A) root beer and orange soda are substitutes.
B) root beer and orange soda are complements.
C) the cross-price elasticity of demand is 1.
D) the cross-price elasticity of demand is equal to 2.
E) the cross-price elasticity of demand is equal to −2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) A perfectly elastic demand curve is a constant-elasticity demand curve.
B) A linear demand curve with a slope of −4 is a constant-elasticity demand curve.
C) A perfectly inelastic demand curve is a constant-elasticity demand curve.
D) Total revenue increases along a unit-elastic demand curve.
E) The elasticity value for a perfectly elastic demand curve is zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.8 shows a horizontal line. The curve shown in the figure below could represent a: Figure 5.8
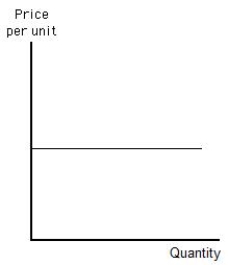
A) perfectly elastic demand or supply curve.
B) perfectly inelastic supply curve or a perfectly elastic demand curve.
C) perfectly elastic supply curve or a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
D) perfectly inelastic supply or demand curve.
E) perfectly inelastic supply curve or a demand that is unit elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The demand for firewood is likely to be more elastic in the summer than in the winter.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand for a good is elastic if:
A) an increase in price leads to a decrease in total revenue.
B) an increase in price leads to an increase in total revenue.
C) an increase in price causes no change in total revenue.
D) a decrease in price causes no changes in total revenue.
E) a decrease in price leads to a decrease in total revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose consumers spent $42 million on Christmas trees last year, when the average tree cost was $30. This year they spend $42 million, when the average tree costs $25. Assume that everything else remains constant. This data suggests that:
A) consumers bought the same number of Christmas trees this year as last year.
B) the price of the Christmas trees stayed the same.
C) total revenue to tree producers rose this year.
D) the demand for trees is unit elastic.
E) the demand for trees is inelastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If supply is perfectly elastic, the supply curve is:
A) vertical.
B) horizontal.
C) downward sloping.
D) upward sloping.
E) u-shaped.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following goods will have a higher price elasticity of demand?
A) A good with few substitutes.
B) A good with many substitutes.
C) A good that represents a small proportion of the consumer's budget.
D) A good that is broadly defined.
E) A good that is a necessity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good that is defined broadly has:
A) more substitutes and a more elastic demand.
B) fewer substitutes and a more elastic demand.
C) more substitutes and a less elastic demand.
D) fewer substitutes and a less elastic demand.
E) more complements and a more elastic demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of Pepsi-Cola increases from 40 cents to 50 cents per can and the quantity demanded decreases from 100 cans to 50 cans, then the value of the price elasticity of demand for Pepsi-Cola is:
A) −0.5.
B) −0.25.
C) −1.
D) −3.
E) −2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The availability of substitutes makes the demand for a good less elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of the cross-price elasticity of demand between golf balls and golf clubs is:
A) negative.
B) positive.
C) zero.
D) greater than 1 but less than 3.
E) equal to 1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply of paintings by Van Gogh is most likely to be:
A) relatively elastic because supply is limited.
B) relatively inelastic because supply is limited.
C) perfectly elastic because the paintings are luxury goods.
D) perfectly inelastic because supply is limited.
E) unit elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For which of the following goods is the value of income elasticity most likely to be negative?
A) Macaroni and cheese.
B) Champagne.
C) Airline tickets.
D) Clothes.
E) Toothpaste.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If demand is inelastic, the percentage change in price is greater than the resulting percentage change in quantity demanded.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.5 shows the total revenue curve for a firm. Which of the following statements is true at a quantity of 10?
Figure 5.5
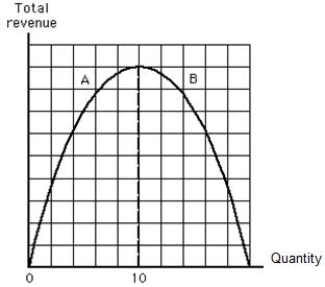
A) Demand is elastic.
B) Demand is inelastic.
C) Demand is unit elastic.
D) Demand is perfectly inelastic.
E) Demand is perfectly elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve for dorm rooms on a university campus is likely to be:
A) downward sloping.
B) relatively flat.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
E) upward sloping.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.6 shows a vertical demand curve. The price elasticity of demand in the figure below is _____.
Figure 5.6

A) 0
B) −1
C) infinity
D) 1
E) −100
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good that takes up a very large percentage of a consumer's budget will tend to have:
A) an elastic demand.
B) a perfectly elastic demand.
C) an inelastic demand.
D) an upward-sloping demand curve.
E) many close substitutes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an increase in price from $1 to $2 per unit leads to an increase in quantity supplied from 20 to 100 units, then the value of the price elasticity of supply is:
A) 0.38.
B) 2.
C) 2.67.
D) 4.
E) 8.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 149
Related Exams