A) 5; 6
B) 7; 6
C) 7; 8
D) 7; 14
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is said to be quantized?
A) the number of eggs in an egg carton
B) the amount of water in a glass
C) the volume of air in a balloon
D) the amount of time in an hour
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An atomic orbital ________.
A) is the path of an electron
B) is a region of space
C) can hold up to four electrons
D) is always spherical
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why can't we see atoms?
A) We see with light energy and the wavelength of light is larger than the atom and is not reflected.
B) Atoms are invisible.
C) We cannot see things that are microscopic.
D) We see with light energy but the atoms absorb all the light and therefore there are no reflections.
E) Atoms do not interact with light energy and therefore we are unable to observe them with light.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An element found in another galaxy exists as two isotopes. If 80.0 percent of the atoms have an atomic mass of 80.00 amu and the other 20.0 percent have an atomic mass of 82.00 amu, what is the atomic mass of the element?
A) 81.0 amu
B) 64.0 amu
C) 80.4 amu
D) 16.4 amu
E) 81.6 amu
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since atoms are mostly empty space, why don't objects pass through one another?
A) The electrons on the atoms repel other electrons on other atoms when they get close.
B) The nucleus of one atom repels the nucleus of another atom when it gets close.
C) The nucleus of one atom attracts the nucleus of a neighboring atom to form a barrier.
D) The electrons of one attracts the nucleus of a neighboring atom to form a barrier.
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron in the outermost shell of which group 1 element experiences the greatest effective nuclear charge?
A) Sodium, Na
B) Potassium, K
C) Rubidium, Rb
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many electrons are there in the third shell of sodium, Na (atomic number 11) ?
A) none
B) one
C) two
D) three
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
List the following atoms in order of increasing atomic size: Thallium, Tl; Germanium, Ge; Tin, Sn; Phosphorus, P.
A) Ge < P < Sn < Tl
B) Tl < Sn < P < Ge
C) Tl < Sn < Ge < P
D) P < Ge < Sn < Tl
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a neutral element has 8 neutrons and 7 electrons, which expression correctly identifies the element?
A) ![]() N
N
B) ![]() O
O
C) ![]() O
O
D) ![]() O
O
E) cannot tell from information given
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not describe a neutron?
A) It has a positive charge equivalent but opposite of an electron's.
B) It is much more massive than an electron.
C) It is a nucleon.
D) It is often associated with protons.
E) It is more difficult to detect than a proton or an electron.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following experiments helped to determine that most of an atom is actually empty space except for a very small positive core?
A) J.J. Thompson's cathode ray deflection experiments
B) R. Millikan's oil drop experiments
C) E. Rutherford's gold foil experiments
D) Avogadro's number experiments
E) Franklin's kite experiments
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a neutral element has the following chemical symbol, how many electrons does it have? 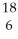 O
O
A) 6
B) 18
C) 12
D) 24
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron in an outermost shell has more energy than one in an innermost shell because ________.
A) it is surrounded by more electrons
B) it is farther from the nucleus
C) its principle quantum number is higher
D) It actually has less energy because of inner-shell shielding
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An element has two different isotopes: one that weighs 65 amu and another that weighs 67 amu. If the average atomic mass of all the isotopes is 66.5 amu, what can be said about the relative abundance of the isotopes?
A) The isotope with the mass of 67 is more abundant than the isotope with the mass of 65.
B) The isotope with the mass of 65 is more abundant than the isotope with the mass of 67.
C) The isotope with the mass of 66.5 is more abundant than the isotope with the mass of 67.
D) The isotope with the mass of 66.5 is more abundant than the isotope with the mass of 65.
E) All the isotopes have the same relative abundance.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Would you use a physical model or a conceptual model to describe the following: a gold coin, dollar bill, car engine, air pollution, virus, spread of sexually transmitted disease?
A) conceptual model-gold coin, car engine, virus; physical model-air pollution, spread of sexually transmitted disease, dollar bill
B) physical model-gold coin, car engine, virus; conceptual model-air pollution, spread of sexually transmitted disease; dollar bill, which could represent wealth, may well be described by either model.
C) You could adequately describe all of the topics by either model. The choice depends only on the characteristics requiring description.
D) physical model-gold coin, dollar bill, car engine; conceptual model-virus, air pollution, spread of sexually transmitted disease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cathode ray consists of ________.
A) positively charged particles
B) negatively charged particles
C) electrically neutral particles
D) massless particles
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes a conceptual model of an atom?
A) a model that illustrates the tendency of an atom to undergo radioactive decay and the products it produces
B) a model that illustrates the physical structure of the atom
C) a model that represents the shape of the nucleus and the location of the electrons
D) a description of the location of the neutrons and protons in an atom
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some older cars vibrate loudly when driving at particular speeds. For example, at 65 mph the car may be most quiet, but at 60 mph the car rattles uncomfortably. How is this analogous to the quantized energy levels of an electron in an atom?
A) A car is designed for maximum performance at particular speeds under given road conditions. Likewise, electron energy level transitions are smooth if they occur while the atom is in a low energy state. Changing the speed of the car for the road conditions is similar to subjecting the atom to unusual energy conditions.
B) New cars and small atoms don't share this behavior because modern technology produces better cars and small atoms don't have enough electrons to move among quantized energy levels to cause vibration.
C) The vibrating car is analogous to one of the energy levels of the electron, which is the point at which the electron experiences resonance.
D) There can be no analogy between a vibrating car and the quantized energy level of an electron in an atom since electrons don't vibrate. Doing so would cause the atom to break apart.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes an isotope?
A) element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
B) element with the same number of protons but a different number of electrons
C) element with the same number of neutrons but a different number of electrons
D) element with the same number of neutrons but a different number of protons
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 146
Related Exams