A) HbAHbA
B) HbAHbS
C) HbSHbS
D) HbS Hbs
E) HbA Hba
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fraction of the original green frog population survives to reproduce and generate the new population.If the survivors of the original population survived by chance,then this event is an example of
A) natural selection.
B) genetic drift.
C) founder effect.
D) industrial melanism.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Polydactylism (possessing more than five fingers per hand)within the Amish population in Pennsylvania is considered an example of founder effect.This is because the frequency of polydactylism among the Amish in Pennsylvania is identical to its frequency among the Amish population in Germany.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In random mating
A) individuals choose the most attractive mate.
B) there is no influence on mate choice.
C) breeding occurs between two different species.
D) breeding occurs between two different subspecies.
E) fertile offspring are not produced.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a population recovers to its original population size after experiencing a bottleneck,which statement is correct regarding this population?
A) The recovered population is as likely to go extinct as is the population prior to the bottleneck.
B) The bottleneck subjected the population to directional selection.
C) The recovered population shows less genetic diversity that the population prior to the bottleneck.
D) The recovered population shows more genetic diversity than the population prior to the bottleneck.
E) The recovered population is more likely to go extinct as is the population prior to the bottleneck
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What statement is false regarding the differences between a biological species and subspecies?
A) Crosses between biological species cannot produce fertile offspring, crosses between subspecies can produce fertile offspring.
B) Subspecies are "races" within a single species.
C) Gene flow exists among different subspecies but not among species.
D) Greater degrees of allelic frequencies exist between species than among subspecies.
E) Phenotypes of different species are easily recognizable; little to no phenotypic variation exists among subspecies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: 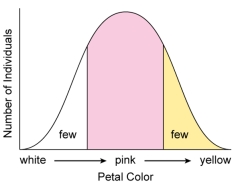 -In the figure shown here,flower color of a population is distributed in a bell-shaped normal curve.If the white and yellow flower colors increase in frequency in the population,this would illustrate
-In the figure shown here,flower color of a population is distributed in a bell-shaped normal curve.If the white and yellow flower colors increase in frequency in the population,this would illustrate
A) stabilizing selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) directional selection.
D) genetic drift.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If people with freckles preferentially mate with other people with freckles,this would be an example of
A) microevolution.
B) natural selection.
C) genetic drift.
D) nonrandom mating.
E) gene flow.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the genes and all of their associated alleles within a population represent the population's
A) genotype.
B) gene flow.
C) gene pool.
D) genome.
E) Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure:  -In the figure shown here,flower color of a population is distributed in a bell-shaped normal curve.If the pink flower color increases in frequency in the population,this would illustrate
-In the figure shown here,flower color of a population is distributed in a bell-shaped normal curve.If the pink flower color increases in frequency in the population,this would illustrate
A) stabilizing selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) directional selection.
D) genetic drift.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not generate genetic variation within a population?
A) genetic recombination
B) independent assortment of alleles
C) sexual reproduction
D) mutations
E) adaptation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
h 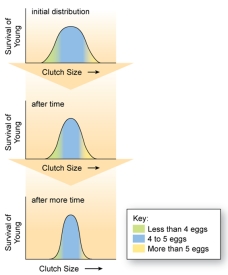 The figure shown here represents stabilizing selection.What happens when an individual is produced that possesses a trait far away from the mean value?
The figure shown here represents stabilizing selection.What happens when an individual is produced that possesses a trait far away from the mean value?
A) That extreme individual will likely not survive and reproduce.
B) That extreme individual will be more likely to survive and reproduce.
C) That extreme individual will have neither an advantage nor a disadvantage than other individuals.
D) All phenotypes have equal likelihood of surviving and reproducing.
E) The average phenotype is less likely to survive and reproduce.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The conditions required by the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are commonly found in nature.
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the average leg size of a reptile continually got smaller through generations,this would be an example of
A) disruptive selection.
B) stabilizing selection.
C) directional selection.
D) genetic drift.
E) bottleneck effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which Hardy-Weinberg condition is violated by sexual selection?
A) no mutations
B) no natural selection
C) random mating
D) no genetic drift
E) no gene flow
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Directional selection in the modern horse is demonstrated by
A) the gradual decrease in size over time.
B) the rapid decrease in size over time.
C) the gradual increase in size over time.
D) the rapid increase in size over time.
E) the extinction of other horse species.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If half of a population is homozygous recessive,what is p?
A) 0.5
B) 0.707
C) 0.25
D) 0.293
E) 0.1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ in their reliance on mutations for generating genetic variation?
A) Prokaryotes are smaller in size than eukaryotes.
B) Prokaryotes sexually reproduce, eukaryotes do not.
C) Eukaryotes sexually reproduce, prokaryotes do not.
D) Eukaryotes possess a nucleus, prokaryotes do not.
E) Prokaryotes are single-celled, eukaryotes are multicellular.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure:  -In the figure shown here,flower color of a population is distributed in a bell-shaped normal curve.If the white flower color increases in frequency in the population,this would illustrate
-In the figure shown here,flower color of a population is distributed in a bell-shaped normal curve.If the white flower color increases in frequency in the population,this would illustrate
A) stabilizing selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) directional selection.
D) genetic drift.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effects of genetic drift are more significant in
A) large populations.
B) small populations.
C) populations that mate randomly.
D) populations that are undergoing natural selection.
E) populations in which the frequency of mutations is high.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 50
Related Exams