A) short position in ¥200,000,000 currency futures.
B) long position in ¥200,000,000 currency futures.
C) either a or b
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sensitivity of "realized" domestic currency values of the firm's contractual cash flows denominated in foreign currency to unexpected changes in the exchange rate is
A) transaction exposure.
B) translation exposure.
C) economic exposure.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In comparison to the current/noncurrent method, the monetary/nonmonetary method
A) differs substantially with regard to the treatment of inventory.
B) classifies accounts on the basis of similarity of attributes rather than the similarity of maturities.
C) both a and b
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Generally speaking,
A) it is not possible to hedge both translation exposure and transaction exposure simultaneously.
B) if a firm can hedge translation exposure then transaction exposure will be simultaneously hedged.
C) if a firm can hedge transaction exposure then translation exposure will be simultaneously hedged.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Translation exposure refers to
A) accounting exposure.
B) the effect that an unanticipated change in exchange rates will have on the consolidated financial reports of an MNC.
C) the change in the value of a foreign subsidiaries assets and liabilities denominated in a foreign currency, as a result of exchange rate change fluctuations, when viewed from the perspective of the parent firm.
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Fill out the 20 missing entries that translate the balance sheet and income statement for this French subsidiary using the Current/Noncurrent Method, the Monetary/Nonmonetary Method, the Temporal Method, and the Current Rate Method 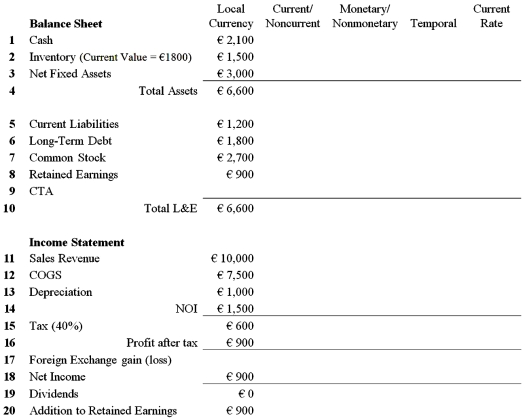
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what year were U.S. MNCs mandated to implement FASB 52?
A) 1952
B) 1962
C) 1972
D) 1982
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the monetary/nonmonetary method, monetary balance sheet accounts include
A) for example, cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, notes payable, accounts payable of a foreign subsidiary.
B) for example stockholders' equity and long term debt.
C) for example inventory paid for in cash, but not working capital.
D) COGs, Sales, Net Income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
FASB 8 is essentially the
A) current/noncurrent method.
B) monetary/nonmonetary method.
C) temporal method.
D) current rate method.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The stated objectives of FASB 52 are
A) to provide information that is generally compatible with the expected economic effects of a rate change on an enterprise's cash flows and equity.
B) to reflect in consolidated statements the financial results and relationships of the individual consolidated entities as measured in their functional currencies in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
C) both a and b
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) The competitive effect is defined as the impact that a currency depreciation may have on the operating cash flow in the foreign currency by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B) The conversion effect is defined as a given accounting cash value in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after currency depreciation.
C) The competitive effect is defined as a given operating cash flow in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after a currency depreciation.
D) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In highly inflationary economies, FASB 52 requires that the foreign entities financial statement be remeasured from the local currency "as if the functional currency were the reporting currency". The purpose of this requirement is
A) to prevent large important balance sheet accounts, carried at historical values, from having insignificant values once translated into the reporting currency at the current rate.
B) to prevent games playing in the accounting books.
C) to prevent having to restate the books at a later date.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The authoritative body in the United States that specifies accounting policy for U.S. business firms and certified public accounting firms.
A) The Federal Accounting Standards Board (FASB) .
B) The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) .
C) The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) .
D) The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The source of translation exposure
A) is a mismatch of net assets and net liabilities denominated in the same currency.
B) is a mismatch of net assets and net liabilities denominated in the different currencies.
C) is a mismatch of current assets and current liabilities denominated in different currencies.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The underlying principle of the monetary/nonmonetary method is
A) assets and liabilities should be translated based on their maturity.
B) monetary accounts have a similarity because their value represents a sum of money whose currency equivalent after translation changes each time the exchange rate changes.
C) monetary accounts are translated at the current exchange rate; other accounts are translated at the current exchange rate if they are carried on the books at current value; items carried at historical cost are translated at historic exchange rates.
D) all balance sheet accounts are translated at the current exchange rate, except for stockholders' equity. A "plug" equity account named cumulative translation adjustment (CTA) is used to make the balance sheet balance, since translation gains or losses do not go through the income statement according to this method.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A U.S. parent firm, as result of its business activities in Germany, has a net exposure of €1,000,000. The consolidated reports were prepared at the year-end for the last two successive years. If the exchange rates on these reporting dates changed from $1.00 = €1.10 to $1.00 = €1.00, then the translation exposure report will indicate a "reporting currency imbalance" of
A) $90,910.
B) $0.
C) -$90,910.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under which accounting method are most income statement accounts are translated at the average exchange rate for the period?
A) Current/noncurrent method
B) Monetary/nonmonetary method
C) Temporal method
D) Current rate method
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The underlying philosophy of the monetary/nonmonetary method is that
A) monetary accounts have a similarity because their value represents a sum of money whose currency equivalent after translation is independent of exchange rate changes.
B) monetary accounts have a similarity because their value represents a sum of money whose currency equivalent after translation changes each time the exchange rate changes.
C) assets and liabilities should be translated based on their maturity.
D) most income statement items are translated at the average exchange rate for the period. Depreciation and cost of goods sold, however, are translated at historical rates if the associated balance sheet accounts are carried at historical costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Translation exposure,
A) is not entity specific, rather it is currency specific.
B) is not currency specific, rather it is entity specific.
C) involves restatement from Italian to French.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A derivatives hedge that seeks to eliminate translation exposure
A) eliminate any mismatch of the rate of change in net assets and the rate of change in net liabilities denominated in the same currency.
B) really involves speculation about foreign exchange rate changes.
C) by simultaneously going long and short in currency futures contracts.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 81
Related Exams