) and not in school and not working.
C) and be a discouraged worker.
D) and not working but is actively seeking employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be a leading indicator?
A) the number of unemployment claims
B) the real interest rate
C) personal income in the United States
D) an increase in stock prices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The statistical measure of a weighted average of prices of goods and services that firms produce and sell is known as
A) the inflation rate.
B) the consumer price index (CPI) .
C) the producer price index (PPI) .
D) the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) deflator.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a small country, the adult population equals 10,000. There are 3,000 people unemployed and 4,000 people are employed. The labor force participation rate equals
A) 70 percent.
B) 57 percent.
C) 40 percent.
D) an undetermined amount given the lack of information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The estimate of the current natural rate of unemployment rate in the United States is approximately
A) 0 percent.
B) 0.5 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) none of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of an item expressed in today's dollars is known as
A) inflation.
B) deflation.
C) the nominal value.
D) the real value.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are examples of a flow EXCEPT
A) a new entrant into the labor force.
B) an individual who voluntarily leaves the labor force.
C) a person who is fired from a job.
D) the current unemployment rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Historically, the United States has experienced
A) continuous decreases in the unemployment rate since World War II.
B) periods of both increases and decreases in the unemployment rate since World War II.
C) continuous increases in the unemployment rate since World War II.
D) no changes in the unemployment rate since World War II.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major change in American labor markets this century is
A) the steady rise of the unemployment rate.
B) the steady rise of the employment rate.
C) the increase in the female labor-force participation rate.
D) the increase in the labor-force participation rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 412
Related Exams