A) P = AR = MR
B) P > AR = MR
C) P = AR > MR
D) P = AR < MR
E) P < AR = MR
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue from selling one more unit of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If price-taking firms are required to install wet scrubbers on their chimneys to meet EPA regulations and their costs increase as a result,we would expect
A) demand for the product to fall
B) the market supply curve to shift to the left
C) the long-run economic profit of individual firms in the industry to fall
D) the short-run economic profit of individual firms in the industry to remain unchanged
E) short-run profits to rise as the industry raises price more than the cost of pollution
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A perfectly competitive firm has reached long run equilibrium at 20 units of output produced with total cost of $1,200.The market price is:
A) $1,200
B) $400
C) $20
D) $60
E) We don't have enough information to calculate it
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would not help identify market structure?
A) number of firms in the industry
B) type of product produced in the industry
C) ease of entry into the industry
D) forms of competition among firms in the industry
E) price of the good
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 8-14
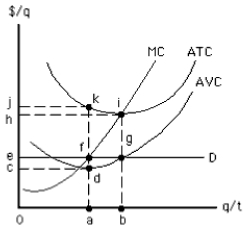 -In Exhibit 8-14,what area represents total revenue at the loss-minimizing output?
-In Exhibit 8-14,what area represents total revenue at the loss-minimizing output?
A) 0cda
B) 0jka
C) 0efa
D) 0hib
E) 0egb
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Harry's Blueberries,a perfectly competitive firm,shuts down in the short run,Harry must pay
A) variable cost but not fixed cost
B) no costs at all
C) variable cost and fixed cost
D) only variable cost
E) only fixed cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A horizontal long-run industry supply curve occurs under conditions of
A) economies of scale
B) diseconomies of scale
C) monopoly
D) increasing costs
E) constant costs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not necessarily a characteristic of perfect competition?
A) low prices
B) a large number of buyers and sellers
C) a homogeneous product
D) perfect information
E) easy entry and exit in the long run
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short run,a perfectly competitive ball bearing manufacturer will continue to produce at a loss if
A) it is covering all of its fixed cost
B) it is covering all of its variable cost plus part of its fixed cost
C) variable cost is less than fixed cost
D) fixed cost is zero
E) fixed cost is minimized
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not characterize a perfectly competitive firm that has shut down in the short run?
A) total revenue equals zero
B) variable costs equal zero
C) the firm suffers a loss
D) fixed cost is positive
E) fixed cost is zero
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a market is productively efficient,
A) the output is being produced at the lowest possible resource cost
B) the output is selling for the lowest possible price
C) economic profit in the market is positive
D) the output being produced is what consumers want
E) no firm can earn a normal profit
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists assume that firms seek to
A) maximize accounting profit
B) maximize economic profit
C) maximize total revenue
D) maximize normal profit
E) minimize cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a perfectly competitive increasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium when market demand suddenly decreases.What might happen to the typical firm in the long run?
A) It would experience no change from the original equilibrium
B) It would experience a higher equilibrium price
C) It would experience a lower equilibrium price
D) It would experience the same equilibrium price but would increase output
E) It would experience a lower average total cost and would increase output
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If average revenue equals average total cost,
A) total revenue is maximized
B) average revenue is maximized
C) average total cost is minimized
D) economic profit is maximized
E) economic profit is zero
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short run,a perfectly competitive firm suffering a loss
A) will close if P < AVC
B) will shut down operations if P < MC
C) cannot leave the industry even if P < AVC
D) can sell off all its resources to competitors
E) can raise the price to increase revenues
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Perfectly competitive firms are sometimes called price makers because they have significant control over product price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A perfectly competitive firm is allocatively efficient because price is identical to marginal cost at every quantity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the market for hot pretzels in New York City is perfectly competitive.What is true of demand in this market?
A) The demand curve facing each seller is perfectly elastic.
B) The demand curve facing each seller is perfectly inelastic.
C) The market demand curve is perfectly elastic.
D) The market demand curve is perfectly inelastic.
E) The market demand curve is elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The significance of the minimum point on the average variable cost curve is that
A) it is the profit-maximizing level
B) it is the selling price
C) it is the point of indifference between producing at a loss or shutting down
D) if the firm produces one more unit,its AVC will be less than MC
E) it shows the amount of total cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 250
Related Exams