Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A strategy that is better than any alternative strategy-regardless of what the other firm does-is called a
A) dominant strategy.
B) simultaneous strategy.
C) positive-sum strategy.
D) one-time strategy.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a general rule, oligopoly exists when the four-firm concentration ratio
A) equals the Herfindahl index.
B) yields a Herfindahl index below 500.
C) is 40 percent or more.
D) is 50 percent or more.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Unlike a monopoly, an oligopoly tends to achieve allocative efficiency due to the rivalry among several firms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In game theory, a credible threat of coercion by a dominant firm tends to
A) prevent cheating in collusive agreements.
B) increase the incentives to cheat.
C) reduce discipline among cartel members.
D) discourage collusive agreements.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If oligopolistic firms facing similar cost and demand conditions successfully collude, price and output results in this industry will be most accurately predicted by which of the following models?
A) the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly
B) the price-leadership model of oligopoly
C) the pure monopoly model
D) the monopolistic competition model
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that currently there are no airlines serving the city of South Podunk. Both Accommodating Airlines and Friendly Flyers are looking to enter that market. (They are the only two.) The figure shows in extensive form the possible outcomes of the two firms' decisions. The payoffs represent, in thousands per month, the profit (or loss) the firm will realize from its decision. Assuming the two firms have perfect information about this game, what can we conclude about the existence of a Nash equilibrium? 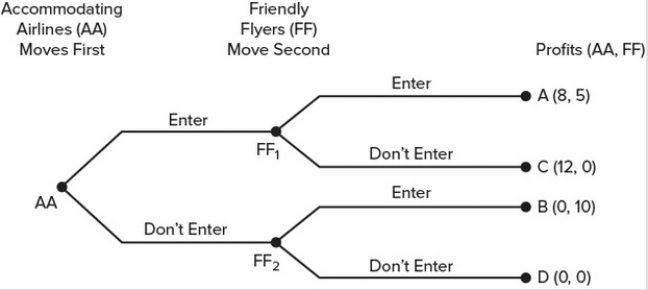
A) The solution to the game is a Nash equilibrium.
B) There are multiple Nash equilibria for this game.
C) There is no Nash equilibrium for this game.
D) There is a Nash equilibrium for this game, but it does not coincide with the solution to the game.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aluminum competes with copper in the market for power transmission lines. This illustrates
A) mutual interdependence.
B) differentiated oligopoly.
C) interindustry competition.
D) homogeneous oligopoly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One major problem with four-firm concentration ratios is that they fail to take into account
A) the localized market for products.
B) excess capacity in production.
C) price leadership.
D) mutual interdependence.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When oligopolists collude, they collectively tend to achieve similar results as a monopolist.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is not illustrated by the so-called Prisoner's Dilemma?
A) Each player in the game ends up with results that depend on the other player's action.
B) It does not pay for the players to collude with each other.
C) Both players would be better off, if they could only agree on which action to take.
D) The results for each player in the game are uncertain, if they are not able to communicate.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The terminal nodes in an extensive form representation
A) are used solely to show payoffs that represent a Nash equilibrium.
B) represent the starting points for a sequential game.
C) indicate the strategies available to the players of a game.
D) indicate the possible outcomes of a game.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A sequential game can be modeled in two forms: payoff-matrix form and game-tree form.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In game theory, credible threats can be used to maintain collusive agreements between firms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, an oligopoly
A) will produce less than a monopoly.
B) may be able to earn positive economic profits.
C) will always produce in the range of decreasing returns to scale.
D) will produce on the portion of the demand curve where demand is price-inelastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A player is said to have a dominant strategy when one of the options available is superior, regardless of what strategy the other player chooses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A natural monopoly's preemption of entry by other firms by exploiting its economies of scale is an example of
A) first-mover advantage.
B) a repeated game with reciprocity.
C) Nash equilibrium in a single-period game.
D) collusion in game theory.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Consider This) The story about three sellers of Native American arts and crafts best illustrates the idea of
A) strategic behavior.
B) excess capacity.
C) the role of advertising.
D) product differentiation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The likelihood of a cartel being successful is greater when
A) firms are producing a differentiated, rather than a homogeneous, product.
B) cost and demand curves of various participants are very similar.
C) the number of firms involved is relatively large.
D) the economy is in the recession phase of the business cycle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An industry having a four-firm concentration ratio of 85 percent
A) approximates pure competition.
B) is monopolistically competitive.
C) is a pure monopoly.
D) is an oligopoly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 265
Related Exams