A) crossing over occurs in prophase of meiosis I but not in prophase of meiosis II.
B) sister chromatids are separated during meiosis I while homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis II.
C) the resulting cells at the end of meiosis I are diploid while the cells at the end of meiosis II are haploid.
D) in telophase of meiosis I four daughter cells form from the parent cell and in telophase of meiosis II each parent cells gives rise to two daughter cells.
E) in meiosis I there is no pairing of chromosomes while homologues pair in meiosis II.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tetrad is composed of
A) two chromosomes with two sister chromatids each.
B) two sister chromatids with separate centromeres.
C) four chromosomes with two sister chromatids each.
D) four sister chromatids with a common centromere.
E) four sister chromatids attached at a common centromere.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During meiosis I,the homologous chromosomes of a tetrad
A) face the same spindle pole.
B) face both spindle poles.
C) face opposite spindle poles.
D) do not face spindle poles, but are aligned at the spindle equator.
E) undergo separation of sister chromatids.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not occur twice during meiosis?
A) production of daughter nuclei
B) spindle formation
C) pairing of homologous chromosomes
D) separation of genetic material
E) alignment of chromosomes at spindle equator
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Klinefelter syndrome can result from
A) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the female parent.
B) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the male parent.
C) nondisjunction during meiosis I in either female parent.
D) nondisjunction during meiosis I or II in the male parent.
E) nondisjunction during meiosis I or II in either parent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During crossing-over
A) genetic material is exchanged between sister chromatids, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
B) genetic material is exchanged between nonsister chromatids, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
C) sister chromatids from each homologous chromosome of a tetrad are exchanged, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
D) nonsister chromatids from each homologous chromosome of a tetrad are exchanged, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
E) one homologous chromosome of a tetrad is exchanged with another tetrad, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An individual with Swyer syndrome (46,XY) differs from an individual with Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) because
A) an individual with Swyer syndrome has a Barr body, while an individual with Klinefelter syndrome does not.
B) an individual with Klinefelter syndrome has a functional SRY gene on his Y chromosome, whereas an individual with Swyer syndrome does not.
C) both individuals have a functional SRY gene, but the extra X chromosome makes the individual with Klinefelter syndrome appear female.
D) neither individual has a functional SRY gene, but the X chromosome of the individual with Swyer syndrome has a functional SRY and appears male.
E) an individual with Swyer syndrome lacks a functional SRY gene, but appears male because it has moved to the X chromosome as in an individual with Klinefelter syndrome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which stage of meiosis will the pairs of homologous chromosomes line up? Rev: 02_06_2014_QC_44511
A) metaphase I
B) metaphase II
C) metaphase
D) anaphase I
E) prophase II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a correct match?
A) separation of tetrads - anaphase II
B) synapsis - metaphase I
C) separation of sister chromatids - anaphase I
D) synapsis - prophase II
E) separation of sister chromatids - anaphase II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During meiosis II,
A) homologous chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing the same spindle pole.
B) chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
C) chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing the same spindle pole.
D) homologous chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
E) homologous chromosomes line up together, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a function of meiosis?
A) cause an organism to grow
B) create genetic variability
C) reduce the chromosome number in gametes
D) keep chromosome number constant from one generation to the next
E) produce gametes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The possibility of Down syndrome increases as the mother's age increases because
A) her DNA is damaged through an accumulation of replication errors.
B) her DNA stops checking for replication errors.
C) fertilization no longer occurs correctly with older eggs.
D) the contents of the egg contains the wrong signals for the correct development of the fetus.
E) the possibility of nondisjunction increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Metaphase II is more similar to metaphase of mitosis than to metaphase I because
A) in metaphase I, tetrads align together at the spindle equator.
B) in metaphase II, tetrads align separately at the spindle equator.
C) in metaphase of mitosis, tetrads align separately at the spindle equator.
D) in metaphase II, dyads align separately at the spindle equator.
E) in metaphase I, dyads align separately at the spindle equator.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: 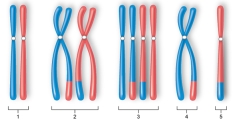 -Which of the diagrams best illustrates the appearance of a chromosome pair in a cell at the end of prophase I?
-Which of the diagrams best illustrates the appearance of a chromosome pair in a cell at the end of prophase I?
A) diagram 1
B) diagram 2
C) diagram 3
D) diagram 4
E) diagram 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement best describes how the members of a tetrad are separated during meiosis I?
A) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad separate into different daughter nuclei.
B) The sister chromatids of each chromosome separate into different daughter nuclei.
C) The nonsister chromatids of each tetrad separate into different daughter nuclei.
D) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad separate into one of two daughter nuclei.
E) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad are duplicated and separate into each daughter nucleus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 55 of 55
Related Exams