A) HNO2
B) H2CO3
C) HNO3
D) HClO
E) HF
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Br∅nsted-Lowry base is defined as a substance that ________.
A) increases [H+] when placed in H2O
B) decreases [H+] when placed in H2O
C) increases [OH-] when placed in H2O
D) acts as a proton acceptor
E) acts as a proton donor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conjugate base of H2PO4- is ________.
A) H3PO4
B) HPO42-
C) PO43-
D) H3O+
E) OH-
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kb for NH3 is 1.8 × 10-5. What is the pH of a 0.40 M aqueous solution of NH4Cl at 25.0 °C?
A) 2.57
B) 11.43
C) 9.18
D) 4.82
E) 11.23
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hydride ion, H-, is a stronger base than the hydroxide ion, OH-. The product(s) of the reaction of hydride ion with water is/are ________.
A) H3O+ (aq)
B) OH- (aq) + H2 (g)
C) OH- (aq) + 2H+ (aq)
D) no reaction occurs
E) H2O2 (aq)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
HA is a weak acid. Which equilibrium corresponds to the equilibrium constant Kb for A-?
A) HA (aq) + H2O (l) ![]() H2A+ (aq) + OH-(aq)
H2A+ (aq) + OH-(aq)
B) A- (aq) + H3O+ (aq) ![]() HA (aq) + H2O (l)
HA (aq) + H2O (l)
C) HA (aq) + OH- (aq) ![]() H2O (l) + H+ (aq)
H2O (l) + H+ (aq)
D) A- (aq) + H2O (l) ![]() HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
HA (aq) + OH- (aq)
E) A- (aq) + OH- (aq) ![]() HOA2- (aq)
HOA2- (aq)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate bases below is the weakest base? 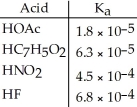
A) OAc-
B) C7H5O2-
C) NO2-
D) F-
E) OAc- and C7H5O2-
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of a 0.020 M aqueous solution of barium hydroxide?
A) 12.60
B) 12.30
C) 1.70
D) 10.41
E) 1.40
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pOH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C that contains 3.98 × 10-9 M hydronium ion?
A) 8.400
B) 5.600
C) 9.000
D) 3.980
E) 7.000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Classify the following compounds as weak bases (W) or strong bases (S) : ammonia fluoride ion sodium hydroxide
A) W W S
B) S S S
C) S W W
D) W S S
E) W S W
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the reaction BF3 + F- → BF4- BF3 acts as a Br∅nsted-Lowry acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the pH of a 0.15 M aqueous solution of KF. For hydrofluoric acid, Ka = 7.0 × 10-4.
A) 0.82
B) 5.83
C) 8.17
D) 5.01
E) 1.17
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Ka of hypochlorous acid (HClO) is 3.0 × 10-8 at 25.0 °C. Calculate the pH of a 0.0385 M hypochlorous acid solution.
A) 3.05
B) 9.53
C) 4.47
D) 6.52
E) -3.05
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the conjugate acid of CO32- ?
A) CO22-
B) HCO22-
C) H2CO3
D) HCO3-
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Classify the following compounds as weak acids (W) or strong acids (S) : hypochlorous acid perchloric acid chloric acid
A) W S S
B) S S S
C) S W W
D) W W W
E) W S W
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate acids below is the strongest acid? 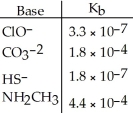
A) HClO
B) HCO3-
C) H2S
D) NH3CH3+
E) H2S and HClO
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A substance that is capable of acting as both an acid and as a base is ________.
A) autosomal
B) conjugated
C) ambiprotic
D) saturated
E) miscible
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 0.1 M aqueous solution of ________ will have a pH of 7.0 at 25.0 °C. LiF RbBr NaClO4 NH4Cl
A) RbBr and NaClO4
B) LiF and RbBr
C) NaClO4 only
D) LiF only
E) NH4Cl only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The base-dissociation constant of ethylamine (C2H5NH2) is 6.4 × 10-4 at 25.0 °C. The [H+] in a 1.4 × 10-2 M solution of ethylamine is ________ M.
A) 3.7 × 4.9 × 10-12
B) 2.7 × 10-3
C) 3.3 × 10-12
D) 3.0 × 10-3
E) 11.43
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the pOH of a 0.0727 M aqueous sodium cyanide solution at 25.0 °C. Kb for CN- is 4.9 × 10-10.
A) 9.33
B) 10.00
C) 5.22
D) 1.14
E) 8.78
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 139
Related Exams