A) phospholipase a2.
B) hormone sensitive lipase.
C) HMG CoA reductase.
D) desaturase.
E) glycerol kinase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
PGH2 is synthesized from ______ and triggers pain and ________.
A) cardiolipins;foam cell development
B) steroids;fever
C) salicylic acid;foam cell development
D) NSAIDS;COX-1
E) arachidonate;inflammation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
______,a condition in which acetoacetate production exceeds it metabolism and results in a sweet breath odor due to nonenyzmatic ___ of acetoacetate to _____.
A) ketosis;decarboxylation;hydroxylbutryate
B) ketosis;carboxylation;hydroxylbutryate
C) ketosis;carboxylation;acetone
D) glyceroneogenesis;decarboxylation;hydroxylbutryate
E) glyceroneogenesis;decarboxylation;acetone
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pain and inflammation are triggered by ___ which are synthesized by an enzyme inhibited by ____.
A) cardiolipins;aspirin
B) prostaglandins;aspirin
C) analgesics;statins
D) prostaglandins;COX-1
E) cyclooxygen;NSAIDS
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following vitamins is part of the prosthetic group 5'-deoxyadenosylcobalamin?
A) B1
B) B2
C) B6
D) B12
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Knoop's experiments with fatty acids
A) involved the novel use of chemical labels to elucidate metabolic mechanisms.
B) demonstrated that fatty acids are broken down by two carbons at a time by oxidation at the ω carbon.
C) demonstrated a distinct difference in the mechanism of odd chain versus.even chain fatty acid oxidation.
D) A and B
E) A,B,and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the net production of ATP from complete catabolism of the following fatty acid to CO2 and H2O?
![What is the net production of ATP from complete catabolism of the following fatty acid to CO<sub>2</sub> and H<sub>2</sub>O? A) < 50 B) 51 - 90 [70] C) 91 - 120 D) 121 - 150 E) 151 +](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6187/11ea8a6e_037e_5d0b_a2a1_315722bc93f5_TB6187_00.jpg)
A) < 50
B) 51 - 90 [70]
C) 91 - 120
D) 121 - 150
E) 151 +
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Matching Choose the correct answer from the list.Not all the answers will be used. -Cholesterol and other lipids are transported from tissues to the liver by ________.
A) HDL
B) propionyl-CoA
C) LDL
D) Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
E) malonyl-CoA
F) ACP
G) chylomicrons
H) phosphopantetheine
I) flavin
J) albumin
K) ketone bodies
L) cholesterol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following could be produced by the reaction of two or more of phosphatidic acids with two or more glycerol-3-phosphates? (I) phosphatidylglycerol (II) cardiolipin (III) phosphatidylinositol (IV) gangliosides
A) I,II,III,IV
B) II,III
C) I,III
D) I,II
E) III only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following compounds is produced by the multistep cyclization of squalene?
A) lanosterol
B) geranyl pyrophosphate
C) fanesyl pyrophosphate
D) isoprene
E) isopentyl pyrophosphate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Matching Choose the correct answer from the list.Not all the answers will be used. -Acyl carrier protein (ACP) contains a ________ prosthetic group.
A) HDL
B) propionyl-CoA
C) LDL
D) Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
E) malonyl-CoA
F) ACP
G) chylomicrons
H) phosphopantetheine
I) flavin
J) albumin
K) ketone bodies
L) cholesterol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two phosphatidylglycerol molecules condense to form the molecule ______,and glycerol is eliminated as the side product.
A) phosphatidic acid
B) cardiolipin
C) plasmalogen
D) sphingomyelin
E) squalene
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an example of a problem sometimes associated with unsaturated fatty acid breakdown?
A) β, double bond
B) α,β double bond
C) unanticipated isomerization
D) inhibition of hydratase by a double bond
E) All of the above are problems.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Matching Choose the correct answer from the list.Not all the answers will be used. -The molecules acetoacetate,acetone,and d- -hydroxybutyrate are metabolic fuels termed ________.
A) HDL
B) propionyl-CoA
C) LDL
D) Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
E) malonyl-CoA
F) ACP
G) chylomicrons
H) phosphopantetheine
I) flavin
J) albumin
K) ketone bodies
L) cholesterol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Matching Choose the correct answer from the list.Not all the answers will be used. -The glycerol backbone of triacylglycerols is catabolized to ________ .
A) HDL
B) propionyl-CoA
C) LDL
D) Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
E) malonyl-CoA
F) ACP
G) chylomicrons
H) phosphopantetheine
I) flavin
J) albumin
K) ketone bodies
L) cholesterol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Matching Choose the correct answer from the list.Not all the answers will be used. -Free fatty acids bind to ________ for circulation in the bloodstream.
A) HDL
B) propionyl-CoA
C) LDL
D) Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
E) malonyl-CoA
F) ACP
G) chylomicrons
H) phosphopantetheine
I) flavin
J) albumin
K) ketone bodies
L) cholesterol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which location listed below does the following reaction take place? HMG-CoA → acetoacetate + Acetyl-CoA
A) cytosol of cardiomyocytes
B) mitochondria of cardiomyocytes
C) cytosol of liver cells
D) mitochondria of liver cells
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes arachidonic acid?
A) a 20-carbon isoprene-based intermediate of cholesterol synthesis
B) a 20-carbon fatty acid essential for cholesterol synthesis
C) a 20-carbon isoprene-based compound used for synthesis of prostaglandins
D) a 20-carbon fatty acid used for synthesis of prostaglandins
E) a 2-carbon compound that functions in conjunction with a fatty acid carrier protein for transport of primed fatty acids
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Considering the figure below,what compound would be formed by action of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase? 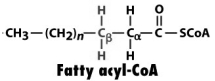
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mechanism of the condensing enzyme (KS) of fatty acid synthase is best described as
A) base catalysis using a glu residue in the active site
B) acid catalysis using a glu residue in the active site
C) base catalysis using a cys residue in the active site
D) acid catalysis using a cys residue in the active site
E) covalent catalysis using a cys residue in the active site
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 51
Related Exams