Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which legislation authorizes federal agencies to sell delinquent and defaulted loan assets?
A) Federal Debt Collection Improvements Act.
B) Financial Services Modernization Act.
C) The Bank Holding Company Act.
D) Depository Institutions Deregulation and Monetary Control Act.
E) Financial Institutions Reform Recovery and Enforcement Act.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
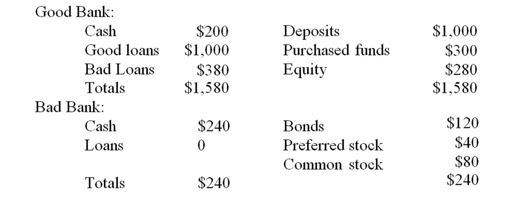 Bad Bank buys the bad loans for $232. The proceeds of the loan sale are used by Good Bank to pay off purchased funds.
-What will be the amount of equity on the balance sheet of Good Bank after the sale of the loans?
Bad Bank buys the bad loans for $232. The proceeds of the loan sale are used by Good Bank to pay off purchased funds.
-What will be the amount of equity on the balance sheet of Good Bank after the sale of the loans?
A) $1,200.
B) $232.
C) $132.
D) $68.
E) $0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most vulture funds are formed by the mutual fund industry as a way around SEC restrictions from participating in the FI-originated loan sales market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following observations is NOT correct?
A) Most loans are sold with recourse.
B) Loan sales are a primitive substitute for securitization.
C) Selling of a loan creates a secondary market for loans.
D) Ownership of the loan is always transferred to the loan purchaser.
E) Loan sales do not involve the creation of new types of securities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a reason for FIs to sell loans?
A) Loan diversification.
B) To reduce required reserves.
C) To reduce required capital.
D) To reduce costs of credit risk assessment.
E) To provide liquidity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
As of 2010, the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) no longer sells loans that were used to purchase multifamily apartment properties.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A loan made to finance a merger and acquisition that usually results in a high leverage ratio for the borrower is a
A) loan sold without recourse.
B) highly leveraged transaction loan.
C) loan sold with recourse.
D) loan assignment transaction.
E) loan participation transaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Loan assignments
A) are common in loan syndications.
B) do not have buyer restrictions.
C) comprise less than 30 percent of the U.S.loan sales market.
D) involve extremely high monitoring costs.
E) expose the buyer to a double risk and involve double monitoring costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a reason for a FI to sell loans with recourse?
A) To reduce capital requirements.
B) To avoid credit risk exposure.
C) To control interest rate risk exposure.
D) To avoid regulatory scrutiny.
E) To make it possible to lend large amounts to an individual borrower.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a reason for using a bad bank as a vehicle to add value in the loan sale process?
A) Contracts for managers can be created to maximize the incentives to generate enhanced values from loan sales.
B) The bad bank enables bad assets to be managed by loan workout specialists.
C) The bad bank does not need to be concerned about liquidity needs since it does not have any deposits.
D) Moving the bad loans off the balance sheet of the good bank will improve the markets perception, and thus performance, of the good bank.
E) The good bank-bad bank structure increases information asymmetries regarding the value of the good bank's assets.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Currently, this basic type of loan sale contracts comprises the bulk of loan sales trading.
A) Participations.
B) Originations.
C) Syndications.
D) Assignments.
E) Transfers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Selling loans without recourse is a way for FIs to remove loans from their balance sheet for the purpose of reducing the cost associated with reserve requirements.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Highly leveraged transaction (HLT) loans typically are used to finance new fixed assets of an ongoing firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The move by regulators toward market value accounting of the loan portfolios will likely encourage sales of loans in the secondary markets.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a portion of a loan is sold from a large bank to a small bank, it is often called a participation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A distinction between distressed and non-distressed is usually made when selling highly leveraged transactions loans (HLTs).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do spreads on HLT loans behave more like investment-grade bonds than like high-yield bonds?
A) They tend to be more junior in bankruptcy.
B) They tend to have greater collateral backing than do high-yield bonds.
C) Because no bank makes a market in this debt.
D) Because securities firms do not make a market in this debt.
E) They tend to have no covenant protection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The traditional interbank loan sale market has been shrinking for which of the following reasons?
A) The barriers to nationwide banking have been largely removed through legislation.
B) Concerns about counterparty risk and moral hazard have increased.
C) The traditional correspondent banking relationships are slowly breaking down.
D) All of the above.
E) Only two of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a contractual mechanism used by FIs to control credit risks?
A) Diversifying across different types of risky borrowers.
B) Requiring higher interest rate spreads for higher risk borrowers.
C) Requiring more collateral for the bank over the assets of more risky borrowers.
D) Making lending decisions only in centralized locations.
E) Placing more restrictive covenants on the actions of more risky borrowers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 92
Related Exams