A) $400,000 for firm X and $400,000 for firm Y.
B) $725,000 for firm X and $475,000 for firm Y.
C) $475,000 for firm X and $725,000 for firm Y.
D) $625,000 for firm X and $625,000 for firm Y.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an oligopolistic market there is likely to be:
A) little consideration of the actions of rival firms.
B) price-taking behavior on the part of firms.
C) homogeneous but not differentiated products.
D) neither allocative nor productive efficiency.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a form of product differentiation for the monopolistically competitive firm?
A) Brand names and trademarks
B) Promotion and packaging
C) Location and accessibility
D) Standard weekday and weekend hours
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Firms in an industry cannot earn long-run economic profits if:
A) fixed costs are zero.
B) the number of firms in the industry is fixed.
C) there is free entry and exit of firms in the industry.
D) production costs for a given level of output are minimized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The incentive to cheat is strong in a cartel because:
A) each firm can increase its output and thus its profits by cutting price.
B) the marginal revenue for an individual firm is greater than marginal cost at the profit-maximizing price set by the cartel.
C) there is a significant lack of government regulation of cartels,especially those in worldwide production.
D) the costs of production are the same for each firm,but the product demand differs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Monopolistically competitive firms exist due to high barriers to entry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The larger the number of firms in an industry and the less the extent of product differentiation,the greater will be the elasticity of the individual seller's demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A prediction from the kinked-demand curve model of noncollusive oligopoly is that,for an individual firm,small changes in:
A) demand will not lead to changes in price or output.
B) marginal revenue will lead to changes in price and output.
C) marginal cost will lead to changes in price and output.
D) marginal cost will not lead to changes in price or output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which cannot be a characteristic of an oligopolistic industry?
A) Differentiated products
B) A large number of consumers
C) Significant barriers to entry
D) A perfectly elastic firm demand curve
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One prediction about monopolistic competition is that firms:
A) operate at minimum average total cost in the long run.
B) will not engage in brand advertising.
C) will be inefficient in the long run.
D) must make economic profits in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major distinction between a monopolistically competitive firm and an oligopolistic firm is that:
A) one is a price taker and the other is a price maker.
B) a recognized interdependence exists between firms in one industry but not in the other.
C) one always produces differentiated products and the other always produces a homogeneous product.
D) one necessarily faces a downward-sloping demand curve and the other a horizontal demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The goal of product differentiation and advertising in monopolistic competition is to make:
A) the firm allocatively efficient even if it is not productively efficient.
B) the firm productively efficient even if it is not allocatively efficient.
C) price less of a factor and product differences more of a factor in consumer purchases.
D) price more of a factor and product differences less of a factor in consumer purchases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The characteristic most closely associated with oligopoly is:
A) easy entry into the industry.
B) a few large producers.
C) product standardization.
D) no control over price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
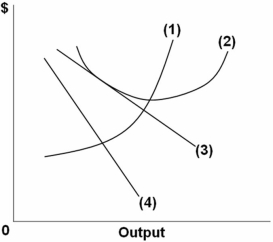 Refer to the above graph of a representative firm in monopolistic competition.What does line 4 represent?
Refer to the above graph of a representative firm in monopolistic competition.What does line 4 represent?
A) Demand
B) Marginal cost
C) Marginal revenue
D) Average total cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement concerning the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly is false?
A) It addresses the question of price stickiness.
B) It assumes when one oligopolist raises the price,all others follow.
C) The portion of the demand curve above the kink is more elastic than the portion below.
D) The firm's marginal costs can sometimes shift without changing the profit-maximizing price and output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
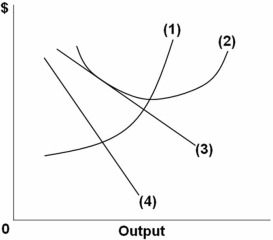 Refer to the above graph of a representative firm in monopolistic competition.What does line 1 represent?
Refer to the above graph of a representative firm in monopolistic competition.What does line 1 represent?
A) Demand
B) Marginal cost
C) Marginal revenue
D) Average total cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the excess capacity problem under monopolistic competition becomes greater,there will be:
A) a narrower range of consumer choice.
B) fewer advertisements and promotions.
C) a wider range of consumer choice.
D) more entry by firms into the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary copper industry in the United States would be an example of a:
A) duopoly.
B) noncollusive oligopoly.
C) homogeneous oligopoly.
D) differentiated oligopoly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Brand names and packaging are forms of product differentiation under monopolistic competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of a monopolistically competitive industry would be:
A) steel.
B) soybeans.
C) electricity.
D) retail clothing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 179
Related Exams