A) real GDP
B) aggregate demand
C) input prices.
D) profits
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Classical economists wrote from the 1770s to the ________.
A) 1850s
B) 1890s
C) 1930s
D) 1960s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Q: How many economists does it take to screw in a light bulb? A: None. If the light bulb really needed changing, market forces would have already caused it to happen. This joke represents the view of
A) classical economists.
B) Keynesian economists.
C) economists who conclude that money illusion is widespread.
D) economists who conclude that wages and prices are inflexible.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gap that exists when equilibrium real GDP is greater than the level of real GDP shown by the position of the long-run aggregate supply curve is
A) the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) money illusion.
C) a recessionary gap.
D) an inflationary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Keynes, involuntary unemployment is possible because of
A) the existence of capital markets.
B) long-term labor contracts and the existence of labor unions.
C) government interference in the market economy.
D) inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the classical model, a change in aggregate demand
A) causes a change in long-run real GDP but not in the price level.
B) causes a change in the price level but not in the long-run real GDP.
C) causes changes in both the long-run real GDP and in the price level.
D) has no effect on either real GDP or the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is NOT true about Say's law?
A) Desired expenditures will equal actual expenditures.
B) Surpluses will be eliminated by falling prices and shortages will be eliminated by increasing prices.
C) People produce more goods than they want for their own use only if they seek to trade them for other goods.
D) Markets would be regularly hit by severe shortages and surpluses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the classical model of the economy is FALSE?
A) Savings and investment will always be equal.
B) Wages and prices are flexible.
C) The economy will always move toward, or be at, full employment.
D) Individuals pursue the public interest, not their own self-interest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The inflation associated with the oil price shocks in the 1970s after OPEC restricted the supply of oil is an example of
A) cost-push inflation due to a supply shock.
B) cost-push inflation due to a demand shock.
C) demand-pull inflation due to a demand shock.
D) demand-pull inflation due to a supply shock.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
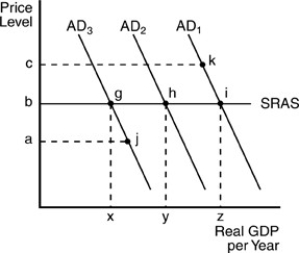 -The above figure presents the view of the economy according to
-The above figure presents the view of the economy according to
A) Keynesian economics.
B) classical economics.
C) microanalysis.
D) Ricardian economics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the classical model, desired saving
A) exceeds investment.
B) is inversely related to real income.
C) is equal to desired investment.
D) is less than desired investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
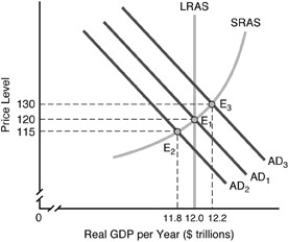 -Consider the above figure. If the aggregate demand went from AD2 to AD3, our nation would have gone from
-Consider the above figure. If the aggregate demand went from AD2 to AD3, our nation would have gone from
A) a recessionary gap to an inflationary gap.
B) a recessionary gap to full-employment real GDP.
C) an inflationary gap to full-employment GDP.
D) full-employment real GDP to an inflationary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the classical theory, the aggregate supply curve is
A) downward sloping.
B) horizontal.
C) upward sloping.
D) vertical.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One key assumption of the classical model is
A) government spending plays a major role.
B) money illusion cannot fool workers.
C) wages are sticky.
D) prices are sticky.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves remain stable, and a decrease in aggregate demand occurs. What is the result in the short run?
A) An increase in the price level and real GDP will occur.
B) A period of expansion and a rise in the unemployment rate could occur.
C) A period of recession and a rise in the unemployment rate could occur.
D) The price level will fall but real GDP will remain the same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a key assumption of the classical model?
A) There is a single monopoly seller in many markets for goods and services.
B) People cannot be fooled by money illusion.
C) People are motivated by self-interest.
D) Wages and prices are flexible.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the U.S. dollar becomes weaker in international markets, the net effects will include
A) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) and an increase in aggregate demand.
B) an increase in short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) and a decrease in aggregate demand.
C) a decrease in both short run aggregate supply (SRAS) and aggregate demand.
D) an increase in both short run aggregate supply (SRAS) and aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the value of the dollar increases, the net effect on the economy
A) will be an increase in short-run aggregate supply and a decrease in aggregate demand.
B) will be decrease in short-run aggregate supply and an increase in aggregate demand.
C) will be an increase in both aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
D) will be a decrease in both aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Say's law states that
A) desired expenditures will equal actual expenditures.
B) people produce only the goods they want.
C) demand is always less than supply.
D) overproduction is never possible because of limited resources.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To explain the existence of excess capacity, Keynes argued that
A) prices and wages are flexible, and eventually markets would go back to equilibrium.
B) the long run average cost curve should not occur at the full employment level.
C) the aggregate demand curve can be manipulated by advertising.
D) prices and wages are inflexible in the downward direction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 365
Related Exams