A) $47,306
B) $72,418
C) $91,110
D) $128,415
E) $169,193
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kristi wants to start training her most junior assistant,Amy,in the art of project analysis.Amy has just started college and has no experience or background in business finance.To get her started,Kristi is going to assign the responsibility for all projects that have initial costs less than $1,000 to Amy to analyze.Which method is Kristi most apt to ask Amy to use in making her initial decisions?
A) discounted payback
B) profitability index
C) internal rate of return
D) payback
E) average accounting return
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are considering two mutually exclusive projects with the following cash flows.Which project(s) should you accept if the discount rate is 8.5 percent? What if the discount rate is 13 percent? 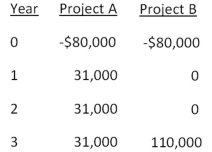
A) accept project A as it always has the higher NPV
B) accept project B as it always has the higher NPV
C) accept A at 8.5 percent and B at 13 percent
D) accept B at 8.5 percent and A at 13 percent
E) accept B at 8.5 percent and neither at 13 percent
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements related to the internal rate of return (IRR) are correct? I.The IRR method of analysis can be adapted to handle non-conventional cash flows. II.The IRR that causes the net present value of the differences between two project's cash flows to equal zero is called the crossover rate. III.The IRR tends to be used more than net present value simply because its results are easier to comprehend. IV.Both the timing and the amount of a project's cash flows affect the value of the project's IRR.
A) I and II only
B) III and IV only
C) I, II, and III only
D) II, III, and IV only
E) I, II, III, and IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are considering two independent projects both of which have been assigned a discount rate of 15 percent.Based on the profitability index,what is your recommendation concerning these projects? 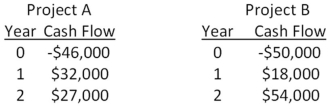
A) You should accept both projects.
B) You should reject both projects.
C) You should accept project A and reject project B.
D) You should accept project B and reject project A.
E) You should accept project A and be indifferent to project B.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following will decrease the net present value of a project?
A) increasing the value of each of the project's discounted cash inflows
B) moving each of the cash inflows forward to a sooner time period
C) decreasing the required discount rate
D) increasing the project's initial cost at time zero
E) increasing the amount of the final cash inflow
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Chandler Group wants to set up a private cemetery business.According to the CFO,Barry M.Deep,business is "looking up".As a result,the cemetery project will provide a net cash inflow of $57,000 for the firm during the first year,and the cash flows are projected to grow at a rate of 7 percent per year forever.The project requires an initial investment of $759,000.The firm requires a 14 percent return on such undertakings.The company is somewhat unsure about the assumption of a 7 percent growth rate in its cash flows.At what constant rate of growth would the company just break even?
A) 4.48 percent
B) 5.29 percent
C) 5.61 percent
D) 6.49 percent
E) 6.75 percent
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sheakley Industries is considering expanding its current line of business and has developed the following expected cash flows for the project.Should this project be accepted based on the discounting approach to the modified internal rate of return if the discount rate is 13.4 percent? Why or why not? 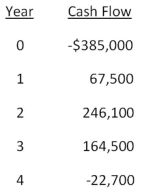
A) Yes; The MIRR is 6.50 percent.
B) No; The MIRR is 8.67 percent.
C) Yes; The MIRR is 8.23 percent.
D) No; The MIRR is 6.50 percent.
E) No; The MIRR is 7.59 percent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rossiter Restaurants is analyzing a project that requires $180,000 of fixed assets.When the project ends,those assets are expected to have an aftertax salvage value of $45,000.How is the $45,000 salvage value handled when computing the net present value of the project?
A) reduction in the cash outflow at time zero
B) cash inflow in the final year of the project
C) cash inflow for the year following the final year of the project
D) cash inflow prorated over the life of the project
E) not included in the net present value
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Applying the discounted payback decision rule to all projects may cause:
A) some positive net present value projects to be rejected.
B) the most liquid projects to be rejected in favor of the less liquid projects.
C) projects to be incorrectly accepted due to ignoring the time value of money.
D) a firm to become more long-term focused.
E) some projects to be accepted which would otherwise be rejected under the payback rule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Douglass Interiors is considering two mutually exclusive projects and have determined that the crossover rate for these projects is 11.7 percent.Project A has an internal rate of return (IRR) of 15.3 percent and Project B has an IRR of 16.5 percent.Given this information,which one of the following statements is correct?
A) Project A should be accepted as its IRR is closer to the crossover point than is Project B's IRR.
B) Project B should be accepted as it has the higher IRR.
C) Both projects should be accepted as both of the project's IRRs exceed the crossover rate.
D) Neither project should be accepted since both of the project's IRRs exceed the crossover rate.
E) You cannot determine which project should be accepted given the information provided.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tedder Mining has analyzed a proposed expansion project and determined that the internal rate of return is lower than the firm desires.Which one of the following changes to the project would be most expected to increase the project's internal rate of return?
A) decreasing the required discount rate
B) increasing the initial investment in fixed assets
C) condensing the firm's cash inflows into fewer years without lowering the total amount of those inflows
D) eliminating the salvage value
E) decreasing the amount of the final cash inflow
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are considering an investment with the following cash flows.If the required rate of return for this investment is 15.5 percent,should you accept the investment based solely on the internal rate of return rule? Why or why not? 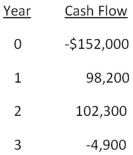
A) Yes; The IRR exceeds the required return.
B) Yes; The IRR is less than the required return.
C) No; The IRR is less than the required return.
D) No; The IRR exceeds the required return.
E) You cannot apply the IRR rule in this case.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Motor City Productions sells original automotive art on a prepaid basis as each piece is uniquely designed to the customer's specifications.For one project,the cash flows are estimated as follows.Based on the internal rate of return (IRR) ,should this project be accepted if the required return is 9 percent? 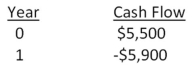
A) Accept the project.
B) Reject the project.
C) The IRR cannot be used to evaluate this type of project.
D) The firm should be indifferent to either accepting or rejecting this project.
E) Insufficient information is provided to make a decision based on IRR.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are considering the following two mutually exclusive projects.Both projects will be depreciated using straight-line depreciation to a zero book value over the life of the project.Neither project has any salvage value. 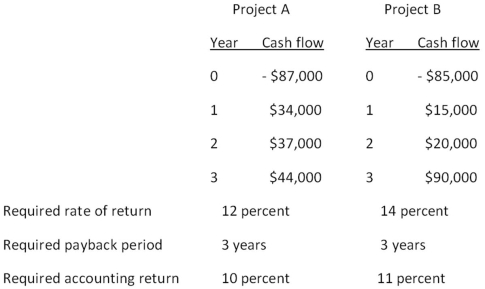 Should you accept or reject these projects based on the average accounting return?
Should you accept or reject these projects based on the average accounting return?
A) accept Project A and reject Project B
B) reject Project A and accept Project B
C) accept both Projects A and B
D) reject both Projects A and B
E) You cannot make this decision based on the information provided.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a project has a net present value equal to zero,then:
A) the total of the cash inflows must equal the initial cost of the project.
B) the project earns a return exactly equal to the discount rate.
C) a decrease in the project's initial cost will cause the project to have a negative NPV.
D) any delay in receiving the projected cash inflows will cause the project to have a positive NPV.
E) the project's PI must be also be equal to zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are considering the following two mutually exclusive projects.Both projects will be depreciated using straight-line depreciation to a zero book value over the life of the project.Neither project has any salvage value. 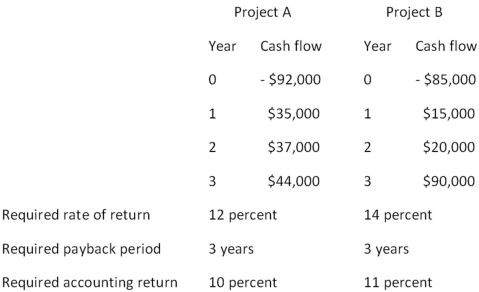 Should you accept or reject these projects based on payback analysis?
Should you accept or reject these projects based on payback analysis?
A) accept Project A and reject Project B
B) reject Project A and accept Project B
C) accept both Projects A and B
D) reject both Projects A and B
E) You cannot make this decision based on payback analysis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Green Fiddle is considering a project that will produce sales of $87,000 a year for the next 4 years.The profit margin is estimated at 6 percent.The project will cost $90,000 and will be depreciated straight-line to a book value of zero over the life of the project.The firm has a required accounting return of 11 percent.This project should be _____ because the AAR is _____ percent.
A) rejected; 10.03
B) rejected; 10.25
C) rejected; 11.60
D) accepted; 10.25
E) accepted; 11.60
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements would generally be considered as accurate given independent projects with conventional cash flows?
A) The internal rate of return decision may contradict the net present value decision.
B) Business practice dictates that independent projects should have three distinct accept indicators before a project is actually implemented.
C) The payback decision rule could override the net present value decision rule should cash availability be limited.
D) The profitability index rule cannot be applied in this situation.
E) The projects cannot be accepted unless the average accounting return decision ruling is positive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
J&J Enterprises is considering an investment that will cost $318,000.The investment produces no cash flows for the first year.In the second year,the cash inflow is $47,000.This inflow will increase to $198,000 and then $226,000 for the following two years,respectively,before ceasing permanently.The firm requires a 15.5 percent rate of return and has a required discounted payback period of three years.Should the project be accepted? Why or why not?
A) accept; The discounted payback period is 2.18 years.
B) accept; The discounted payback period is 2.32 years.
C) accept; The discounted payback period is 2.98 years.
D) reject; The discounted payback period is 2.18 years.
E) reject; The project never pays back on a discounted basis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 115
Related Exams