A) the profit made by the parent on the sale of the shares.
B) the profit made by the economic entity on the sale of the shares.
C) the amount accruing to the minority interest of the subsidiary.
D) the share of profits derived by the subsidiary for the entire current period.
E) the share of profits derived by the subsidiary in the current period, up to the time of divestment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under the single-date method,goodwill would be recognised.
A) at the point in time when the parent entity ultimately gains control of the subsidiary.
B) at the time when each additional acquisition of shares is made.
C) as part of equity in the parent's books.
D) at the point in time when the subsidiary shareholders acknowledge that they will sell their shareholdings to the parent entity.
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a reason for a parent to lose control of a subsidiary?
A) When the parent makes a decision to sell its controlling interest in the subsidiary to another party.
B) Where the subsidiary issues additional shares to parties other than the parent.
C) The expiry of a contractual agreement that previously permitted the parent entity to control a subsidiary.
D) The subsidiary becoming subject to the control of a voluntary administrator due to bankruptcy.
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When shares in a subsidiary are sold during a period,any income and expenses recorded in the consolidated accounts that relate to the subsidiary,are eliminated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On 1 July 2002,City Ltd acquired 65 per cent of the issued capital of Town Ltd for $850,000 when the fair value of the net assets of Town Ltd was $1.2 million (share capital $1 million and retained earnings $0.2 million) .On 30 June 2005 City Ltd purchased a further 25 per cent of Town's issued capital for $300,000.The net assets of Town Ltd were not stated at fair value in the accounts,which are summarised as follows: 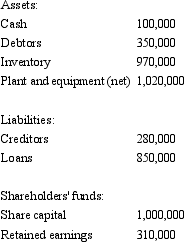 The fair value of the plant and equipment is $1,090,000 at year end.Goodwill has been deemed not to have been impaired.There were no inter-company transactions during the period.
What are the consolidation journal entries required for the period ended 30 June 2005? (Ignore the tax effect of the revaluation)
The fair value of the plant and equipment is $1,090,000 at year end.Goodwill has been deemed not to have been impaired.There were no inter-company transactions during the period.
What are the consolidation journal entries required for the period ended 30 June 2005? (Ignore the tax effect of the revaluation)
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Star Trek Ltd acquires shares in Vulcan Ltd at various stages summarised as follows: 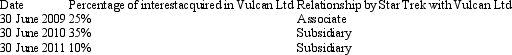 Which of the following statements is not? in accordance with AASB 127 "Consolidated Financial Statements"?
Which of the following statements is not? in accordance with AASB 127 "Consolidated Financial Statements"?
A) Recognise goodwill (bargain gain on purchase) on the acquisition of shares purchased in 2010 and 2011 on consolidation of financial statements for the year 2010 and 2011, respectively, when Star Trek Ltd has control of Vulcan Ltd.
B) Recognise goodwill (bargain gain on purchase) on acquisition of shares made in 2010, when Star Trek Ltd ultimately gained control of the equity of Vulcan Ltd.
C) Difference between purchase consideration and net identifiable assets of Vulcan Ltd for share interests acquired in 2011 is taken to equity.
D) Star Trek Ltd should recognize goodwill using single-date method.
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The consolidated balance sheet at year-end,in a period when the parent sold its interests in a subsidiary:
A) includes the assets and liabilities of the former subsidiary, to ensure that the opening balances reconcile.
B) does not include the assets and liabilities of the former subsidiary, if the subsidiary is no longer controlled by the parent.
C) reports the investment account at cost less proceeds of the sale.
D) includes the assets and liabilities of the former subsidiary, proportionately adjusted for the proceeds of sale.
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Where a parent entity with a controlling interest in a subsidiary obtains additional equity,the carrying amounts of the controlling and non-controlling interests should be adjusted to reflect the changes in their relative interests in the subsidiary.Any difference between the fair value paid and the carrying amount of the additional interest acquired is recognised directly in profit or loss of the parent entity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a parent sells its interest in a subsidiary,any profit or loss generated by the subsidiary:
A) is transferred to the parent's investment in subsidiary account, and used to calculate the amount of profit or loss on the sale of the shares.
B) is immediately transferred to the equity section of the consolidated accounts, and is then available from distribution to shareholders.
C) is set off against any remaining balance in the goodwill on acquisition account, with any remaining amount distributed as dividends to the new owners.
D) is to be recorded in the consolidated financial statements for the period of the year that the parent had control of the subsidiary.
E) is to be recorded in the parent's financial statements for the period of the year that the parent had control of the subsidiary.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Additional purchases of shares in a subsidiary should be accounted for by the combined tranche method,according to AASB 3:
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mickey Ltd acquired a 70 per cent interest in Mouse Ltd on 1 July 2003 for a cash consideration of $1,700,000.At that date the shareholders' funds of Mouse Ltd were: 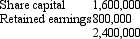 The assets of Mouse Ltd were recorded at fair value at the time of the purchase.
On 1 July 2005 Mickey Ltd purchased a further 20 per cent of the issued capital of Mouse Ltd for a cash consideration of $530,000.At this date the fair value of the net assets of Mouse Ltd were represented by:
The assets of Mouse Ltd were recorded at fair value at the time of the purchase.
On 1 July 2005 Mickey Ltd purchased a further 20 per cent of the issued capital of Mouse Ltd for a cash consideration of $530,000.At this date the fair value of the net assets of Mouse Ltd were represented by:
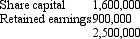 Impairment of goodwill was assessed at $9,000; of which $5,000 relates to the current period.There were no intragroup transactions.What are the consolidation entries to eliminate the investment in the subsidiary and account for goodwill for the period ended 30 June 2006?
Impairment of goodwill was assessed at $9,000; of which $5,000 relates to the current period.There were no intragroup transactions.What are the consolidation entries to eliminate the investment in the subsidiary and account for goodwill for the period ended 30 June 2006?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hill Ltd acquired an 80 per cent interest in Dale Ltd on 1 July 2004 for a cash consideration of $1,200,000.At that date the shareholders' funds of Dale Ltd were: 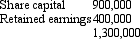 The assets of Dale Ltd were recorded at fair value at the time of the purchase.
On 1 July 2005 Hill Ltd purchased the remaining 20 per cent of the issued capital of Dale Ltd for a cash consideration of $336,000.At this date the fair value of the net assets of Dale Ltd were represented by:
The assets of Dale Ltd were recorded at fair value at the time of the purchase.
On 1 July 2005 Hill Ltd purchased the remaining 20 per cent of the issued capital of Dale Ltd for a cash consideration of $336,000.At this date the fair value of the net assets of Dale Ltd were represented by:
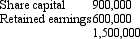 Impairment of goodwill amounted to $35,600; $16,000 of which related to the year ended 30 June 2006.There were no inter-company transactions.What are the consolidation entries to eliminate the investment in the subsidiary and account for goodwill for the period ended 30 June 2006?
Impairment of goodwill amounted to $35,600; $16,000 of which related to the year ended 30 June 2006.There were no inter-company transactions.What are the consolidation entries to eliminate the investment in the subsidiary and account for goodwill for the period ended 30 June 2006?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The required method (according to AASB 3)of accounting for the acquisition of additional shares in a subsidiary is the single-date method.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The profit or loss on the sale of shares in a subsidiary will be reported in both the books of the parent legal entity and the consolidated accounts.The method of calculating the profit or loss in the parent's individual legal entity books is to:
A) Revalue the investment in the subsidiary by adjusting that amount for operating profits recognised in the group accounts over the life of the holding of the shares. The adjusted amount is then compared to the consideration received for the shares and the profit or loss calculated as the difference.
B) The investment in the subsidiary may be recognised in the accounts at either cost or fair value. If it is at cost the amount should be revalued by reference to the last quoted price on the stock exchange. A revaluation difference will be taken to an asset revaluation reserve if it is an increase in value, or written off in the income statement if it is a decrease in value. Any remaining difference between the consideration received and the revalued investment is recognised as a profit or loss in the period of the sale.
C) The profit or loss recognised in the income statement is calculated as the difference between the consideration received and the book value of the investment at the time of sale. The book value may have been fair value or it may be at cost.
D) The investment recorded in the books of the parent entity is first adjusted for any amount of purchased goodwill amortised over the period that the shares have been held, by netting the accumulated amortisation against the investment. The adjusted amount is compared to the consideration received for the shares and where the amount received is greater than the adjusted investment a profit is recognised in the income statement. A loss is recognised in the alternative case, where the consideration is less than the adjusted investment.
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spock Ltd acquired a 10 per cent holding in Kirk Ltd on 1 July 2011 for $350,000 cash,being the fair value of consideration transferred. On 30 June 2012,Spock Ltd acquired a further 75 per cent of the contributed capital of Kirk Ltd for $3,300,000,which represents the fair value of consideration transferred.After the latest acquisition,Spock Ltd gained control of Kirk Ltd.The fair value of the net assets acquired and the liabilities assumed of Kirk Ltd at the acquisition date of 30 June 2012 was $3,500,000 and all assets were recorded at far value in the financial statements of Kirk Ltd.
At that date fair value of the net assets of Kirk Ltd were represented by:
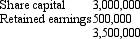 Goodwill is also attributed to the non-controlling interest.
What is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Kirk Ltd on consolidation for the financial year ended 30 June 2012?
Goodwill is also attributed to the non-controlling interest.
What is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Kirk Ltd on consolidation for the financial year ended 30 June 2012?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An immediate parent entity may purchase shares in its subsidiary in separate transactions with long periods of time between transactions.It is possible that one transaction may give rise to goodwill on consolidation and another to an excess.How would the excess on consolidation be calculated and treated in the consolidated accounts?
A) The difference between the fair value of the total consideration paid in all transactions to date should be compared to the proportion of the fair value of the net assets of the subsidiary as at the last purchase date. An excess arises where the consideration is less than the share of the fair value of the net assets purchased. The excess should be eliminated pro-rata against the subsidiary's monetary items. Where the excess is greater than the amount of non-monetary items the balance should be eliminated against the non-monetary assets of the subsidiary.
B) The difference between the fair value of the consideration paid for the shares and the fair value of the proportion of net assets acquired in each transaction should be calculated separately. An excess arises where the consideration is less than the share of the fair value of the net assets purchased. The excess should be recognised as revenue.
C) The difference between the value of the total consideration paid in all transactions to date should be compared to the proportion of the book value of the net assets of the subsidiary as at the last purchase date. An excess arises where the consideration is less than the share of the fair value of the net assets purchased. The excess should be amortised over a period of not greater than 10 years.
D) The difference between the fair value of the consideration paid for the shares and the fair value of the proportion of net assets acquired in each transaction should be calculated. While the Standard does not permit goodwill to be recognised on a purchase of further shares after control has been achieved, an excess will be recognised if the consideration is less than the share of the fair value of the net assets purchased. The excess should be eliminated pro-rata against the subsidiary's monetary items. The excess should be amortised over a period of not greater than 10 years.
E) None of the given answers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Under the step-by-step method,the aggregate costs of the investments would be eliminated against the parent's share of capital and reserves at the date control of the subsidiary has been ultimately established and only one amount of goodwill (or bargain gain on purchase)is calculated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Once control over a subsidiary has been lost,the parent entity must derecognise the individual assets,liabilities and equity including any non-controlling interest relating to that subsidiary.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a business combination achieved in stages,the acquirer shall re-measure its previously held equity interest in the acquiree at its acquisition-date fair value and recognise the resulting gain or loss,if any,in equity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 39 of 39
Related Exams