A) Tacit collusion.
B) High concentration ratios.
C) High barriers to entry.
D) Independent pricing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An oligopolistic market may be difficult to enter because of government regulation or the expense of nonprice competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the article "ATamp;T Plan to Buy T-Mobile Means Higher Prices, Fewer Phones," the opportunity cost of the merger between ATamp;T and T-Mobile is
A) Better service quality.
B) Increased coverage.
C) Reduced phone selection.
D) T-Mobile customers will be able to get iPhones.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an effort to maximize profits, oligopolists could participate in all of the following but
A) Price leadership.
B) Price-fixing.
C) Cartels.
D) Self-destructive behavior.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
RC Cola lost market share in the 1980s due to
A) Its decision not to advertise.
B) Consumers not liking the taste of its colas.
C) Wasting precious resources on advertising.
D) Its lack of shelf space at supermarkets.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following market structures is characterized by the absence of market power?
A) Monopolistic competition.
B) Oligopoly.
C) Monopoly.
D) Perfect competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How might an oligopolist increase total revenue without changing price?
A) Reduce output.
B) Reduce marketing efforts.
C) Through nonprice competition.
D) Reduce costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to "Coke and Pepsi May Call Off Pricing Battle," price discounting (price wars) can destroy oligopoly profits.When profit destruction occurs,
A) Firms are powerless to change prices.
B) Firms will wait for one firm to increase prices.
C) Rival oligopolists seek to end it as quickly as possible.
D) The entire industry will always collapse.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an oligopolist is going to change its price or output, its initial concern is
A) The response of its competitors.
B) A change in its cost structure.
C) The concentration ratio.
D) The response of the Federal Trade Commission.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Patents are a barrier to entry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a business advertises that its product has unique features that make it superior to other similar products, it is engaging in
A) Price competition.
B) Predatory pricing.
C) Product differentiation.
D) Contestable market advertising.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A kinked demand curve indicates that rival oligopolists match all
A) Increased advertising.
B) Advertising reductions.
C) Price increases.
D) Price reductions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Market share is the percentage of total
A) Market output produced by the largest firm in an industry.
B) Market output produced by a single firm.
C) Market output produced by the four largest firms in an industry.
D) Industry profit earned by a single firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Concentration ratios tend to overstate the power of some corporations to influence economic outcomes because they measure output
A) For single firms rather than markets.
B) For the whole United States, which is too large a geographic market for some firms or industries.
C) Only for domestic production when the true market boundaries are international for some markets.
D) Over many industries rather than a single market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When oligopoly firms collude to raise prices,
A) Each firm benefits, but society loses.
B) Both the colluding firms and society benefit.
C) Everyone is eventually a loser.
D) Only the price leader benefits while other firms and society lose.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Market power leads to market failure when it results in
A) Decreased market output.
B) Lower market prices.
C) Normal economic profits.
D) The demise of the industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Given the payoff matrix in Table 25.1, if the probability of rivals matching a price reduction is 99 percent, what is the expected payoff for a price cut by Company ABC?
Given the payoff matrix in Table 25.1, if the probability of rivals matching a price reduction is 99 percent, what is the expected payoff for a price cut by Company ABC?
A) $0.
B) $5.
C) -$500.
D) -$5,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
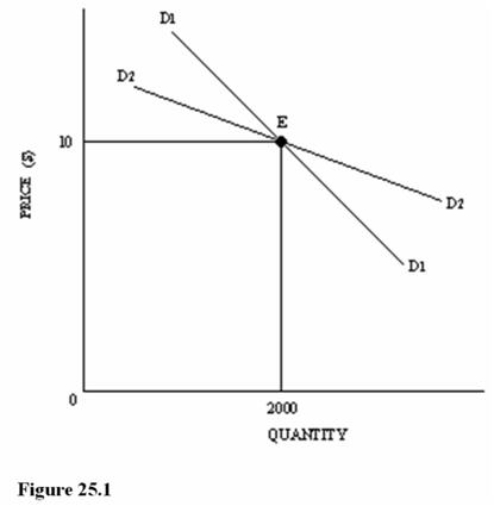 Refer to Figure 25.1 for an oligopoly firm.Assume that the existing price and quantity are $10 and 2,000 units.Which of the following statements is most likely correct?
Refer to Figure 25.1 for an oligopoly firm.Assume that the existing price and quantity are $10 and 2,000 units.Which of the following statements is most likely correct?
A) Demand curves D1 and D2 both assume that rivals will not match any price changes.
B) Demand curves D1 and D2 both assume that rivals match any price changes.
C) Demand curve D1 assumes that rivals match any price changes.
D) Demand curve D2 assumes that rivals match any price changes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A demand curve will be kinked if rivals match price reductions but not price increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The concentration ratio measures the
A) Number of plants owned by an oligopoly.
B) Percentage of total profits made by a firm in a specific market.
C) Proportion of total output produced by the four largest producers in a specific market.
D) Relative size of a firm compared to other industries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 152
Related Exams