A) Rate = k[(CH3) 2CHCl][H2O]
B) Rate = k[(CH3) 2CHCl]
C) Rate = k[(CH3) 2CH]+[H2O]
D) Rate = k[(CH3) 2CH]+
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the Keq corresponds to the lowest value of G°?
A) "Keq = 10-3"
B) "Keq = 10-2"
C) "Keq = 10-1"
D) "G° cannot be determined"
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reaction quantities will have an effect on reaction rate?
A) "G°"
B) "H°"
C) "Keq"
D) "Ea"
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following expressions summarizes the correct relationship between the free energy change, G°, and the equilibrium constant, Keq?
A) Keq > 1 when G° > 0
B) Keq > 1 when G° < 0
C) Keq < 1 when G° < 0
D) Keq < 1 when G° = 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name given to the reaction species that lies at an energy minimum between steps on a reaction energy diagram?
A) Transition state
B) Activation energy
C) Reactive intermediate
D) Equilibrium product
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about bond breaking is true?
A) Homolysis and heterolysis require energy.
B) In homolysis, the electrons in the bond are divided unequally.
C) In heterolysis, the electrons in the bond are divided equally.
D) Homolysis generates charged intermediates.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the Keq corresponds to the highest value of G°?
A) Keq = 10-1
B) Keq = 10-2
C) Keq = 10-3
D) Keq = 10-5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The G° (free energy change) for the conversion of A to B is predicted to be which of the following? 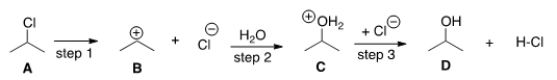
A) "G° = 0"
B) "G° < 0"
C) "G° > 0"
D) "Cannot be determined from the information provided"
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many transition states and intermediates would the reaction profile have for the reaction shown below? 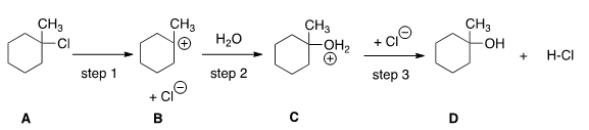
A) Three transition states and three intermediates
B) Two transition states and two intermediates
C) Three transition states and two intermediates
D) Two transition states and three intermediates
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reaction is fast and has Keq= 1? 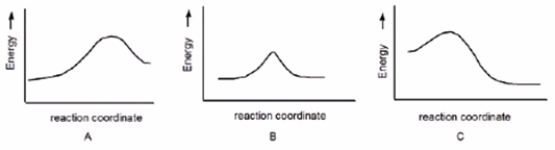
A) A
B) B
C) C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about bond breaking is not true?
A) Homolysis generates uncharged reactive intermediates with unpaired electrons.
B) Homolysis require energy but heterolysis does not require energy.
C) Heterolysis generates charged intermediates.
D) Heterolysis involves unequal sharing of bonding electrons by atoms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the bond dissociation energies given, calculate ?H° for the following reaction. Bond A-B ?H° KJ/mol CH3CH2-Br 285 H-OH 498 CH3CH2-OH 393 H-Br 368
A) +108 KJ/mol
B) -130 KJ/mol
C) -22 KJ/mol
D) +22 KJ/mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What kind of reaction does the conversion of A to B represent? 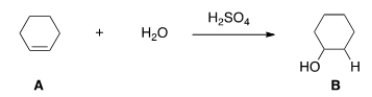
A) Acid-base reaction.
B) Elimination reaction.
C) Substitution reaction.
D) Addition reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Bond breaking is endothermic.
B) The bond dissociation energy for bond breaking is always negative.
C) Bond making is exothermic.
D) The bond dissociation energy for bond formation is always negative.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) In polar reactions, a nucleophile reacts with an electrophile.
B) Carbocations are electrophiles.
C) Carbanions are nucleophiles.
D) A half-headed curved arrow shows the movement of an electron pair.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many transition states are present in the reaction in the energy diagram? 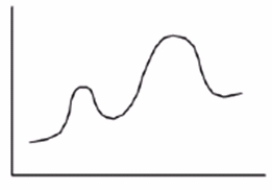
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about elimination reactions is true?
A) Two bonds are broken.
B) Two bonds are formed.
C) Two bonds are broken.
D) Two bonds are formed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in which of the following results in an increase in the rate of a chemical reaction?
A) Energy of activation
B) Concentration
C) Temperature
D) Kinetic energy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Fast reactions have small rate constants.
B) Slow reactions have large rate constants.
C) A rate equation contains concentration terms for all reactants involved in a one-step mechanism.
D) A rate equation contains concentration terms for all the reactants involved in a multi-step reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following letters represents H° for the forward reaction in the following energy diagram? 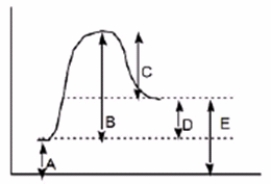
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 43
Related Exams