A) falls by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
B) falls by the change in the nominal interest rate.
C) rises by the change in the nominal interest rate.
D) rises by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPC is 2/3 then the multiplier is
A) 3/2,so a $100 increase in government spending increases aggregate demand by $150.
B) 3/2,so a $100 increase in government spending increases aggregate supply by $150.
C) 3,so a $100 increase in government spending increases aggregate demand by $300.
D) 3,so a $100 increase in government spending increases aggregate supply by $300.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Employment Act of 1946 states that
A) the Fed should use monetary policy only to control the rate of inflation.
B) the government should promote full employment and production.
C) the government should periodically increase the minimum wage and unemployment insurance benefits.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the money supply decreases the interest rate in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynes used the term "animal spirits" to refer to
A) policy makers harming the economy in the pursuit of self interest.
B) arbitrary changes in attitudes of household and firms.
C) mean-spirited economists who believed in the classical dichotomy.
D) firms' relentless efforts to maximize profits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to classical macroeconomic theory,
A) the price level is sticky in the short run and it plays only a minor role in the short-run adjustment process.
B) for any given level of output,the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply of,and demand for,money.
C) output is determined by the supplies of capital and labor and the available production technology.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 24-2.The following facts apply to a small,imaginary economy. • Consumption spending is $5,200 when income is $8,000. • Consumption spending is $5,536 when income is $8,400. -Refer to Scenario 24-2.In response to which of the following events could aggregate demand increase by $1,500?
A) A stock-market boom stimulates consumer spending by $300,and there is an operative crowding-out effect.
B) A stock-market boom stimulates consumer spending by $225,and there is an operative crowding-out effect.
C) An economic boom overseas increases the demand for U.S.net exports by $300,and there is no crowding-out effect.
D) An economic boom overseas increases the demand for U.S.net exports by $225,and there is no crowding-out effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a $1,000 increase in income leads to a $750 increase in consumption expenditures,then the marginal propensity to consume is
A) 0.75 and the multiplier is 1 1/3.
B) 0.75 and the multiplier is 4.
C) 0.25 and the multiplier is 1 1/3.
D) 0.25 and the multiplier is 4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The interest-rate effect is partially explained by the fact that a higher price level reduces money demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the MPC is 0.625.Assuming only the multiplier effect matters,a decrease in government purchases of $10 billion will shift the aggregate demand curve to the
A) left by about $13.3 billion.
B) left by about $26.7 billion.
C) right by about $36.7 billion.
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same,automatic stabilizers tend to
A) raise expenditures during expansions and recessions.
B) lower expenditures during expansions and recessions.
C) raise expenditures during recessions and lower expenditures during expansions.
D) raise expenditures during expansions and lower expenditures during recessions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that businesses and consumers become much more optimistic about the future of the economy.To stabilize output,the Federal Reserve could
A) buy bonds to raise interest rates.
B) buy bonds to lower interest rates.
C) sell bonds to raise interest rates.
D) sell bonds to lower interest rates.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in government spending
A) increases the interest rate and so investment spending increases.
B) increases the interest rate and so decreases investment spending decreases.
C) decreases the interest rate and so investment spending increases.
D) decreases the interest rate and so investment spending decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,the opportunity cost of holding money is
A) the interest rate on bonds.
B) the inflation rate.
C) the cost of converting bonds to a medium of exchange.
D) the difference between the inflation rate and the interest rate on bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynes argued that aggregate demand is
A) stable,because the economy tends to return to its long-run equilibrium quickly after any disturbance to aggregate demand.
B) stable,because changes in consumption are mostly offset by changes in investment and vice versa.
C) unstable,because waves of pessimism and optimism create fluctuations in aggregate demand.
D) unstable,because of long and variable policy lags that worsen economic fluctuations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the economic downturn of 2008-2009,the Federal Reserve
A) used open-market operations to purchase mortgages and corporate debt,just as it frequently does even when the economy is functioning normally.
B) took the unusual step of using open-market operations to purchase mortgages and corporate debt.
C) explicitly set its target rate of inflation at zero.
D) explicitly set its target rate of inflation well above zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both monetary policy and fiscal policy affect aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal,in the short run a higher price level leads households to
A) increase consumption and firms to buy more capital goods.
B) increase consumption and firms to buy fewer capital goods.
C) decrease consumption and firms to buy more capital goods.
D) decrease consumption and firms to buy fewer capital goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 24-5.On the figure,MS represents money supply and MD represents money demand. 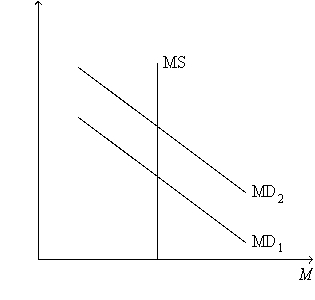 -Refer to Figure 24-5.A shift of the money-demand curve from MD2 to MD1 is consistent with which of the following sets of events?
-Refer to Figure 24-5.A shift of the money-demand curve from MD2 to MD1 is consistent with which of the following sets of events?
A) The government cuts taxes,resulting in an increase in people's incomes.
B) The government reduces government spending,resulting in a decrease in people's incomes.
C) The Federal Reserve increases the supply of money,which decreases the interest rate.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would not be an expected response from a decrease in the price level and so help to explain the slope of the aggregate-demand curve?
A) When interest rates fall,In-and-Out Convenience Stores decides to build some new stores.
B) The exchange rate falls,so French restaurants in Paris buy more Kansas beef.
C) Tyler feels wealthier because of the price-level decrease and so he decides to remodel his kitchen.
D) With prices down and wages fixed by contract,Fargo Concrete Company decides to lay off workers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 415
Related Exams