A) smaller the proportion of total costs accountable for by labor costs.
B) smaller the elasticity of demand for the product it produces.
C) larger the number of close substitute resources available.
D) more rapid the decline in its marginal productivity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If MRP < Wage rate,a firm should hire more workers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In monopsony situations,a minimum wage might increase wage and employment levels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If two resources are complementary,an increase in the price of one will increase the demand for the other.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A college graduate who works at a firm is also working part-time on a master's degree in business and expects to be paid a higher wage after earning the degree.The basic reason for this wage differential is:
A) efficiency wages.
B) compensating differences.
C) investment in human capital.
D) nonmonetary aspects of work.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reason that the supply curve for labor in a purely competitive market rises is because:
A) the wage rate paid to workers falls as more are hired.
B) the marginal product of labor falls as output increases.
C) marginal resource cost rises as productivity increases.
D) higher wages must be paid to bid workers away from other opportunities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Increased resource productivity will,ceteris paribus,increase a firm's demand for an input.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
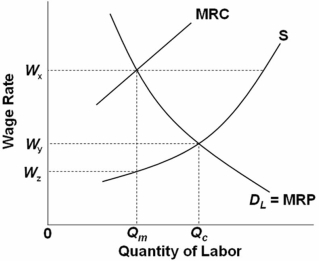 Refer to the above graph.A monopsonist will set the wage at:
Refer to the above graph.A monopsonist will set the wage at:
A) Wy.
B) Wx.
C) Wz.
D) Cannot be determined.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The carpenters' union is an industrial union.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the price of a product produced by an input decreases,the quantity demanded,but not demand,for the input will also decrease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to proponents of human capital theory,education:
A) increases a worker's productivity.
B) identifies more productive workers for employers but does not directly increase productivity.
C) should result in all workers with college degrees earning more than all workers who hold only high school diplomas.
D) is an investment with primarily higher returns and lower risks than those available through investments in physical or financial capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is an example of a change in the price of another resource that increases labor demand?
A) Software sales rise,thus increasing the demand for software developers.
B) Snowboarding increases in popularity,thus increasing the demand for the workers who make snowboards.
C) A decrease in the price of wood decreases the cost of furniture,thus increasing the demand for furniture workers.
D) A technological change increases output per worker in the computer industry,thus increasing the demand for computer workers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If all firms in an industry are price takers in the market for resource A,then:
A) the price of resource A will increase if a single firm increases its output.
B) more efficient firms will produce at levels where the marginal revenue product of the last unit of resource A is higher.
C) less efficient firms will produce where the marginal revenue product of the last unit of resource A is higher.
D) the marginal product of the last unit of resource A will be the same in all firms in the industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
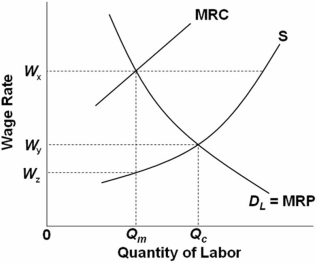 Refer to the above graph.An inclusive union or an industrial union will set the wage rate at:
Refer to the above graph.An inclusive union or an industrial union will set the wage rate at:
A) Wy.
B) Wx.
C) Wz.
D) Cannot be determined.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Equilibrium price differentials for productive resources:
A) tend to be self-eliminating.
B) may be caused by differences in the quality of those resources.
C) are eliminated when the allocation of resources is in a state of equilibrium.
D) are unrelated to differences in nonmonetary benefits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which would decrease a firm's demand for a particular resource?
A) A decrease in the productivity of the resource
B) A decrease in the price of the particular resource
C) An increase in the demand for the firm's product
D) An increase in the price of the product the resource produces
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which would decrease the demand for a particular type of labor?
A) An increase in the demand for the products produced by that type of labor
B) An increase in the prices of the resources that are complements to that type of labor
C) A decrease in the prices of those resources that are complements for that type of labor
D) An increase in the wages of that type of labor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Craft unions typically attempt to increase wage rates for their members by:
A) organizing all of the employees in a factory or industry.
B) opposing increases in the minimum wage that benefit nonunion workers.
C) supporting regulations and policies that increase the price of complementary resources.
D) restricting the supply of skilled workers through worker licensing and training requirements.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The lack of job information for workers would be an example of what explanation for wage differentials among workers?
A) Noncompeting groups
B) Compensating differences
C) Market imperfections
D) Principal-agent problems
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major reason that presidents of major corporations receive an average salary of over $1 million a year and truck drivers receive an average salary of about $55,000 a year can best be explained by:
A) discrimination.
B) lack of job information.
C) compensating differences.
D) noncompeting labor groups.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 164
Related Exams