A) revenue
B) land,labor,and capital
C) factors of production
D) profit
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Efficiency is illustrated by
A) both the production possibilities frontier and the circular-flow diagram.
B) neither the production possibilities frontier nor the circular-flow diagram.
C) the production possibilities frontier only.
D) the circular-flow diagram only.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-9
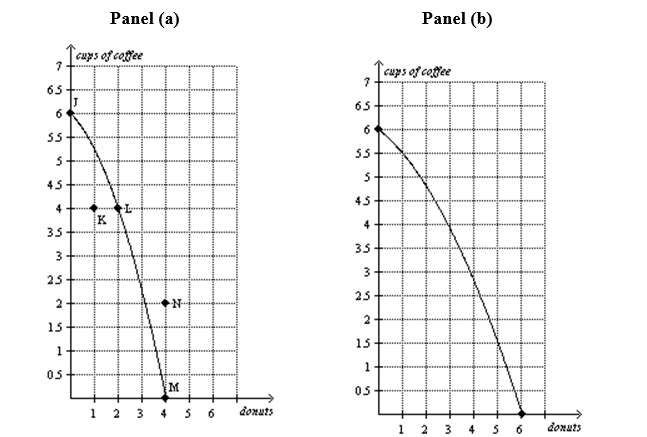 -Refer to Figure 2-9,Panel (a) .To gain 2 donuts by moving from point L to point M,society must sacrifice
-Refer to Figure 2-9,Panel (a) .To gain 2 donuts by moving from point L to point M,society must sacrifice
A) efficiency.
B) employment.
C) 4 cups of coffee.
D) More than one of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-2 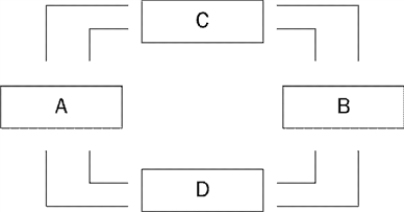 -Refer to Figure 2-2.Boxes C and D of this circular-flow diagram represent
-Refer to Figure 2-2.Boxes C and D of this circular-flow diagram represent
A) households and government.
B) firms and government.
C) the markets for goods and services and the markets for financial assets.
D) the markets for goods and services and the markets for factors of production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In economics,capital refers to
A) the finances necessary for firms to produce their products.
B) buildings and machines used in the production process.
C) the money households use to purchase firms' output.
D) stocks and bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the circular-flow diagram,
A) factors of production flow from government to firms.
B) goods and services flow from households to firms.
C) income paid to the factors of production flows from firms to households.
D) spending on goods and services flows from firms to households.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-14 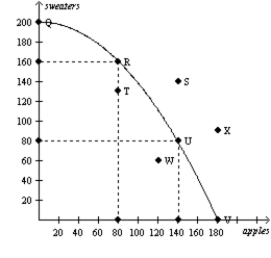 Consider the production possibilities curve for a country that can produce sweaters,apples (in bushels) ,or a combination of the two
-Refer to Figure 2-14.Which combination of points show production possibilities only achievable with improvements in technology or increases in resources?
Consider the production possibilities curve for a country that can produce sweaters,apples (in bushels) ,or a combination of the two
-Refer to Figure 2-14.Which combination of points show production possibilities only achievable with improvements in technology or increases in resources?
A) Q,R,U,and V
B) S and X
C) T and W
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When studying the effects of changes in public policy,economists believe that
A) it is important to distinguish between the short run and the long run.
B) the assumptions used in studying those effects should be the same for the short run as for the long run.
C) the short-run effects of those changes are always more beneficial to society than are the long-run effects.
D) the long-run effects of those changes are always more beneficial to society than are the short-run effects.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-6 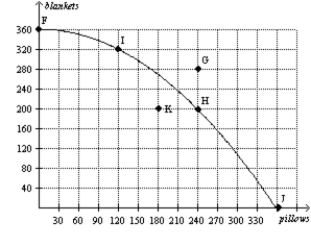 -Refer to Figure 2-6.If this economy devotes one-half of its available resources to the production of blankets and the other half to the production of pillows,it could produce
-Refer to Figure 2-6.If this economy devotes one-half of its available resources to the production of blankets and the other half to the production of pillows,it could produce
A) 120 pillows and 320 blankets.
B) 180 pillows and 180 blankets.
C) 240 pillows and 200 blankets.
D) We would have to know the details of this economy's technology in order to determine this.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-10
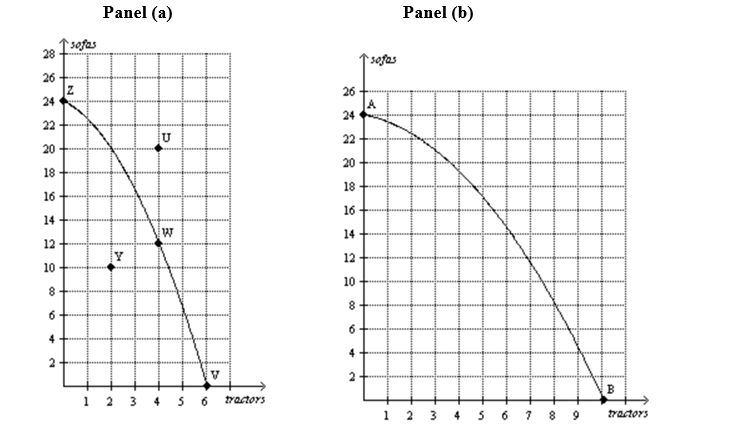 -Refer to Figure 2-10,Panel (a) .The movement from point W to point Y could be caused by
-Refer to Figure 2-10,Panel (a) .The movement from point W to point Y could be caused by
A) economic growth.
B) unemployment.
C) an improvement in efficiency.
D) an advance in production technology.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-16 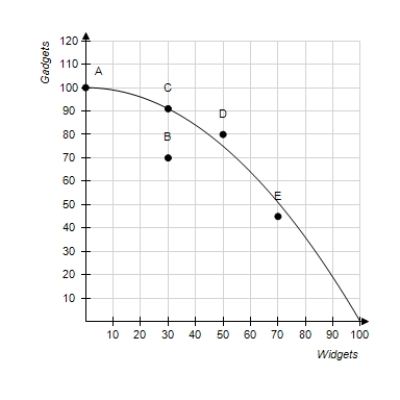 -Refer to Figure 2-16.The opportunity cost of obtaining 30 additional widgets by moving from point A to point C is approximately
-Refer to Figure 2-16.The opportunity cost of obtaining 30 additional widgets by moving from point A to point C is approximately
A) 10 gadgets.
B) 30 widgets
C) 10 gadgets and 30 widgets.
D) 0 gadgets.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-7 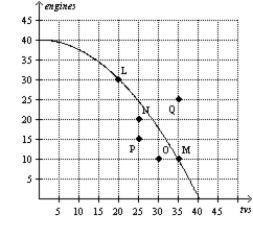 -Refer to Figure 2-7.Efficient production is represented by which point(s) ?
-Refer to Figure 2-7.Efficient production is represented by which point(s) ?
A) L,M
B) L,M,N,P,Q
C) N,O,P
D) Q
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy is producing efficiently,then
A) there is no way to produce more of one good without producing less of another good.
B) it is possible to produce more of both goods without increasing the quantities of inputs that are being used.
C) it is possible to produce more of one good without producing less of another good.
D) it is not possible to produce more of any good at any cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-5 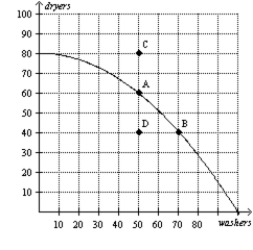 -Refer to Figure 2-5.The opportunity cost of obtaining 20 additional dryers by moving from point D to point A is
-Refer to Figure 2-5.The opportunity cost of obtaining 20 additional dryers by moving from point D to point A is
A) 0 washers.
B) 20 washers.
C) 40 washers.
D) None of the above;the economy cannot move from point D to point A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-1 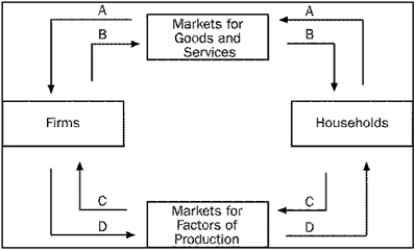 -Refer to Figure 2-1.Which arrow represents the flow of goods and services?
-Refer to Figure 2-1.Which arrow represents the flow of goods and services?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Production is efficient if the economy is producing at a point
A) on the production possibilities frontier.
B) outside the production possibilities frontier.
C) on or inside the production possibilities frontier.
D) inside the production possibilities frontier.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-6  -Refer to Figure 2-6.A movement from point H to point K could be caused by
-Refer to Figure 2-6.A movement from point H to point K could be caused by
A) unemployment.
B) a decrease in society's preference for pillows.
C) fewer resources available for production of pillows.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Instead of conducting laboratory experiments to generate data to test their theories,economists often
A) ask winners of the Nobel Prize in Economics to evaluate their theories.
B) argue that data is impossible to collect in economics.
C) gather data from historical episodes of economic change.
D) assume that data would support their theories.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economy's production of two goods is efficient if
A) all members of society consume equal portions of the goods.
B) the goods are produced using only some of society's available resources.
C) it is impossible to produce more of one good without producing less of the other.
D) the opportunity cost of producing more of one good is zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the circular-flow diagram is correct?
A) One must imagine that the economy operates without money in order to make sense of the diagram.
B) The diagram leaves out details that are not essential for understanding the economic transactions that occur between households and firms.
C) The government cannot be excluded as a decision maker in a circular-flow diagram.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 256
Related Exams