A) construction expenditures, raw materials, and inventories of finished goods.
B) goods in process, raw materials, and purchases of office machinery.
C) Raw materials, goods in process, and construction expenditures.
D) Inventories of finished goods, goods in process, and raw materials.
E) used finished goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose that an economy produces only food and clothing, and that price and quantity data are given in the table below.
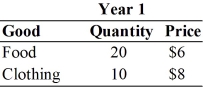
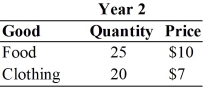 -Year 2 nominal GDP is
-Year 2 nominal GDP is
A) $200.
B) $270.
C) $310.
D) $390.
E) $450.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Value added is equal to the value of a firm's production minus
A) all of its costs of production.
B) labour costs.
C) investment expenditures.
D) intermediate goods used in production.
E) costs of production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in a given country in a given year,GNP equals $2000,investment expenditures equal $200,government expenditures equal $150,and the current account surplus equals $50.Consumption expenditures therefore equals
A) $1000.
B) $120.
C) $140.
D) $160.
E) $230.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose that an economy produces only food and clothing, and that price and quantity data are given in the table below.

 -Year 1 nominal GDP is
-Year 1 nominal GDP is
A) $200.
B) $270.
C) $310.
D) $390.
E) $450.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Government expenditures includes
A) federal defense spending.
B) consumer spending.
C) residential spending.
D) financial investment.
E) inventory investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acme Steel Co.produces 1000 tons of steel.Steel sells for $30 per ton.Acme pays wages of $10,000.Acme buys $15,000 worth of coal,which is needed to produce the steel.Acme pays $2,000 in taxes.Acme's profit is
A) $0.
B) $2,000.
C) $3,000.
D) $15,000.
E) $25,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of a producer's output minus the value of all intermediate goods used in the production of that output is called the producer's
A) net output.
B) accounting profit.
C) value added.
D) profit margin.
E) costs of production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose that an economy produces only bread and computers. Assume that all production is consumed in each year, and that price and quantity data are given in the table below.

 -If Year 1 is the base year,the GDP price deflator for Year 2 is approximately
-If Year 1 is the base year,the GDP price deflator for Year 2 is approximately
A) 100.0.
B) 126.3.
C) 131.3.
D) 181.0.
E) 211.0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose that an economy produces only bread and computers. Assume that all production is consumed in each year, and that price and quantity data are given in the table below.

 -If Year 1 is the base year,the CPI for Year 2 is approximately
-If Year 1 is the base year,the CPI for Year 2 is approximately
A) 100.0.
B) 126.3.
C) 131.3.
D) 181.0.
E) 211.0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose that an economy produces only food and clothing, and that price and quantity data are given in the table below.

 -Suppose that Year 2 is the base year.Year 1 real GDP is
-Suppose that Year 2 is the base year.Year 1 real GDP is
A) $200.
B) $270.
C) $310.
D) $390.
E) $450.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gross domestic product is defined as
A) the value of all goods produced in the economy in a given time period within the borders of Canada.
B) the market value of all goods and services produced in the economy during a given time period within the borders of Canada.
C) the total market value of the final goods and services produced during a given time period within the borders of Canada.
D) the total market value of all the intermediate goods and services produced in the economy for a given time period within the borders of Canada.
E) the market value of all goods and services produced by Canadian residents domestically and abroad.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of a flow would be the
A) rate at which water goes down the drain.
B) amount of water in a bathtub.
C) percent of pollutants in tap water.
D) pressure of water in a pipe.
E) rate at which the cold water comes out of the tap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
GDP and GNP may differ
A) because some income generated by domestic production may be received as income by foreign residents.
B) because some intermediate good inputs are imported.
C) because some workers are illegal aliens.
D) whenever tariff rates become excessively high.
E) when business cycles are unpredictable and volatile.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that GDP is equal to 1000,national saving is equal to 200,the current account deficit is equal to 100,and the government budget deficit is equal to 50.Private savings must equal
A) 150.
B) 200.
C) 250.
D) 300.
E) 350.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is difficult to accurately measure real GDP because
A) it does not include taxes.
B) it does not include money transfers.
C) does not accurately take into account the introduction of new goods.
D) it cannot take into account changes in government policy over time.
E) does not take into account intermediate goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following question(s) , suppose an economy produces only pens and pencils, and that the quantity and price data is given by this table:
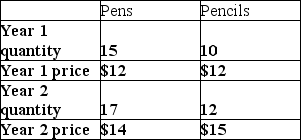 -What is the real GDP in year 2 using base year 2?
-What is the real GDP in year 2 using base year 2?
A) $418.
B) $300.
C) $360.
D) $338.
E) $414.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To calculate value added,we need to subtract
A) only the cost of domestically-produced intermediate inputs.
B) only the cost of foreign-produced intermediate inputs.
C) the cost of domestic- and foreign-produced intermediate inputs.
D) total imports.
E) the cost of all goods and services exported.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The components of investment expenditures include
A) investment in stocks and bonds.
B) residential investment.
C) investment in plant and equipment abroad.
D) investment in consumer's education.
E) investment in health care.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the Ford truck plant in Oakville,Ontario,produces $10 million worth of vehicles in a given year.Of this total amount,$1 million in profits are returned to the owners of the company in the U.S.The $1 million in profits
A) contributes to both Canadian GDP and Canadian GNP.
B) contributes to Canadian GNP, but not Canadian GDP.
C) contributes to Canadian GDP, but not Canadian GNP.
D) contributes to neither Canadian GDP, nor Canadian GNP.
E) contributes to the expenditure side of GDP only.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 80
Related Exams