A) will realize an economic profit if price exceeds ATC at the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing level of output.
B) will realize an economic profit if ATC exceeds MR at the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing level of output.
C) will realize an economic loss if MC intersects the downsloping portion of MR.
D) always realizes an economic profit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) In the short run, the pure monopolist will maximize total profits by producing at that level of output where the difference between price and average total cost is greatest.
B) In the short run, the pure monopolist will charge the highest price it can get for its product.
C) Because of its ability to set its own price, the pure monopolist can increase price and increase its volume of sales simultaneously.
D) Pure monopolists do not always realize positive profits, sometimes they suffer losses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The data relate to a pure monopolist and the product it produces. What is the profit-maximizing output and price for this monopolist?
A) P = $12; Q = 5
B) P = $14; Q = 4
C) P = $15; Q = 3
D) P = $18; Q = 2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
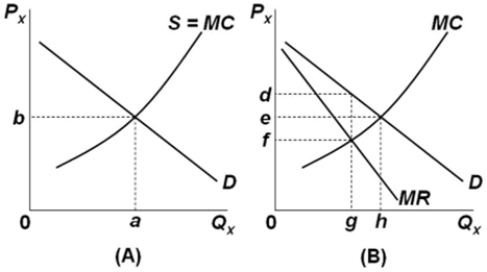 Refer to the diagrams. With the industry structures represented by diagram
Refer to the diagrams. With the industry structures represented by diagram
A) (B) , there will be allocative efficiency.
B) (A) , economic profit can persist in the long run.
C) (B) , output will be less than in diagram (A) .
D) (B) , output will be the same as in diagram (A) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In response to a cost-reducing technological breakthrough in the production of its product, a profit-maximizing monopolist will normally
A) increase price and decrease production.
B) not change its level of output or price.
C) decrease the price it charges for its product.
D) increase its output and practice price discrimination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the long-run equilibrium, a monopolist will earn zero economic profits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Natural monopolies result from
A) patents and copyrights.
B) pricing strategies.
C) extensive economies of scale in production.
D) control over an essential natural resource.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 20 units of output at $10 per unit and 21 units at $9.75 per unit. The marginal revenue of the 21st unit of output is
A) $9.75.
B) $204.75.
C) $4.75.
D) $.25.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopolist will avoid setting a price in the elastic segment of the demand curve and prefer to set the price in the inelastic segment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows the relationship between output, total costs, and total revenue for a pure monopoly. Within which of the following ranges of output will the firm earn maximum economic profits?
A) 50 to 60 units
B) 60 to 70 units
C) 70 to 80 units
D) 80 to 90 units
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is incorrect? Imperfectly competitive producers
A) face downsloping demand curves.
B) do not compete with one another.
C) can alter their output by changing price.
D) find that, when they reduce price, their total revenue increases by less than the new price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nondiscriminating monopolist will find that marginal revenue
A) exceeds average revenue or price.
B) is identical to price.
C) is sometimes greater and sometimes less than price.
D) is less than average revenue or price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A pure monopoly firm will never charge a price in the inelastic range of its demand curve because lowering price to get into this region will
A) increase total revenue, increase total cost, and decrease profit.
B) decrease total revenue, increase total cost, and decrease profit.
C) increase total revenue, decrease total cost, and decrease profit.
D) decrease total revenue, total cost, and profit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistic firm has a sales schedule such that it can sell 10 prefabricated garages per week at $10,000 each, but if it restricts its output to 9 per week it can sell these at $11,000 each. The marginal revenue of the 10th unit of sales per week is
A) âˆ'$1,000.
B) $9,000.
C) $10,000.
D) $1,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a pure monopolist can price discriminate by separating buyers into two or more groups,
A) the marginal revenue curve and the total revenue curve will now coincide.
B) the marginal revenue curve will now shift to a position above the demand curve.
C) the firm will face multiple marginal revenue curves.
D) marginal revenue will become less at each level of output than it would be without price discrimination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The vertical distance between the horizontal axis and any point on a nondiscriminating monopolist's demand curve measures
A) the quantity demanded.
B) product price and marginal revenue.
C) total revenue.
D) product price and average revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Last Word) : The ability of personalized pricing by online retailers to price discriminate
A) is enhanced by Big Data's ability to accurately determine a buyer's reservation price.
B) is only effective at the group level.
C) means that buyers with more elastic demand face systematically higher prices.
D) is limited by buyers' willingness and ability to easily search out lower prices at other online sites.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Extensive network effects may drive a market toward natural monopoly because consumers tend to choose a common, standard product that everyone else is using.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic profit in the long run is
A) possible for both a pure monopoly and a pure competitor.
B) possible for a pure monopoly but not for a pure competitor.
C) impossible for both a pure monopolist and a pure competitor.
D) only possible when barriers to entry are nonexistent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When compared with the purely competitive industry with identical costs of production, a monopolist will produce
A) more output and charge the same price.
B) more output and charge a higher price.
C) less output and charge a higher price.
D) less output and charge the same price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 224
Related Exams