A) 0.017
B) 1.4
C) 14
D) 80.
E) 10.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the rate constant (s-1) for this reaction?
A) 3.0 × 10-2
B) 14
C) 0.46
D) 4.0 × 102
E) 7.8 × 10-2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes why nitrogen fixation is a difficult process?
A) there is so little nitrogen in the atmosphere
B) nitrogen is very unreactive, largely due to its triple bond
C) nitrogen exists in the atmosphere primarily as its oxides which are very unreactive
D) of the high polarity of nitrogen molecules preventing them from dissolving in biological fluids, such as those inside cells
E) of the extreme toxicity of nitrogen
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Define a homogeneous catalyst.
Correct Answer

verified
A CATALYST THAT IS P...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
The average rate of disappearance of I- between 400.0 s and 800.0 s is ________ M/s.
A) 2.8 × 10-5
B) 1.4 × 10-5
C) 5.8 × 10-5
D) 3.6 × 104
E) 2.6 × 10-4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular first-order reaction has a rate constant of 1.35 × 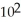
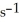 at 25.0 °C.What is the magnitude of k at
at 25.0 °C.What is the magnitude of k at 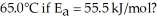
A) 1.92 × 103
B) 1.95 × 104
C) 358
D) 3.48 × 1073
E) 1.35 × ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A first-order reaction has a rate constant of 0.33 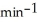 .It takes ________ min for the reactant concentration to decrease from 0.13 M to 0.066 M.
.It takes ________ min for the reactant concentration to decrease from 0.13 M to 0.066 M.
A) 0.085
B) 0.13
C) 0.89
D) 2.4
E) 2.1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the concentration (M) of S2O82- remaining at 1200 s?
A) +0.035
B) +0.038
C) -0.038
D) +0.012
E) -0.012
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following,only ________ is a valid unit for reaction rate.
A) M/s
B) mol/g
C) mmol/mL
D) g/L
E) atm/g
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reaction was found to be zero order in A.Increasing the concentration of A by a factor of 3 will cause the reaction rate to ________.
A) remain constant
B) increase by a factor of 27
C) increase by a factor of 9
D) triple
E) decrease by a factor of the cube root of 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mechanism for formation of the product X is: A + B → C + D (slow) B + D → X (fast) The intermediate reactant in the reaction is ________.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) X
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average rate disappearance of A between 20 s and 30 s is ________ mol/s.
A) 5.0 × 10-4
B) 1.6 × 10-2
C) 1.5 × 10-3
D) 670
E) 0.15
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The overall order of a reaction is 1.The units of the rate constant for the reaction are ________.
A) M/s
B) M-1s-1
C) 1/s
D) 1/M
E) s/M2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the units below,________ are appropriate for a third-order reaction rate constant.
A) M-2s-1
B) M s-1
C) s-1
D) M-1s-1
E) mol/L
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the rate constant ( 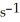 ) of a first-order process that has a half-life of 550 s?
) of a first-order process that has a half-life of 550 s?
A) 3.81 × 102
B) 7.94 × 102
C) -9.09 × 10-4
D) 1.26 × 10-3
E) 1.82 × 10-3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A possible mechanism for the overall reaction Br2 (g) + 2NO (g) → 2NOBr (g)
Is
Step 1) NO (g) + Br2 (g) 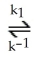 NOBr2 (g) (fast)
Step 2) NOBr2 (g) + NO (g)
NOBr2 (g) (fast)
Step 2) NOBr2 (g) + NO (g) 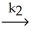 2NOBr (slow)
What is the rate determining step for this reaction?
2NOBr (slow)
What is the rate determining step for this reaction?
A) step 2
B) reverse of step 1
C) both steps 1 and 2
D) step 1
E) reverse of step 2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) If we know that a reaction is an elementary reaction, then we know its rate law.
B) The rate-determining step of a reaction is the rate of the fastest elementary step of its mechanism.
C) Since intermediate compounds can be formed, the chemical equations for the elementary reactions in a multistep mechanism do not always have to add to give the chemical equation of the overall process.
D) In a reaction mechanism, an intermediate is identical to an activated complex.
E) All of the above statements are true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
According to the collision model,reaction rates are affected by reactant ________ and ________.
Correct Answer

verified
concentrat...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
True/False
Heterogeneous catalysts have different phases from reactants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Units of the rate constant of a reaction are independent of the overall reaction order.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 134
Related Exams