A) genetic material is exchanged between sister chromatids, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
B) genetic material is exchanged between nonsister chromatids, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
C) sister chromatids from each homologous chromosome of a tetrad are exchanged, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
D) nonsister chromatids from each homologous chromosome of a tetrad are exchanged, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
E) one homologous chromosome of a tetrad is exchanged with another tetrad, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During G1 stage of interphase, a diploid organism contains how many copies of each gene?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Turner syndrome is associated with which of the following karyotypes?
A) 47, XXY
B) 47, XXX
C) 46, XY
D) 47, XY, trisomy 21
E) 45, XO
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Klinefelter syndrome can result from
A) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the female parent.
B) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the male parent.
C) nondisjunction during meiosis I in either female parent.
D) nondisjunction during meiosis I or II in the male parent.
E) nondisjunction during meiosis I or II in either parent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following lists is in the correct order, from the least inclusive to the most inclusive?
A) allele - gene - chromosome
B) gene - allele - chromosome
C) allele - chromosome - gene
D) chromosome - gene - allele
E) gene - chromosome - allele
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During prophase II, a diploid organism contains how many copies of each gene?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes of a tetrad
A) face the same spindle pole.
B) face both spindle poles.
C) face opposite spindle poles.
D) do not face spindle poles, but are aligned at the spindle equator.
E) undergo separation of sister chromatids.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement best describes how the members of a tetrad are separated during meiosis I?
A) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad separate into different daughter nuclei.
B) The sister chromatids of each chromosome separate into different daughter nuclei.
C) The nonsister chromatids of each tetrad separate into different daughter nuclei.
D) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad separate into one of two daughter nuclei.
E) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad are duplicated and separate into each daughter nucleus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the figure shown here, indicate the correct stage of meiosis and diploid chromosome number. 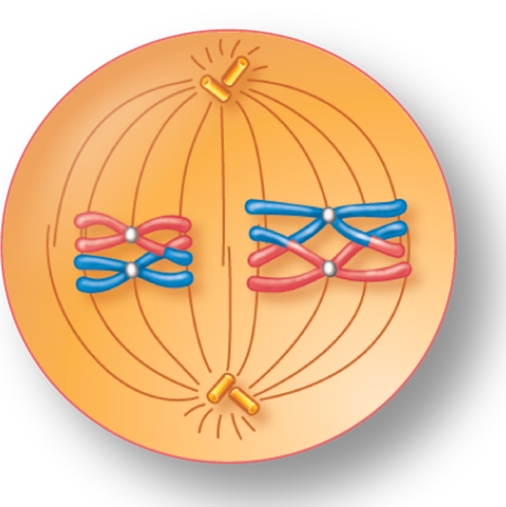
A) metaphase II, 2n=4
B) metaphase II, 2n=2
C) metaphase II, 2n=8
D) metaphase I, 2n=4
E) metaphase I, 2n=8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The failure of sister chromatids to separate would result in how many normal gametes?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Metaphase II is more similar to metaphase of mitosis than to metaphase I because
A) in metaphase I, tetrads align together at the spindle equator.
B) in metaphase II, tetrads align separately at the spindle equator.
C) in metaphase of mitosis, tetrads align separately at the spindle equator.
D) in metaphase II, dyads align separately at the spindle equator.
E) in metaphase I, dyads align separately at the spindle equator.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Armadillos have a diploid chromosome number of 64. At prophase I, an armadillo's cell would have ____ tetrads present.
A) 16
B) 32
C) 64
D) 80
E) 128
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Crossing over between sister chromatids does not result in recombination of genetic material while crossing over between non-sister chromatids does because
A) sister chromatids have the same alleles while non-sister chromatids have different ones.
B) sister chromatids have the same genes while non-sister chromatids have different ones.
C) sister chromatids have the same alleles but different genes while non-sister chromatids have different alleles but the same genes.
D) non-sister chromatids have the same alleles while sister chromatids have different ones.
E) non-sister chromatids have the same genes while sister chromatids have different ones.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The possibility of Down syndrome increases as the mother's age increases because
A) her DNA is damaged through an accumulation of replication errors.
B) her DNA stops checking for replication errors.
C) fertilization no longer occurs correctly with older eggs.
D) the contents of the egg contains the wrong signals for the correct development of the fetus.
E) the possibility of nondisjunction increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: 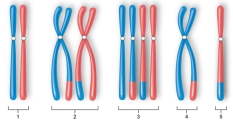 -Which of the diagrams represents a chromosome pair in a cell at the end of prophase II?
-Which of the diagrams represents a chromosome pair in a cell at the end of prophase II?
A) diagram 1
B) diagram 2
C) diagram 3
D) diagram 4
E) diagram 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not occur twice during meiosis?
A) production of daughter nuclei
B) spindle formation
C) pairing of homologous chromosomes
D) separation of genetic material
E) alignment of chromosomes at spindle equator
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tetrad is composed of
A) two chromosomes with two sister chromatids each.
B) two sister chromatids with separate centromeres.
C) four chromosomes with two sister chromatids each.
D) four sister chromatids with a common centromere.
E) four sister chromatids attached at a common centromere.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis is called
A) synapsis.
B) crossing-over.
C) tetrad formation.
D) disjunction.
E) nondisjunction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An individual with the karyotype 48, XYYY would have how many Barr bodies?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An egg with 22 chromosomes that is fertilized by a normal sperm will result in
A) a zygote with trisomy.
B) a zygote with disomy.
C) a zygote with monosomy.
D) a zygote with normal chromosome number.
E) nondisjunction during subsequent mitosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 52
Related Exams