A) /4
B) /2
C)
D) 2
E) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A hollow sphere of radius 0.25 m is rotating at 13 rad/s about an axis that passes through its center. The mass of the sphere is 3.8 kg. Assuming a constant net torque is applied to the sphere, how much work is required to bring the sphere to a stop?
A) 1.0 J
B) 3.8 J
C) 13 J
D) 25 J
E) 38 J
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform 13-kg trap door is oriented horizontally and hinged as shown. What is the magnitude of the torque on the door at the instant that the release is activated and the door can freely rotate? 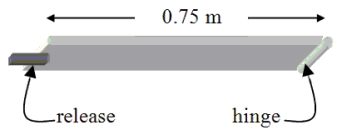
A) 4.9 N . m
B) 9.8 N . m
C) 48 N . m
D) 72 N . m
E) 96 N . m
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two uniform solid spheres, A and B have the same mass. The radius of sphere B is twice that of sphere A. The axis of rotation passes through each sphere. Which one of the following statements concerning the moments of inertia of these spheres is true?
A) The moment of inertia of A is one-fourth that of B.
B) The moment of inertia of A is one-half that of B.
C) The moment of inertia of A is 5/4 that of B.
D) The moment of inertia of A is 5/2 that of B.
E) The two spheres have equal moments of inertia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An 80-kg man balances the boy on a teeter-totter as shown. Note: Ignore the weight of the board. 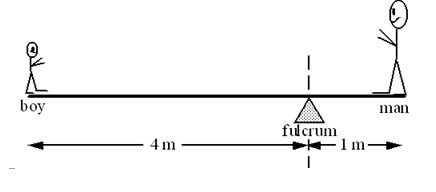 -What is the approximate mass of the boy?
-What is the approximate mass of the boy?
A) 10 kg
B) 20 kg
C) 40 kg
D) 45 kg
E) 50 kg
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1500-kg satellite orbits a planet in a circular orbit of radius 6.2 × 106 m. What is the angular momentum of the satellite in its orbit around the planet if the satellite completes one orbit every 1.5 × 104 s?
A) 3.9 × 106 kg . m2/s
B) 1.4 × 1014 kg . m2/s
C) 6.2 × 108 kg .m2/s
D) 8.1 × 1011 kg . m2/s
E) 2.4 × 1013 kg . m2/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 60.0-kg skater begins a spin with an angular speed of 6.0 rad/s. By changing the position of her arms, the skater decreases her moment of inertia to one-half its initial value. What is the skater's final angular speed?
A) 3.0 rad/s
B) 4.5 rad/s
C) 9.0 rad/s
D) 12 rad/s
E) 18 rad/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 66-N . m torque acts on a wheel with a moment of inertia 175 kg .m2. If the wheel starts from rest, how long will it take the wheel to make one revolution?
A) 0.37 s
B) 0.71 s
C) 2.4 s
D) 5.8 s
E) 6.9 s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 45-N brick is suspended by a light string from a 2.0-kg pulley. The brick is released from rest and falls to the floor below as the pulley rotates through 5.0 rad. The pulley may be considered a solid disk of radius 1.5 m. What is the angular speed of the pulley? 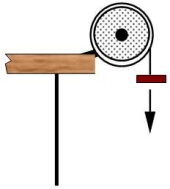
A) 17 rad/s
B) 15 rad/s
C) 9.4 rad/s
D) 8.1 rad/s
E) 7.3 rad/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three objects are positioned along the x axis as follows: 4.4 kg at x = + 1.1 m, 3.7 kg at x = -0.80 m, and 2.9 kg at x = -1.6 m. The acceleration due to gravity is the same everywhere. What is the distance from the location of the center of gravity to the location of the center of mass for this system?
A) zero meters
B) -0.52 m
C) -0.26 m
D) +0.26 m
E) +0.52 m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A string is wrapped around a pulley of radius 0.20 m and moment of inertia 0.40 kg . m2. The string is pulled with a force of 28 N. What is the magnitude of the resulting angular acceleration of the pulley?
A) 22 rad/s2
B) 14 rad/s2
C) 68 rad/s2
D) 0.55 rad/s2
E) 8.0 rad/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The drawing shows the top view of a door that is 1.68 m wide. Two forces are applied to the door as indicated. What is the magnitude of the net torque on the door with respect to the hinge? 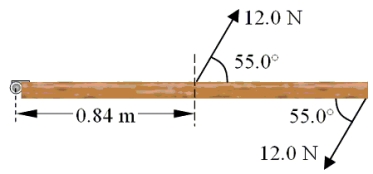
A) 0 N . m
B) 4.4 N . m
C) 8.3 N . m
D) 9.1 N . m
E) 11 N . m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A meter stick is pivoted at the 0.50-m line. A 3.0-kg object is hung from the 0.15-m line. Where should a 5.0-kg object be hung to achieve equilibrium (the meter stick oriented horizontal and motionless) ?
A) 0.06-m line
B) 0.24-m line
C) 0.56-m line
D) 0.71-m line
E) A 5.0-kg object cannot be placed anywhere on the meter stick to result in equilibrium in this system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 14-kg beam is hinged at one end. A 6.0-kg triangular object and a 7.5-kg I-shaped object are positioned as shown. Dots indicate the individual centers of gravity of the beam and the two objects. What is the distance from the axis of rotation to the center of gravity for this system? 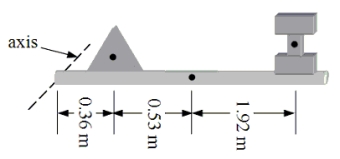
A) 1.3 m
B) 1.1 m
C) 0.96 m
D) 0.89 m
E) 0.71 m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A horizontal, 10-m plank weighs 100 N. It rests on two supports that are placed 1.0 m from each end as shown in the figure. How close to one end can an 800-N person stand without causing the plank to tip? 
A) 0 m
B) 0.3 m
C) 0.5 m
D) 0.7 m
E) 0.9 m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A steady horizontal force 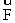 of magnitude 21 N is applied at the axle of a solid disk as shown. The disk has mass 2.0 kg and diameter 0.10 m. What is the linear speed of the center of the disk after it has moved 12 m?
of magnitude 21 N is applied at the axle of a solid disk as shown. The disk has mass 2.0 kg and diameter 0.10 m. What is the linear speed of the center of the disk after it has moved 12 m? 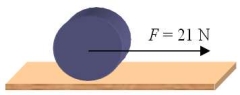
A) 9.0 m/s
B) 13 m/s
C) 16 m/s
D) 22 m/s
E) 44 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.0-kg hoop rolls without slipping on a horizontal surface so that its center proceeds to the right with a constant linear speed of 6.0 m/s. 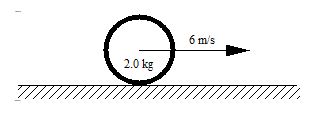 -Which one of the following statements is true concerning the angular momentum of this hoop?
-Which one of the following statements is true concerning the angular momentum of this hoop?
A) It points into the paper.
B) It points out of the paper.
C) It points to the left.
D) It points to the right.
E) It varies from point to point on the hoop.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid cylinder with a mass m and radius r is mounted so that it can be rotated about an axis that passes through the center of both ends. At what angular speed . must the cylinder rotate to have the same total kinetic energy that it would have if it were moving horizontally with a speed v without rotation?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A spinning skater draws in her outstretched arms thereby reducing her moment of inertia by a factor of 2. Determine the ratio of her final kinetic energy to her initial kinetic energy.
A) 0.5
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4
E) 16
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid cylinder of radius 0.35 m is released from rest from a height of 1.8 m and rolls down the incline as shown. What is the angular speed of the cylinder when it reaches the horizontal surface? 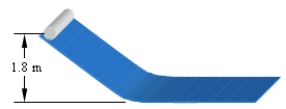
A) 8.2 rad/s
B) 14 rad/s
C) 34 rad/s
D) 67 rad/s
E) This cannot be determined because the mass is unknown.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 57
Related Exams