A) sigmoidal.
B) pseudo-first-order.
C) unimolecular.
D) zero-order.
E) hyperbolic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Lineweaver-Burk plot is also referred to as (I) a sigmoidal plot. (II) a linear plot. (III) a Michaelis-Menten plot. (IV) a double reciprocal plot.
A) II
B) II,III
C) IV
D) II,IV
E) III,IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the figure in the question above (question 54) ,which of the following expressions would correctly define KM?
A) A= KM
B) KM = A/2
C) B = KM
D) C = - KM
E) D= 1/ KM
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Irreversible enzyme inhibitors
A) inactivate the enzyme
B) inhibit competitively
C) maximize product by minimizing ES E+S
D) behave allosterically
E) function via Ping Pong mechanism
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Michaelis constant KM is defined as (I) (k-1 + k2) /k1 (II) ½ Vmax (III) [S] = [ES] (IV) [ES]/2
A) I
B) I,II
C) II
D) I,IV
E) II,IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fourth-order reactions.
A) have three or more sequential rate determining steps.
B) require a 'Ping Pong' mechanism.
C) are best analyzed using Lineweaver-Burk plots.
D) exist only when enzymatically catalyzed.
E) none of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Matching -A common type of covalent modification of regulatory enzymes involves ______ of serine residues.
A) isozymes
B) [A]
C) the rate constant
D) Ping Pong
E) bimolecular
F) ES complex
G) random ordered
H) competitive inhibition
I) unimolecular
J) [A]2
K) Competitive inhibition
L) phosphorylation
M) small KS
N) large KS
O) uncompetitive inhibition
P) [B]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for an enzymatic reaction obeying the Michaelis-Menten equation to reach 3/4 of its maximum velocity,
A) [S] would need to be equal to KM
B) [S] would need to be ½ KM
C) [S] would need to be 3KM
D) [S] would need to be ¾ KM
E) not enough information is given to make this calculation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Determine the KM and Vmax from the following graph.(Note: On the x-axis the minor tick mark spacing is 0.005;on the y-axis the minor tick mark spacing is 0.002) ![Determine the K<sub>M</sub> and V<sub>max</sub> from the following graph.(Note: On the x-axis the minor tick mark spacing is 0.005;on the y-axis the minor tick mark spacing is 0.002) A) K<sub>M</sub> = [0.006];V<sub>max</sub> = 0.0075/s B) K<sub>M</sub> = [0.196];V<sub>max</sub> = 0.0075/s C) K<sub>M</sub> = [165];V<sub>max</sub> = 33/s D) K<sub>M</sub> = [33];V<sub>max</sub> = 167/s E) K<sub>M</sub> = [270];V<sub>max</sub> x = 68/s](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6187/11ea8a6e_0355_ed41_a2a1_7dfb699a5fef_TB6187_00.jpg)
A) KM = [0.006];Vmax = 0.0075/s
B) KM = [0.196];Vmax = 0.0075/s
C) KM = [165];Vmax = 33/s
D) KM = [33];Vmax = 167/s
E) KM = [270];Vmax x = 68/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to the diagram (with boxes where it has been left incomplete) : 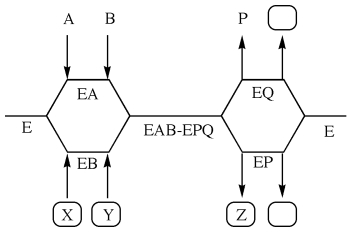 -This diagram refers to a (an)
-This diagram refers to a (an)
A) Ping Pong reaction.
B) ordered bisubstrate reaction.
C) random bisubstrate reaction.
D) double order ping pong reaction
E) X,Y,and Z must be provided in order to answer correctly
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
KM is
A) a measure of the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme.
B) equal to half of Vmax
C) the rate constant for the reaction ES E + P.
D) the [S] that half-saturates the enzyme.
E) a ratio of substrate concentration relative to catalytic power.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The KM can be considered to be the same as the dissociation constant KS for E + S binding if
A) the concentration of [ES] is unchanged.
B) ES E + P is fast compared to ES E + S.
C) k1 >> k2
D) k2 << k-1.
E) this statement cannot be completed because KM can never approximate KS.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the plot below,can the KM be determined? If so,what is its value? 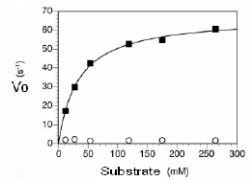
A) Yes,it is 30 mM.
B) Yes,it is 30 mM/sec.
C) Yes,it is 60 mM/sec
D) Yes,it is 60 mM
E) No this data does not follow Michaelis-Menten kinetics
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
[S] = KM for a simple enzymatic reaction.When [S] is doubled the initial velocity is
A) 2 Vmax
B) equal to Vmax
C) (1/3) Vmax
D) 0) 5 Vmax
E) 2 KM/[S]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme is near maximum efficiency when
A) its turnover number is near Vmax.
B) kcat/KM is near 108 M-1s-1.
C) k1 << k-1.
D) kcat/KM is equal to kcat.
E) KM is large when k2 exceeds k1.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Matching -The type of enzyme inhibition in which Vmax is unaffected is ______.
A) isozymes
B) [A]
C) the rate constant
D) Ping Pong
E) bimolecular
F) ES complex
G) random ordered
H) competitive inhibition
I) unimolecular
J) [A]2
K) Competitive inhibition
L) phosphorylation
M) small KS
N) large KS
O) uncompetitive inhibition
P) [B]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From the graph below plotting data that was collected under steady state conditions,velocity on the y-axis in units of μM/s and substrate concentration of the x-axis in units of μM,what is the KM? 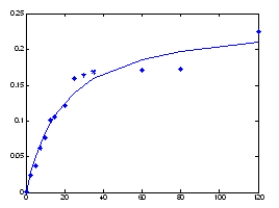
A) 0) 24 μM/s
B) 18 μM
C) 0) 2 μM
D) 0) 24 μM
E) 0) 12 μM/s
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A new drug has been discovered which inhibits the reaction catalyzed by enzyme A.Based on the information shown below,what is this drug? 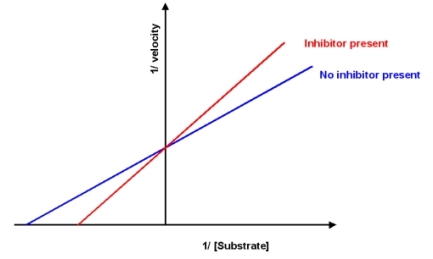
A) competitive inhibitor
B) uncompetitive inhibitor
C) mixed inhibitor
D) allosteric activator
E) More information is required to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From the graph below plotting data that was collected under steady state conditions,velocity on the y-axis in units of μM/s and substrate concentration of the x-axis in units of μM,what is the Vmax? 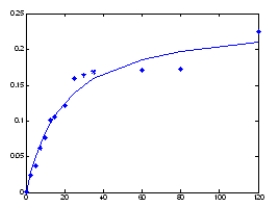
A) 0) 24 μM/s
B) 18 μM
C) 0) 2 μM
D) 0) 24 μM
E) 0) 12 μM/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to the overall transformation shown in the following reaction: ![The following questions refer to the overall transformation shown in the following reaction: -For the reaction,the steady state assumption A) implies that k<sub>1</sub>=k<sub>−</sub><sub>1</sub> B) implies that k<sub>−</sub><sub>1</sub> and k<sub>2</sub> are such that the [ES] = k1[ES] C) [P]>>[E] D) [S] = [P] E) ES breakdown occurs at the same rate as ES formation](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6187/11ea8a6e_0354_3f8f_a2a1_a1ae4bf8cc22_TB6187_00_TB6187_00.jpg) -For the reaction,the steady state assumption
-For the reaction,the steady state assumption
A) implies that k1=k−1
B) implies that k−1 and k2 are such that the [ES] = k1[ES]
C) [P]>>[E]
D) [S] = [P]
E) ES breakdown occurs at the same rate as ES formation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 54
Related Exams