A) will not work if the money market is in disequilibrium,and may end up making the economy worse.
B) will not work unless alternative sources of energy are employed.
C) may not work if buyers and sellers are out of sync with one another,and may end up making the economy worse.
D) are always successful in pushing the economy to full-employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 15-3 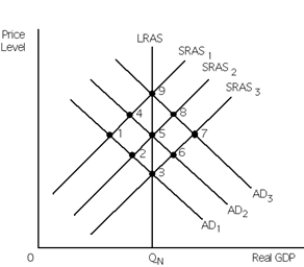 -Refer to Exhibit 15-3.The economy is initially at point 1.Ideally,__________ monetary policy will move the economy to point __________.
-Refer to Exhibit 15-3.The economy is initially at point 1.Ideally,__________ monetary policy will move the economy to point __________.
A) expansionary;9
B) contractionary;4
C) expansionary;8
D) expansionary;7
E) contractionary;2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rules-based monetary policy
A) is advocated by activists.
B) is advocated by nonactivists.
C) could involve a predetermined steady growth rate in the money supply.
D) b and c
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Investment spending is insensitive to changes in the interest rate and the SRAS curve is upward sloping.According to a monetarist,an increase in the money supply will __________ Real GDP.According to a Keynesian,an increase in the money supply will __________ Real GDP.
A) raise;not change
B) not change;raise
C) lower;lower
D) raise;lower
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Traditional monetarists advocate for a rule for _____________ ,while market monetarists argue that monetary policy should focus on a ______________________.
A) nominal GDP target;money supply growth
B) Real GDP target;nominal GDP target
C) money supply growth;Real GDP target
D) money supply growth;nominal GDP target
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Keynesians,__________ monetary policy will not remove the economy from a(an) __________ gap if __________.
A) contractionary;recessionary;investment is interest-insensitive
B) expansionary;recessionary;the economy is in the liquidity trap
C) expansionary;inflationary;investment is interest-insensitive
D) contractionary;inflationary;the economy has been in the inflationary gap for more than one year
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic fine-tuning is the (usually frequent) use of
A) monetary policy that is based on a predetermined steady growth rate in the money supply to counteract even small undesirable movements in economic activity.
B) only fiscal policy to counteract even small undesirable movements in economic activity.
C) monetary and fiscal policies to counteract even small undesirable movements in economic activity.
D) fiscal policy that both balances the budget and counteracts even small undesirable movements in economic activity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rules-based monetary policy that some nonactivists have proposed to maintain price stability reads this way:
A) The annual growth rate in the money supply will equal the average annual growth rate in Real GDP minus the growth rate in velocity.
B) The annual growth rate in the money supply will equal the average annual growth rate in Real GDP plus the growth rate in velocity.
C) The annual growth rate in the money supply will equal the average annual growth rate in Real GDP divided by the growth rate in velocity.
D) The annual growth rate in the money supply will equal the average annual growth rate in Real GDP times the growth rate in velocity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rules-based monetary policy reads: The money supply will increase 3 percent each year.If the average annual growth rate in Real GDP is 2 percent and velocity increases by 1 percent each year,it follows that
A) the price level will,on average,rise 2 percent a year.
B) the price level will rise 2 percent this year.
C) in some years the price level will rise by more than in other years.
D) in some years the price level may not change at all.
E) a,c and d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy is in the horizontal portion of the AS curve,investment spending is interest insensitive and there is no liquidity trap.According to the Keynesian transmission mechanism,if the money supply increases the interest rate will __________,investment spending will __________,the AD curve will __________,and Real GDP will __________.
A) fall;fall;left;fall
B) rise;drop;left;fall
C) fall;remain unchanged;not shift;not change
D) rise;remain unchanged;not shift;not change
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand for money rises.According to the Keynesian transmission mechanism,the interest rate __________,investment spending __________ (assuming it is interest-sensitive) ,the AD curve shifts to the __________ and if the AS curve is horizontal,Real GDP __________.
A) rises;falls;left;rises
B) falls;rises;right;does not change
C) rises;falls;right;rises
D) falls;falls;left;does not change
E) rises;falls;left;falls
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Nonactivists argue against the use of discretionary monetary policy and rules-based monetary policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To try to eliminate a recessionary gap the Fed typically__________ the money supply,and to try to eliminate an inflationary gap the Fed typically __________ the money supply.
A) increases;decreases
B) increases;increases
C) decreases;increases
D) decreases;decreases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The price of old (or existing)bonds and interest rates have an inverse relationship.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do Keynesians mean when they say that "you can't push on a string"?
A) An increase in the supply of goods does not really create its own demand.
B) If the government reduces taxes in an attempt to increase household consumption,it will not always work.
C) An increase in the money supply will not always stimulate the economy.
D) If the government wants to get something done,the best way is not to force the issue,but to offer incentives.
E) If the government puts too much expansionary pressure on the economy,it will probably "overheat."
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The money supply curve is usually horizontal.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When an economist states that the monetarist transmission mechanism is "direct" it means that a change in the money supply creates a direct impact on the goods and services market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Equilibrium in the money market exists when
A) at a given interest rate,excess supply of money is equal to the quantity demanded of money.
B) at a given interest rate,excess demand for money is equal to the quantity demanded of money.
C) the supply of money curve intersects the demand for money curve at the prevailing interest rate.
D) b and c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which scenario best explains the Keynesian transmission mechanism when the money supply increases while the money market is in a liquidity trap?
A) The interest rate and investment are not affected;there is no shift in the AD curve.
B) The interest rate falls,investment rises,total expenditures rise,and the AD curve shifts rightward.
C) The interest rate falls,investment falls instead of rising,and the AD curve ends up shifting leftward.
D) The interest rate falls,but investment does not respond;there is no change in total expenditures and no shift in the AD curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Keynesian transmission mechanism,if the money market is in the liquidity trap,an increase in the money supply will
A) cause total expenditures and aggregate demand to increase.
B) cause total expenditures and aggregate demand to decrease.
C) have no impact on total expenditures and aggregate demand.
D) cause total expenditures to increase and aggregate demand to decrease.
E) cause total expenditures to decrease and aggregate demand to increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 174
Related Exams