A) the extinction theory.
B) Batesian mimicry.
C) the coexistence hypothesis.
D) the competitive exclusion principle.
E) resource partitioning.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Exponential growth is rare because resources usually limit population size.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are studying with a classmate who asks you about the concept of a replacement rate.She wants to know what happens to a population if the replacement rate is reached? She assumes the average human replacement rate is 2.0.What would you tell her?
A) When replacement rate is reached,the population declines.The replacement rate is slightly greater than 2.0 because of childhood mortality.
B) When replacement rate is reached,the population increases.The replacement rate is slightly lower than 2.0 to make up for increasing birth rates.
C) When replacement rate is reached,the population begins to decline.The replacement rate is equal to 2.0 to replace both mother and father.
D) When replacement rate is reached,the population is in equilibrium.The replacement rate is greater than 2.0 because some individuals die before they reproduce.
E) When replacement rate is reached,the population begins to declinE.The replacement rate is slightly higher than 2.0 to make up for decreasing fertility rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A group of interbreeding individuals occupying the same habitat at the same time is a(n)
A) species.
B) guild.
C) population.
D) niche.
E) quadrat.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is an example of a +/+ interaction?
A) competition
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) parasitism
E) ammensalism
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The per capita growth rate of a population is best defined as
A) the change in population size per unit time.
B) having a constant value for a particular species.
C) per capita birth rate minus per capita death rate.
D) growth rate when a population is at equilbrium.
E) logistic growth.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the simplest method to measure population density in a given area?
A) Count the number of organisms.
B) Perform a line transect.
C) Look for random dispersion patterns.
D) Count the number of reproductive adults.
E) Calculate a survivorship curvE.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is an example of a +/- interaction?
A) competition
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) predation
E) amensalism
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
World human population in 2012 was approximately
A) 6 billion.
B) 800 million.
C) 8 billion.
D) 7 billion.
E) 15.8 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the age structure of a country's population is evenly distributed,what prediction can confidently be made about the near future?
A) The birth rate will decline.
B) The death rate will decline.
C) The population will not increase rapidly.
D) The population will increase rapidly.
E) The population will decrease rapidly.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A plot of population size vs time that displays a J-shape is indicative of
A) parasitism.
B) exponential growth.
C) logistic growth.
D) competition.
E) density dependencE.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The ecological footprint of an average Egyptian is greater than that of an average American.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Parasitism usually affects populations in a ____________ manner.
A) density-independent
B) density-dependent
C) inverse density-dependent
D) cyclic
E) random
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Several butterfly species that are edible to birds have very similar color patterns to the generally inedible monarch butterfly.This is best described as an example of what?
A) Müllerian mimicry
B) Batesian mimicry
C) camouflage
D) intimidation
E) aposematic coloration
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
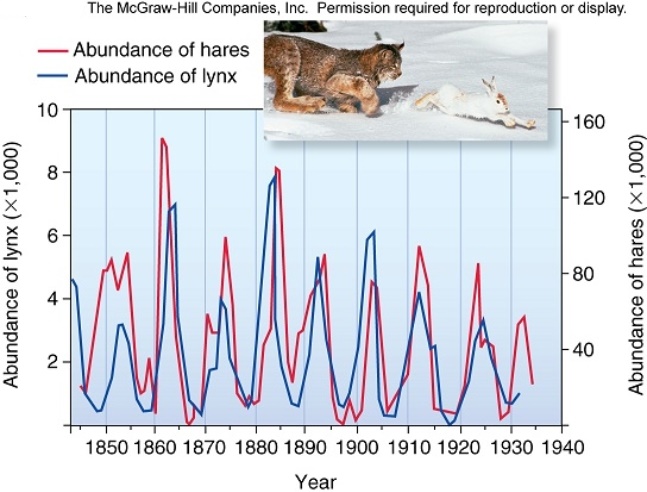 Scientists have discovered that when they provide supplemental food for hares,their density tripled.Based on the figure above,showing cycles of lynx and hare populations over a century's time,what do you predict would happen to a lynx population in an area where hares were provided supplemental food?
Scientists have discovered that when they provide supplemental food for hares,their density tripled.Based on the figure above,showing cycles of lynx and hare populations over a century's time,what do you predict would happen to a lynx population in an area where hares were provided supplemental food?
A) The lynx population would remain the same size because it is in equilibrium with its prey.
B) The lynx population would increase simultaneously with the hare population.
C) The lynx population would decrease as hares increased due to competition for space resources.
D) The lynx population would increase 1-2 years after the hares increaseD.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A survivorship curve with uniform death rates over time is most likely to be a type _______ curve.
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relationship of disease-causing organisms to an infected rabbit is one of
A) parasitism.
B) commensalism.
C) competition.
D) herbivory.
E) predation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A line transect would probably be the preferred method to quantify the population density of
A) blackbirds.
B) lions.
C) clown fish.
D) Ponderosa pines.
E) swallowtail butterflies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gopher tortoises regularly abandon their burrows and build new ones to accomadate their changing size and food requirements.The eastern indigo snake often makes its home in these abandoned burrows.How would you characterize this relationship and its effect on each member?
A) parasitism: indigo snake +,gopher tortoise -
B) competition: indigo snake -,gopher tortoise -
C) commensalism: indigo snake 0,gopher tortoise +
D) parasitism: indigo snake 0,gopher tortoise -
E) commensalism: indigo snake +,gopher tortoise 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What information is used to calculate the age-specific fertility rate,mx?
A) the net reproductive rate of females
B) total number of offspring born to females within a reproductive age class
C) the per capita growth rate of all females
D) number of female offspring born to females within a reproductive age class
E) the average age of first reproduction for females
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 47
Related Exams