A) 6.8
B) 18
C) 14
D) 28
E) 54
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under constant conditions, the half-life of a first-order reaction ________.
A) is the time necessary for the reactant concentration to drop to half its original value
B) is constant
C) can be calculated from the reaction rate constant
D) does not depend on the initial reactant concentration
E) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A flask is charged with 0.124 mol of A and allowed to react to form B according to the reaction A(g) →B(g) . The following data are obtained for [A] as the reaction proceeds: ![A flask is charged with 0.124 mol of A and allowed to react to form B according to the reaction A(g) →B(g) . The following data are obtained for [A] as the reaction proceeds: -The average rate of disappearance of A between 10 s and 20 s is ________ mol/s. A) 2.2 × 10<sup>-3</sup> B) 1.1 × 10<sup>-3</sup> C) 4.4 × 10<sup>-</sup><sup>3</sup> D) 454 E) 9.90 × 10<sup>-3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f63_2626_a2ab_9b6fd935b612_TB2701_00_TB2701_00_TB2701_00_TB2701_00_TB2701_00_TB2701_00.jpg) -The average rate of disappearance of A between 10 s and 20 s is ________ mol/s.
-The average rate of disappearance of A between 10 s and 20 s is ________ mol/s.
A) 2.2 × 10-3
B) 1.1 × 10-3
C) 4.4 × 10-3
D) 454
E) 9.90 × 10-3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
SO2Cl2 decomposes in the gas phase by the reaction SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g) The reaction is first order in SO2Cl2 and the rate constant is 3.0 × 10-6 s-1at 600 K. A vessel is charged with 3.6 atm of SO2Cl2 at 600 K. The partial pressure of SO2Cl2 at 3.0 × 105 s is ________ atm.
A) 0.85
B) 3.2
C) 1.5
D) 0.19
E) 9.3 × 104
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Reaction rate data showing temperature dependence obey an equation devised by ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nitrogen fixation is a difficult process because ________.
A) there is so little nitrogen in the atmosphere
B) nitrogen exists in the atmosphere primarily as its oxides which are very unreactive
C) nitrogen is very unreactive, largely due to its triple bond
D) of the extreme toxicity of nitrogen
E) of the high polarity of nitrogen molecules preventing them from dissolving in biological fluids, such as those inside cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
For the reaction aA + Bb → cC + dD, the rate law is ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The data in the table below were obtained for the reaction:
2 ClO2 (aq) + 2 OH- (aq) → ClO3- (aq) + ClO2- (aq) + H2O (1) 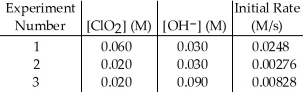 -What is the order of the reaction with respect to ClO2?
-What is the order of the reaction with respect to ClO2?
A) 1
B) 0
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The overall reaction order is the sum of the orders of each reactant in the rate law.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the rate law for the reaction 2A + 3B → products Is first order in A and second order in B, then the rate law is rate = ________.
A) k[A][B]
B) k[A]2[B]3
C) k[A][B]2
D) k[A]2[B]
E) k[A]2[B]2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The binding of molecules to the surface of a catalyst is referred to as ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At elevated temperatures, methylisonitrile (CH3NC) isomerizes to acetonitrile (CH3CN) : CH3NC (g) → CH3CN (g)
The reaction is first order in methylisonitrile. The attached graph shows data for the reaction obtained at 198.9 °C. 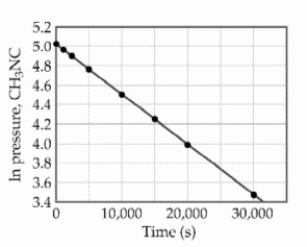 The rate constant for the reaction is ________ s-1.
The rate constant for the reaction is ________ s-1.
A) -1.9 × 104
B) +1.9 × 104
C) -5.2 × 10-5
D) +5.2 × 10-5
E) +6.2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The peroxydisulfate ion (S2O82-) reacts with the iodide ion in aqueous solution via the reaction:
S2O82- (aq) + 3I- → 2SO4 (aq) + I3- (aq)
An aqueous solution containing 0.050 M of S2O82- ion and 0.072 M of I- is prepared, and the progress of the reaction followed by measuring [I-]. The data obtained is given in the table below. ![The peroxydisulfate ion (S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>) reacts with the iodide ion in aqueous solution via the reaction: S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup> (aq) + 3I<sup>-</sup> → 2SO<sub>4</sub> (aq) + I<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) An aqueous solution containing 0.050 M of S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup> ion and 0.072 M of I<sup>-</sup> is prepared, and the progress of the reaction followed by measuring [I<sup>-</sup>]. The data obtained is given in the table below. -The average rate of disappearance of I<sup>-</sup> between 400.0 s and 800.0 s is ________ M/s. A) 2.8 × 10<sup>-5</sup> B) 1.4 × 10<sup>-5</sup> C) 5.8 × 10<sup>-5</sup> D) 3.6 × 10<sup>4</sup> E) 2.6 × 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f63_4d37_a2ab_fd7b3e9826f6_TB2701_00_TB2701_00_TB2701_00.jpg) -The average rate of disappearance of I- between 400.0 s and 800.0 s is ________ M/s.
-The average rate of disappearance of I- between 400.0 s and 800.0 s is ________ M/s.
A) 2.8 × 10-5
B) 1.4 × 10-5
C) 5.8 × 10-5
D) 3.6 × 104
E) 2.6 × 10-4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, as temperature goes up, reaction rate ________.
A) goes up if the reaction is exothermic
B) goes up if the reaction is endothermic
C) goes up regardless of whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic
D) stays the same regardless of whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic
E) stays the same if the reaction is first order
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Arrhenius equation, k = Ae-Ea/RT ________ is the frequency factor.
A) k
B) A
C) e
D) Ea
E) R
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction CH3-N≡C → CH3-C≡N
Is a first-order reaction. At 230.3 °C, k = 6.29 × 10-4s-1. If 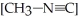 is 1.00 × 10-3 initially,
is 1.00 × 10-3 initially, 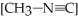 is ________ after 1.000 × 103 s.
is ________ after 1.000 × 103 s.
A) 5.33 × 10-4
B) 2.34 × 10-4
C) 1.88 × 10-3
D) 4.27 × 10-3
E) 1.00 × 10-6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The peroxydisulfate ion (S2O82-) reacts with the iodide ion in aqueous solution via the reaction:
S2O82- (aq) + 3I- → 2SO4 (aq) + I3- (aq)
An aqueous solution containing 0.050 M of S2O82- ion and 0.072 M of I- is prepared, and the progress of the reaction followed by measuring [I-]. The data obtained is given in the table below. ![The peroxydisulfate ion (S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>) reacts with the iodide ion in aqueous solution via the reaction: S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup> (aq) + 3I<sup>-</sup> → 2SO<sub>4</sub> (aq) + I<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> (aq) An aqueous solution containing 0.050 M of S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup> ion and 0.072 M of I<sup>-</sup> is prepared, and the progress of the reaction followed by measuring [I<sup>-</sup>]. The data obtained is given in the table below. -The average rate of disappearance of I<sup>-</sup> in the initial 400.0 s is ________ M/s. A) 6.00 B) 3.8 × 10<sup>-5</sup> C) 1.4 × 10<sup>-4</sup> D) 2.7 × 10<sup>4</sup> E) 3.2 × 10<sup>-4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f63_4d37_a2ab_fd7b3e9826f6_TB2701_00_TB2701_00_TB2701_00.jpg) -The average rate of disappearance of I- in the initial 400.0 s is ________ M/s.
-The average rate of disappearance of I- in the initial 400.0 s is ________ M/s.
A) 6.00
B) 3.8 × 10-5
C) 1.4 × 10-4
D) 2.7 × 104
E) 3.2 × 10-4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown below depicts the relationship between concentration and time for the following chemical reaction. ![The graph shown below depicts the relationship between concentration and time for the following chemical reaction. The slope of this line is equal to ________. A) k B) -1/k C) ln [A]<sub>o</sub> D) -k E) 1/k](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f64_108d_a2ab_77028f1f7b2a_TB2701_00.jpg) The slope of this line is equal to ________.
The slope of this line is equal to ________.
A) k
B) -1/k
C) ln [A]o
D) -k
E) 1/k
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The data in the table below were obtained for the reaction:
2 ClO2 (aq) + 2 OH- (aq) → ClO3- (aq) + ClO2- (aq) + H2O (1)  -What is the order of the reaction with respect to OH-?
-What is the order of the reaction with respect to OH-?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A possible mechanism for the overall reaction Br2 (g) + 2NO (g) → 2NOBr (g)
Is
NO (g) + Br2 (g) ![A possible mechanism for the overall reaction Br<sub>2</sub> (g) + 2NO (g) → 2NOBr (g) Is NO (g) + Br<sub>2 </sub>(g) NOBr<sub>2</sub> (g) (fast) NOBr<sub>2</sub><sub> </sub>(g) + NO (g) 2NOBr (slow) The rate law for formation of NOBr based on this mechanism is rate = ________. A) k<sub>1</sub>[NO]<sup>1/2</sup> B) k<sub>1</sub>[Br<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup> C) (k<sub>2</sub>k<sub>1</sub>/k<sup>-1</sup>) [NO]<sup>2</sup>[Br<sub>2</sub>] D) (k<sub>1</sub>/k<sup>-1</sup>) <sup>2</sup>[NO]<sup>2</sup> E) (k<sub>2</sub>k<sub>1</sub>/k<sup>-1</sup>) [NO][Br<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f62_b0f4_a2ab_55b0478d0c59_TB2701_11.jpg) NOBr2 (g) (fast)
NOBr2 (g) + NO (g)
NOBr2 (g) (fast)
NOBr2 (g) + NO (g) ![A possible mechanism for the overall reaction Br<sub>2</sub> (g) + 2NO (g) → 2NOBr (g) Is NO (g) + Br<sub>2 </sub>(g) NOBr<sub>2</sub> (g) (fast) NOBr<sub>2</sub><sub> </sub>(g) + NO (g) 2NOBr (slow) The rate law for formation of NOBr based on this mechanism is rate = ________. A) k<sub>1</sub>[NO]<sup>1/2</sup> B) k<sub>1</sub>[Br<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup> C) (k<sub>2</sub>k<sub>1</sub>/k<sup>-1</sup>) [NO]<sup>2</sup>[Br<sub>2</sub>] D) (k<sub>1</sub>/k<sup>-1</sup>) <sup>2</sup>[NO]<sup>2</sup> E) (k<sub>2</sub>k<sub>1</sub>/k<sup>-1</sup>) [NO][Br<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2701/11ea7cce_1f62_d805_a2ab_21b3bed4c917_TB2701_11.jpg) 2NOBr (slow)
The rate law for formation of NOBr based on this mechanism is rate = ________.
2NOBr (slow)
The rate law for formation of NOBr based on this mechanism is rate = ________.
A) k1[NO]1/2
B) k1[Br2]1/2
C) (k2k1/k-1) [NO]2[Br2]
D) (k1/k-1) 2[NO]2
E) (k2k1/k-1) [NO][Br2]2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 134
Related Exams