A) Because the WACC incorporates the tax savings from debt, we can compute the levered value of an investment, which is its value including the benefit of interest tax shields given the firm's leverage policy, by discounting its future free cash flow using the WACC.
B) The WACC incorporates the benefit of the interest tax shield by using the firm's before-tax cost of capital for debt.
C) When the market risk of the project is similar to the average market risk of the firm's investments, then its cost of capital is equivalent to the cost of capital for a portfolio of all of the firm's securities; that is, the project's cost of capital is equal to the firm's weighted average cost of capital (WACC) .
D) A project's cost of capital depends on its risk.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information for the question(s) below.
Iota Industries' Market Value Balance Sheet ($ millions) and Cost of Capital 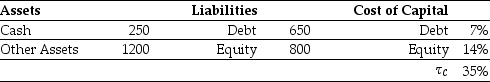 Iota Industries' New Project Free Cash Flows
Iota Industries' New Project Free Cash Flows 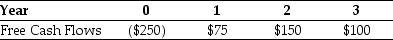 Assume that this new project is of average risk for Iota and that the firm wants to hold constant its debt-to-equity ratio.
-The NPV for Iota's new project is closest to:
Assume that this new project is of average risk for Iota and that the firm wants to hold constant its debt-to-equity ratio.
-The NPV for Iota's new project is closest to:
A) $25.25
B) $13.25
C) $9.00
D) $18.50
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information for the question(s) below.
Omicron Industries' Market Value Balance Sheet ($ millions) and Cost of Capital 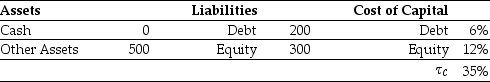 Omicron Industries' New Project Free Cash Flows
Omicron Industries' New Project Free Cash Flows 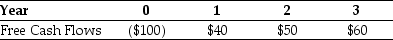 Assume that this new project is of average risk for Omicron and that the firm wants to hold constant its debt-to-equity ratio.
-The interest tax shield provided by Omicron's new project in year 1 is closest to:
Assume that this new project is of average risk for Omicron and that the firm wants to hold constant its debt-to-equity ratio.
-The interest tax shield provided by Omicron's new project in year 1 is closest to:
A) $3.00
B) $1.05
C) $50.25
D) $17.60
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The APV method is the approach that determines the ________ level of debt according to the tradeoff theory.
A) optimal
B) minimal
C) maximal
D) nominal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is false?
A) In the flow-to-equity valuation method, the cash flows to equity holders are then discounted using the weighted average cost of capital.
B) In the WACC and APV methods, we value a project based on its free cash flow, which is computed ignoring interest and debt payments.
C) In the flow-to-equity (FTE) valuation method, we explicitly calculate the free cash flow available to equity holders taking into account all payments to and from debt holders.
D) The first step in the FTE method is to determine the project's free cash flow to equity (FCFE) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information for the question(s) below. Suppose that Rose Industries is considering the acquisition of another firm in its industry for $100 million. The acquisition is expected to increase Rose's free cash flow by $5 million the first year, and this contribution is expected to grow at a rate of 3% every year thereafter. Rose currently maintains a debt-to-equity ratio of 1, its marginal tax rate is 40%, its cost of debt rD is 6%, and its cost of equity rE is 10%. Rose Industries will maintain a constant debt-equity ratio for the acquisition. -Given that Rose issues new debt of $50 million initially to fund the acquisition,the present value of the interest tax shield for this acquisition is closest to:
A) $24 million
B) $50 million
C) $20 million
D) $15 million
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the firm keeps its interest payments to a target fraction of its FCF,we say it has a(n) ________ interest coverage ratio.
A) constant
B) average
C) variable
D) zero
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three main methods of capital budgeting are
A) the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) method, the net present value (NPV) method, and the flow-to-equity (FTE) method.
B) the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) method, the adjusted present value (APV) method, and the debt-to-equity (DTE) method.
C) the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) method, the adjusted present value (APV) method, and the flow-to-equity (FTE) method.
D) the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) method, the adjusted future value (AFV) method, and the flow-to-equity (FTE) method.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The APV method is more complicated than the WACC method because we must compute two separate valuations: ________.
A) the unlevered project and the income tax shield
B) the unlevered project and the CCA tax shield
C) the levered project and the interest tax shield
D) the unlevered project and the interest tax shield
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The WACC incorporates the benefit of the ________ by using the firm's ________ cost of capital for debt.
A) interest tax shield; before-tax
B) expense tax shield; before-tax
C) interest tax shield; after-tax
D) expense tax shield; after-tax
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The APV approach explicitly values the market imperfections and therefore allows managers to measure their contribution to value.
B) We need to know the debt level to compute the APV, but with a constant debt-equity ratio we need to know the project's value to compute the debt level.
C) The WACC method is more complicated than the APV method because we must compute two separate valuations: the unlevered project and the interest tax shield.
D) Implementing the APV approach with a constant debt-equity ratio requires solving for the project's debt and value simultaneously.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Aardvark Corporation is considering launching a new product and is trying to determine an appropriate discount rate for evaluating this new product. Aardvark has identified the following information for three single division firms that offer products similar to the one Aardvark is interested in launching: 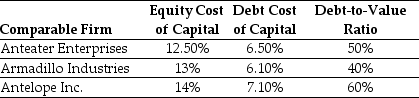 -The unlevered cost of capital for Antelope Incorporated is closest to:
-The unlevered cost of capital for Antelope Incorporated is closest to:
A) 10.3%
B) 9.9%
C) 10.1%
D) 9.5%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the information for the question(s) below. Suppose that Rose Industries is considering the acquisition of another firm in its industry for $100 million. The acquisition is expected to increase Rose's free cash flow by $5 million the first year, and this contribution is expected to grow at a rate of 3% every year thereafter. Rose currently maintains a debt-to-equity ratio of 1, its marginal tax rate is 40%, its cost of debt rD is 6%, and its cost of equity rE is 10%. Rose Industries will maintain a constant debt-equity ratio for the acquisition. -Rose's unlevered cost of capital is closest to:
A) 8.0%
B) 7.5%
C) 7.0%
D) 9.0%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the information for the following four firms: 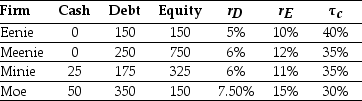 -The weighted average cost of capital for "Moe" is closest to:
-The weighted average cost of capital for "Moe" is closest to:
A) 10.00%
B) 7.75%
C) 8.25%
D) 8.50%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 94 of 94
Related Exams