A) unemployed workers divided by the number of employed workers.
B) people in the civilian labor force divided by the number of unemployed.
C) unemployed divided by the number of people in the civilian labor force.
D) employed workers divided by the number of unemployed workers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Environmental regulation reduces the demand for West Virginia coal and the unemployment rate in West Virginia increases. This is an example of
A) frictional unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) regulatory unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The year that is chosen as the point of reference for comparison of prices in other years is known as the
A) base year.
B) price index.
C) purchasing power.
D) consumer price index.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements is true?
A) The existence of unemployment places the economy at a point inside its production possibilities curve.
B) The unemployment rate is the percentage of the population not working.
C) To be counted as part of the labor force, an individual must be working more than 40 hours a week.
D) The sum of wages lost by all unemployed workers gives an accurate, comprehensive estimate of the total cost of unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which category of unemployed individuals makes up the greatest share of those who are unemployed?
A) New entrants
B) Reentrants
C) Job losers
D) Job leavers
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deflation is the situation when
A) the rate at which prices increase falls.
B) the average of all prices is declining.
C) the real rate of interest is negative.
D) some prices are increasing and some are declining.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unemployment that is caused by business recessions is called
A) frictional unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) seasonal unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The unemployment rate will decrease when
A) the duration of unemployment increases.
B) the average workweek falls from 40 to 39 hours.
C) the age of the labor force increases.
D) people get discouraged and quit looking for work.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The U.S. Department of Labor classifies all individuals in the United States as
A) labor force participants.
B) either employed, unemployed, or not in the labor force.
C) either overemployed or underemployed.
D) potential employees.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a
A) statistical measure of a weighted average of prices of a specific set of goods and services purchased by consumers in urban areas.
B) statistical measure of a weighted average of prices of commodities that firms produce and sell.
C) price index measuring the changes in prices of all new goods and services produced in the economy.
D) statistical measure of average prices using annually updated weights based on surveys of consumer spending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One criticism of the unemployment rate is that it
A) does not include the number of discouraged workers as unemployed.
B) does not include people who are not working and are not looking for work.
C) counts a new entrant that is actively seeking work as unemployed.
D) is a stock measure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nominal value of a good is
A) the good's value expressed in purchasing power terms.
B) the good's anticipated value one year from now.
C) the price of the good in today's dollars, minus an anticipated inflation premium.
D) the price of the good in today's dollars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The largest category of the unemployed are
A) job losers.
B) reentrants.
C) job leavers.
D) new entrants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inflation can be defined as
A) an increase in the purchasing power of money.
B) a decrease in the purchasing power of money.
C) no change in the purchasing power of money.
D) an increase in real income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cyclical unemployment is
A) related to job search difficulties for potential workers.
B) a result of a poor match of worker's abilities and skills with current requirements of employers.
C) a result of business recessions that occur when aggregate demand is insufficient to create full employment.
D) a result of the seasonal pattern of work in specific industries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The index that is not based on a fixed market basket of goods and services is the
A) CPI.
B) PPI.
C) Wholesale Price Index.
D) GDP Price Deflator.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be considered a member of the labor force?
A) an engineer who has been laid off a year ago and since then has not looked for work
B) an inmate in a state prison making license plates
C) a person in a mental institution
D) a computer programmer looking for work
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
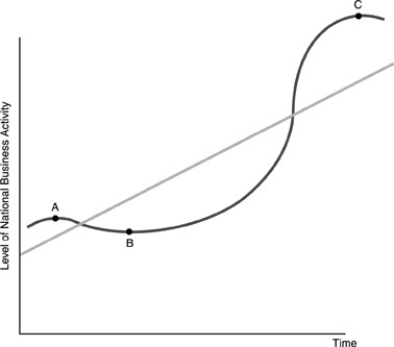 -Refer to the above figure. Point B is known as
-Refer to the above figure. Point B is known as
A) a peak.
B) a trough.
C) an expansion.
D) a contraction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following people would be considered unemployed?
A) Homer, who lost his job at the power plant and is not looking for work
B) Lenny, who is working part time at a fast food restaurant
C) Abe, who is retired
D) Edna, who lost her job as a teacher and is currently searching for a new job
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The natural rate of unemployment when seasonally adjusted includes
A) frictional and structural unemployment but not cyclical.
B) frictional and cyclical unemployment but not structural.
C) frictional unemployment only.
D) cyclical and structural unemployment but not frictional.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 412
Related Exams