A) water at 10°C
B) water at 20°C
C) water at 30°C
D) water at 40°C
E) water at 50°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the phase diagram shown below.If you start at 0.75 atm and 0 °C,and move to 0.10 atm and 25C,you will move from the ________ phase to the ________ phase. 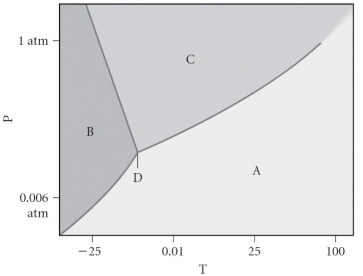
A) liquid, gas
B) gas, gas
C) liquid, liquid
D) gas, solid
E) liquid, solid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the normal boiling point of a substance whose vapor pressure is 55.1 mm Hg at 35°C and has a ΔHvap of 32.1 kJ/mol.
A) 255 K
B) 368 K
C) 412 K
D) 390. K
E) 466 K
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An unknown substance has a boiling point of 150°C at 650 torr,and a boiling point of 195°C at 780 torr.What is the heat of vaporization?
A) 22.2 kJ/mol
B) 12.6 kJ/mol
C) 6.67 kJ/mol
D) 29.4 kJ/mol
E) 18.4 kJ/mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the figure above,the boiling point of diethyl ether under an external pressure of 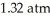 is ________ °C.
is ________ °C.
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40
E) 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the pair of substances that are most likely to form a homogeneous solution.
A) K I and Hg
B) Li Cl and C6H14
C) C3H8 and C2H5OH
D) F2 and PF3
E) NH3 and CH3OH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The forces between polar molecules is known as
A) hydrogen bonding.
B) ion-dipole forces.
C) dipole-dipole forces.
D) dispersion forces.
E) ionic forces.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How much energy is required to vaporize 98.6 g of ethanol (C2H5OH) at its boiling point,if its ΔHvap is 40.5 kJ/mol?
A) 86.7 kJ
B) 11.5 kJ
C) 18.9 kJ
D) 52.8 kJ
E) 39.9 kJ
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the phase diagram shown.Choose the statement below that is TRUE. 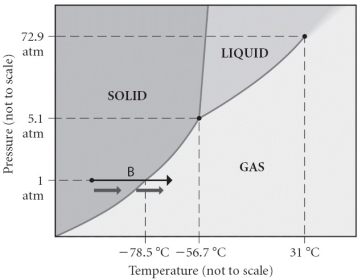
A) The triple point of this substance occurs at a temperature of 31°C.
B) At 10 atm of pressure, there is no temperature where the liquid phase of this substance would exist.
C) The solid phase of this substance is higher in density than the liquid phase.
D) The line separating the solid and liquid phases represents the ΔHvap.
E) None of the above are true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Place the following substances in order of decreasing vapor pressure at a given temperature. PF5 BrF3 CF4
A) BrF3 > PF5 > CF4
B) BrF3 > CF4 > PF5
C) PF5 > BrF3 > CF4
D) CF4 > BrF3 > PF5
E) CF4 > PF5 > BrF3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The boiling point of H2O is much higher than that of the analogous molecule H2S.This is mostly due to
A) dispersion forces being much stronger in H2S than in H2O.
B) dipole-dipole forces being much stronger in H2S than in H2O.
C) hydrogen bonding being much stronger in H2S than in H2O.
D) dipole-dipole forces being much stronger in H2O than in H2S.
E) hydrogen bonding being much stronger in H2O than in H2S.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Define deposition.
A) A liquid becomes a gas.
B) A gas becomes a liquid.
C) A gas becomes a solid.
D) A solid becomes a gas.
E) A solid becomes a liquid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following compounds has dipole-dipole interactions as the strongest intermolecular force?
A) Br2
B) CH3Br
C) CBr4
D) BrCH2CH2OH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Define fusion.
A) the phase transition from solid to liquid
B) the phase transition from gas to solid
C) the phase transition from gas to liquid
D) the phase transition from liquid to gas
E) the phase transition from liquid to solid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the compound that does not have hydrogen bonding.
A) (CH3) 3N
B) H2O
C) CH3OH
D) HF
E) CH3NH2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the compound that does not have dipole-dipole forces as its strongest force.
A) CH2Br2
B) CH3OCH3
C) CH3Cl
D) HCBr3
E) CO2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the pair of substances that are most likely to form a homogeneous solution.
A) C6H14 and C10H20
B) K Cl and C5H12
C) N2O4 and NH4I
D) C6H14 and H2O
E) None of the pairs above will form a homogeneous solution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fluorocarbon C2CL3F3 has a normal boiling point of 47.6°C.The specific heats of C2CL3F3(1) and C2CL3F3(g) are 0.91 J/gK and 0.67 J/gK,respectively.The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ/mol.The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at 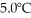 to the gas at 80.0°C is ________ kJ.
to the gas at 80.0°C is ________ kJ.
A) 8.19
B) 1454
C) 30.51
D) 3031
E) 10.36
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How much energy is required to vaporize 48.7 g of dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) at its boiling point,if its ΔHvap is 31.6 kJ/mol?
A) 31.2 kJ
B) 6.49 kJ
C) 55.1 kJ
D) 15.4 kJ
E) 18.1 kJ
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The freezing point of water is
A) 32oF
B) 32oC
C) 212oC
D) 100°C
E) 273°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 132
Related Exams