A) 24 hours.
B) three months.
C) six months.
D) one year.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The liquidity preference model uses the demand for and supply of money to determine:
A) GDP.
B) the price level.
C) the interest rate.
D) nominal output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An individual who decides to hold money instead of other assets:
A) is giving up the interest that other assets could have earned.
B) is likely to be subject to money illusion.
C) is not affected by unanticipated inflation.
D) can maintain a higher standard of living.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Inflation targeting is different from the Taylor rule because the Taylor rule is based on a forecast of inflation, but inflation targeting adjusts monetary policy to past inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To close an inflationary gap using monetary policy, the Federal Reserve should _____ the money supply to _____ investment and consumer spending and shift the aggregate demand curve to the _____.
A) increase; increase; left
B) decrease; decrease; left
C) increase; increase; right
D) decrease; decrease; right
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a new regulation lowers the interest rates banks can offer on checking account funds. This will result in a shift _____ of the money _____ curve.
A) leftward; demand
B) rightward; demand
C) rightward; supply
D) leftward; supply
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy affects GDP and the price level by:
A) changing aggregate supply.
B) changing aggregate demand.
C) changing the aggregate amount of labor supplied.
D) changing exports.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Figure: Money Market I 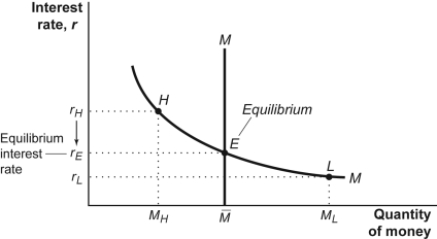 -(Figure: Money Market I) Look at the figure Money Market I. If the money market is initially in equilibrium at point E and the central bank sells Treasury bills, then the interest rate will:
-(Figure: Money Market I) Look at the figure Money Market I. If the money market is initially in equilibrium at point E and the central bank sells Treasury bills, then the interest rate will:
A) move toward point H.
B) move toward point L.
C) remain at point E.
D) shift rightward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Short-term interest rates:
A) fluctuate widely depending on their terms.
B) tend to move together.
C) move in the same direction as long-term interest rates.
D) are always less than long-term interest rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy that lowers the interest rate is called _____ because it _____.
A) contractionary; aims to head off inflation
B) expansionary; increases short-run aggregate supply
C) contractionary; reduces saving and increases consumption
D) expansionary; increases aggregate demand
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When long-term rates are lower than short-term rates, the market is signaling that it expects short-term rates to fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the long-run changes in the money supply will change prices but not real GDP or interest rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Federal Reserve conducts an open market purchase, holding everything else constant, in the long run there will be:
A) an increase in the aggregate price level.
B) an increase in the aggregate output level.
C) a decrease in unemployment.
D) no effects on output, unemployment, or the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
To decrease interest rates, the Fed should make an open-market sale of Treasury bills.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
To decrease interest rates, the Fed should increase the money supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Usually there is an inverse relationship between the federal funds rate and the output gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Contractionary monetary policy entails _____ the money supply, _____ interest rates, and _____ aggregate demand.
A) increasing; increasing; increasing
B) increasing; decreasing; decreasing
C) decreasing; decreasing; decreasing
D) decreasing; increasing; decreasing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Federal Open Market Committee does NOT directly control the _____ with monetary policy.
A) discount rate
B) reserve ratio
C) prime rate
D) federal funds rate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Figure: Monetary Policy and the AD-SRAS Model 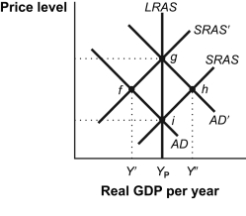 -(Figure: Monetary Policy and the AD-SRAS Model) Look at the figure Monetary Policy and the AD-SRAS Model. If the economy is in a recessionary gap at point f, it could move to point g as a result of:
-(Figure: Monetary Policy and the AD-SRAS Model) Look at the figure Monetary Policy and the AD-SRAS Model. If the economy is in a recessionary gap at point f, it could move to point g as a result of:
A) a decrease in government spending.
B) an increase in the discount rate.
C) a decrease in the money supply.
D) purchases of government securities in the open market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since the short-run increase in the aggregate price level that follows a monetary expansion is smaller than the ensuing long-run increase, it follows that:
A) money is neutral in the short run.
B) in the short run, the interest rate remains constant.
C) in the long run, the real money supply increases.
D) in the short run, the real money supply increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 359
Related Exams