A) The marginal cost curve is U-shaped for a perfectly competitive firm but not for a monopolist.
B) Price is equal to average revenue for a perfectly competitive firm in equilibrium but not for a monopolist.
C) Price is equal to marginal revenue for a perfectly competitive firm in equilibrium but not for a monopolist.
D) The average revenue curve is the demand curve for a perfectly competitive firm but not for a monopolist.
E) A monopolist aims to maximize profits, while a perfectly competitive firm tries to maximize total revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm facing a downward-sloping demand curve sells 50 units of output at $10 each. Which of the following can be concluded about the firm's marginal revenue for this output level?
A) Marginal revenue is equal to $500.
B) Marginal revenue is more than $10.
C) Marginal revenue is equal to $10.
D) Marginal revenue is less than $10 but more than zero.
E) Marginal revenue is zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true for a monopolist that engages in perfect price discrimination?
A) Perfect price discrimination restricts the total output produced by the monopolist.
B) Perfect price discrimination allows the monopolist to just break even and transfers the gain to consumers.
C) Perfect price discrimination results in the maximization of consumer surplus.
D) Perfect price discrimination creates a deadweight loss.
E) Perfect price discrimination allows the monopolist to reap the entire gains from production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for the non-discriminating monopolist is _____.
Figure 9.6
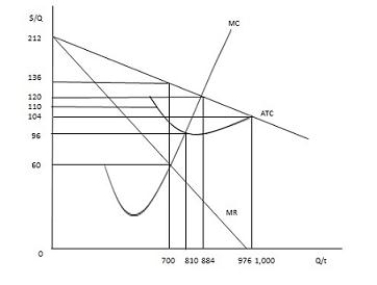
A) $60
B) $76
C) $110
D) $120
E) $136
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopolist maximizes profit at the quantity where the slope of its total revenue curve equals the slope of its total cost curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the price and output combinations at different output levels for a non price-discriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing output for this monopolist is _____.
Table 9.6
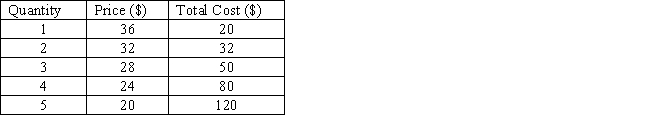
A) 1 unit
B) 2 units
C) 3 units
D) 4 units
E) 5 units
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A monopolist that fails to recover a short-run loss in the long run generally leaves the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following prevents potential competitors from entering a monopolized market?
A) Legal restrictions
B) Diseconomies of scale
C) Product differentiation
D) Stable market demand
E) An abundant supply of resources
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The actual deadweight loss from monopoly in the United States is likely to be greater than the calculated estimates because some:
A) monopolies experience strong economies of scale.
B) monopolists spend resources to secure and maintain their monopoly.
C) monopolists often keep price lower than their profit-maximizing level in order to increase barriers to entry.
D) monopolists' markets are contestable.
E) monopolists' prices and profits are regulated by the government.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true when a perfectly competitive firm is in short-run equilibrium but not when a non-discriminating monopolist is in equilibrium?
A) Price equals marginal cost.
B) Price is greater than marginal cost.
C) Marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) Marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
E) Marginal revenue is greater than average revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a profit-maximizing monopolist. If the monopolist engages in perfect price discrimination, its profit-maximizing output will be _____.
Figure 9.6
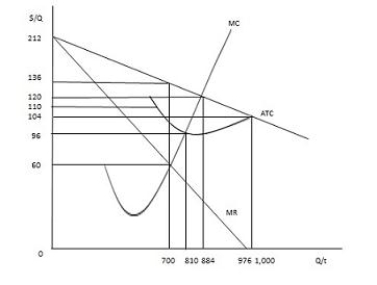
A) 700 units
B) 810 units
C) 884 units
D) 976 units
E) 1,000 units
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the total cost and total revenue curves for a monopolist. The total profit earned by the monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is _____.
Figure 9.3
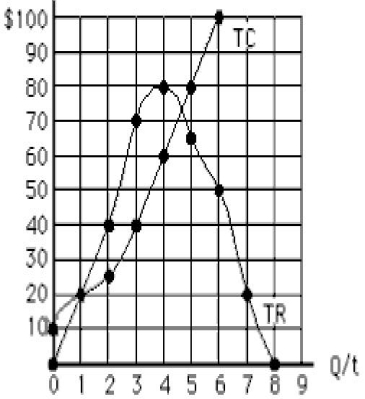
A) $20
B) $30
C) $0
D) $70
E) $40
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a restaurant has a monopoly in a certain small town. Its rent, which is one of the several fixed costs it incurs whether it sells food or not, has gone up. In the short run, the restaurant should:
A) pay the higher rent and increase menu prices.
B) pay the higher rent and leave menu prices unchanged.
C) pay the higher rent and lower menu prices.
D) open another restaurant in the same town.
E) shut down.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors explain the difference in long-run profits earned by a monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm?
A) Monopolists experience economies of scale.
B) Perfectly competitive firms have high opportunity costs.
C) The demand for the monopolist's output is inelastic.
D) The demand for the monopolist's output is elastic.
E) There are no barriers to entry in perfect competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve for a monopolist:
A) is its marginal cost curve.
B) is vertical because there are no close substitutes for its product.
C) is horizontal because there are no close substitutes for its product.
D) slopes upward.
E) does not exist.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government breaks up a monopoly that does not practice discrimination and faces a horizontal marginal cost curve into a perfectly competitive market, _____.
A) output and price will decrease
B) output will increase and price will decrease
C) output and price will increase
D) output will decrease and price will increase
E) output and price will remain unchanged
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A profit-maximizing monopolist will always operate where demand is unit elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Rent-seeking activities are socially wasteful because they use scarce resources but do not add to society's output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the marginal cost for the 1,000th unit of a monopolist's output is $40, marginal revenue is $30, the average variable cost of producing 1,000 units is $30, and the average total cost is $50. In order to maximize profit or minimize loss in the short run, the firm should:
A) shut down.
B) continue to produce 1,000 units.
C) produce fewer than 1,000 units but still operate.
D) produce more than 1,000 units.
E) increase its plant size to gain economies of scale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist must choose between two points on its demand curve. It can either sell 100 units for $3 each, or sell 150 units for $2 each. This implies that, for the given range of output, elasticity of demand for the monopolist's product is:
A) zero.
B) one.
C) more than one but less than two.
D) infinite.
E) between zero and one.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 150
Related Exams