A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q2 - Q1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
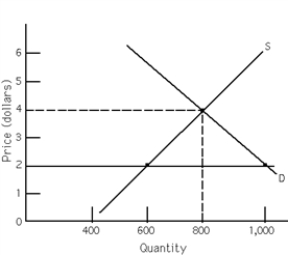 -Exhibit 4-2 represents the orange juice market.The horizontal line at $2 shows a price ceiling imposed by the government.Which of the following statements is true at this price?
-Exhibit 4-2 represents the orange juice market.The horizontal line at $2 shows a price ceiling imposed by the government.Which of the following statements is true at this price?
A) At the price ceiling the surplus equals 400 units.
B) At the price ceiling the shortage equals 400 units.
C) At the price ceiling the surplus equals 300 units.
D) At the price ceiling the shortage equals 200 units.
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
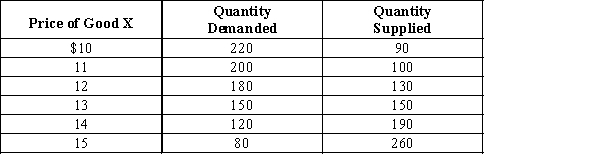 -Refer to Exhibit 4-9.Suppose that the government imposes a price ceiling at a price of $10._________ units would be exchanged in a free market,and ____________ units would be exchanged with the price ceiling in effect.
-Refer to Exhibit 4-9.Suppose that the government imposes a price ceiling at a price of $10._________ units would be exchanged in a free market,and ____________ units would be exchanged with the price ceiling in effect.
A) 150; 220
B) 150; 70
C) 110; 180
D) 150; 90
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of good X is $30 and the price of good Y is $5,it follows that the relative price of one unit of good X is approximately_____________ unit(s) of good Y.
A) 6.00
B) 2.00
C) 0.75
D) 0.25
E) 0.50
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A price floor (set above the equilibrium price) on rice will
A) force otherwise profitable farmers out of business.
B) result in a shortage of rice.
C) result in a surplus of rice.
D) clear the market for rice.
E) both a and b
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
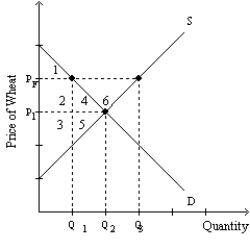 -Refer to Exhibit 4-8.Suppose that wheat producers lobby the government for a price floor and receive one.This price floor is set at PF.What is the size of the total surplus at PF?
-Refer to Exhibit 4-8.Suppose that wheat producers lobby the government for a price floor and receive one.This price floor is set at PF.What is the size of the total surplus at PF?
A) area 1 + 2 + 3
B) area 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
C) area 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5
D) area 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
7/30/2017 4:16 PM
 -Refer to Situation 4-1.If no price controls had been in place,the effect of the oil embargo on the equilibrium price and quantity of gasoline would have been
-Refer to Situation 4-1.If no price controls had been in place,the effect of the oil embargo on the equilibrium price and quantity of gasoline would have been
A) an increase in both price and quantity.
B) an increase in price and a decrease in quantity.
C) a decrease in price and an increase in quantity.
D) a decrease in both price and quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Someone says,"Even though the equilibrium wage rate is $8 an hour in the unskilled labor market,if we impose a minimum wage of $10 an hour,no one currently working will lose his or her job." This person must believe that the
A) demand curve for unskilled labor is vertical.
B) demand curve for unskilled labor is downward-sloping.
C) supply curve for unskilled labor is downward-sloping.
D) supply curve for unskilled labor is horizontal.
E) none of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Refer to Exhibit 4-9.Suppose that the government imposes a price ceiling at a price of $10.The number of units that would be exchanged in this market would be
-Refer to Exhibit 4-9.Suppose that the government imposes a price ceiling at a price of $10.The number of units that would be exchanged in this market would be
A) 150,since that is the equilibrium quantity and the price ceiling is below the equilibrium price.
B) 220,since that is the number of units demanded at the price ceiling (and the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied) .
C) 90,since that is the number of units supplied at the price ceiling (and the quantity supplied is less than the quantity demanded) .
D) 155,since that is the average of the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied at the price ceiling.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
7/30/2017 4:16 PM
 -Refer to Situation 4-1.An economist would have most likely predicted that the oil embargo imposed in 1974 would result in a
-Refer to Situation 4-1.An economist would have most likely predicted that the oil embargo imposed in 1974 would result in a
A) leftward shift in the supply (curve) of gasoline.
B) rightward shift in the supply (curve) of gasoline.
C) leftward shift in the demand (curve) for gasoline.
D) rightward shift in the demand (curve) for gasoline.
E) both a and d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of good X is $90 and the price of good Y is $30,it follows that the relative price of one unit of good Y is ___________ unit(s) of good X.
A) 0.33
B) 1.33
C) 3.00
D) 2.00
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of good X is $100 and the price of good Y is $25,it follows that the relative price of one unit of good X is _____________ unit(s) of good Y.
A) 1.00
B) 4.00
C) 0.25
D) 1.33
E) 0.75
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A deadweight loss is the loss to society of not producing the supply-and-demand determined level of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
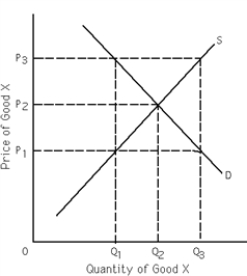 -Refer to Exhibit 4-3.Which of the following is true?
-Refer to Exhibit 4-3.Which of the following is true?
A) If price P3 is set as a price ceiling it will have an effect on the market for good X.
B) If price P3 is set as a price floor it will have an effect on the market for good X.
C) Price P3 is the equilibrium price for good X.
D) Price P3 is the highest price that can legally be charged in the market for good X.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Price ceilings set below the equilibrium price cause shortages.
B) Surpluses result when a price floor is set above the equilibrium price.
C) Price ceililngs set above the equilibrium price cause surpluses.
D) Price ceilings are set by the market and price floors are set by the government.
E) a and b
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A price floor is a government-mandated
A) minimum price below which legal trades cannot be made.
B) maximum price above which legal trades cannot be made.
C) minimum price at which all units of the good must be legally sold.
D) minimum price below which legal trades can be made.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price of a good rises,the price is transmitting information indicating that the good has become relatively
A) scarcer.
B) less scarce.
C) more plentiful in supply.
D) b and c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
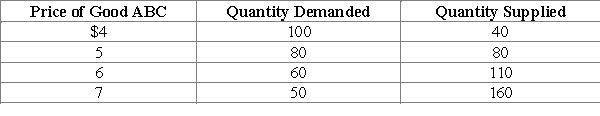 -Refer to Exhibit 4-11.Suppose that the government imposes a price floor in the market for good ABC at a price of $7.The result of the price floor would be a ____________ of ______ units of good ABC.
-Refer to Exhibit 4-11.Suppose that the government imposes a price floor in the market for good ABC at a price of $7.The result of the price floor would be a ____________ of ______ units of good ABC.
A) shortage; 110
B) surplus; 110
C) shortage; 30
D) surplus; 30
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
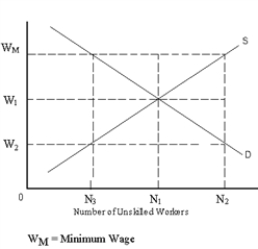 -Refer to Exhibit 4-7.How many unskilled workers do firms want to employ at the minimum wage?
-Refer to Exhibit 4-7.How many unskilled workers do firms want to employ at the minimum wage?
A) N2
B) N1
C) N3
D) N1 + N3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
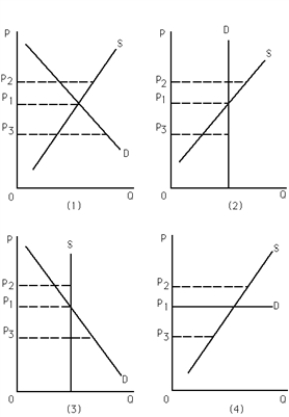 -Refer to Exhibit 4-4.Which of the following statements is false?
-Refer to Exhibit 4-4.Which of the following statements is false?
A) Graph (1) : A price ceiling set at P2 would not have an impact on the market.
B) Graph (2) : As supply increases,equilibrium price remains constant.
C) Graph (3) : As demand increases,equilibrium quantity remains constant.
D) Graph (4) : As supply increases,equilibrium quantity increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 122
Related Exams