Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Corrective taxes differ from most taxes in that corrective taxes
A) enhance economic efficiency.
B) do not raise revenue for the government.
C) cause deadweight loss.
D) cannot be divided between the buyer and seller.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a way to address an externality problem?
A) command and control solution
B) corrective tax
C) corrective subsidy
D) all of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-19 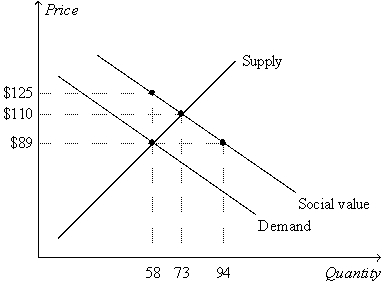 -Refer to Figure 10-19.Which of the following quantities decreases as the quantity of the good is increased?
-Refer to Figure 10-19.Which of the following quantities decreases as the quantity of the good is increased?
A) the private cost of the good
B) the social cost of the good
C) the private value of the good
D) the external benefit of the good
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a positive externality?
A) Sue not catching the flu because she got a flu vaccine
B) Mary not catching the flu from Sue because Sue got a flu vaccine
C) Sue catching the flu because she did not get a flu vaccine
D) Mary catching the flu from Sue because Sue did not get a flu vaccine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A negative externality arises when a person engages in an activity that has
A) an adverse effect on a bystander who is not compensated by the person who causes the effect.
B) an adverse effect on a bystander who is compensated by the person who causes the effect.
C) a beneficial effect on a bystander who pays the person who causes the effect.
D) a beneficial effect on a bystander who does not pay the person who causes the effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When externalities cause markets to be inefficient,
A) government action is always needed to solve the problem.
B) private solutions can be developed to solve the problem.
C) given enough time,externalities can be solved through normal market adjustments.
D) there is no way to eliminate the problem of externalities in a market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-8 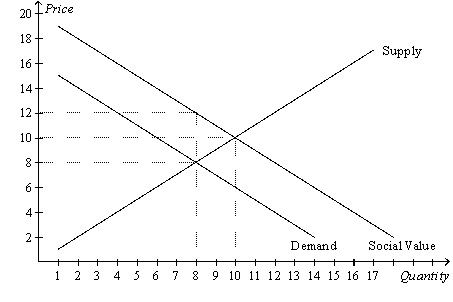 -Refer to Figure 10-8.What is the equilibrium price in this market?
-Refer to Figure 10-8.What is the equilibrium price in this market?
A) $8
B) Between $8 and $10
C) $10
D) More than $10
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An externality
A) results in an equilibrium that does not maximize the total benefits to society.
B) causes demand to exceed supply.
C) strengthens the role of the "invisible hand" in the marketplace.
D) affects buyers but not sellers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to the Coase theorem,whatever the initial distribution of rights,the interested parties can bargain to an efficient outcome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a positive externality?
A) air pollution
B) a person littering in a public park
C) a nice garden in front of your neighbor's house
D) the pollution of a stream
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 10-4
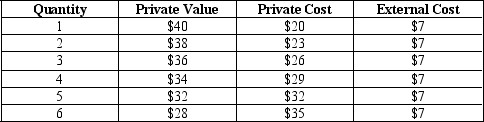 -Refer to Table 10-4.The market equilibrium quantity of output is
-Refer to Table 10-4.The market equilibrium quantity of output is
A) 3 units.
B) 4 units.
C) 5 units.
D) 6 units.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Private solutions may not be possible due to the costs of negotiating and enforcing these solutions.Such costs are called
A) transaction costs.
B) corrective costs.
C) input costs.
D) private costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following policies is an example of a command-and-control policy?
A) subsidies to education
B) maximum levels of pollution that factories may emit
C) tradable pollution permits
D) None of the above is an example of a command-and-control policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 10-3
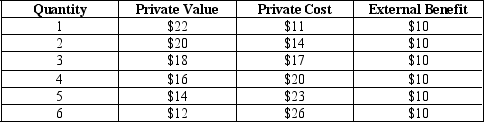 -Refer to Table 10-3.The social value of the 4th unit of output that is produced is
-Refer to Table 10-3.The social value of the 4th unit of output that is produced is
A) $10.
B) $16.
C) $26.
D) $30.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two firms,A and B,each currently dump 50 tons of chemicals into the local river.The government has decided to reduce the pollution and from now on will require a pollution permit for each ton of pollution dumped into the river.It costs Firm A $100 for each ton of pollution that it eliminates before it reaches the river,and it costs Firm B $50 for each ton of pollution that it eliminates before it reaches the river.The government gives each firm 20 pollution permits.Government officials are not sure whether to allow the firms to buy or sell the pollution permits to each other.What is the total cost of reducing pollution if firms are not allowed to buy and sell pollution permits from each other? What is the total cost of reducing pollution if the firms are allowed to buy and sell permits from each other?
A) $3,000; $1,500
B) $4,500; $3,500
C) $4,500; $4,000
D) $4,500; $2,500
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of markets characterized by positive externalities?
A) Social value exceeds private value,and market quantity exceeds the socially optimal quantity.
B) Social value is less than private value,and market quantity exceeds the socially optimal quantity.
C) Social value exceeds private value,and market quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
D) Social value seldom exceeds private value; therefore,social quantity is less than private quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A technology spillover is a type of negative externality.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A positive externality will cause a market to produce
A) more than is socially desirable.
B) less than is socially desirable.
C) the socially optimal equilibrium amount.
D) more than the same market would produce in the presence of a negative externality.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Corrective taxes are often preferred over direct regulation because they typically reduce externalities at a lower cost.
B) Corrective taxes distort economic incentives.
C) Corrective taxes are often preferred over direct regulation because they typically reduce externalities at a faster rate.
D) Both a and b are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 439
Related Exams