A) It is probably an herbaceous eudicot.
B) It will probably get annual rings of wood.
C) It is probably a monocot.
D) It could be either a young eudicot or a monocot.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which part of a plant absorbs most of the water and minerals taken up from the soil?
A) root cap
B) root hairs
C) the thick parts of the roots near the base of the stem
D) storage roots
E) sections of the root that have secondary xylem
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When you eat Brussels sprouts, you are eating ________.
A) immature flowers
B) large axillary buds
C) petioles
D) storage leaves
E) storage roots
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Loss of water from the aerial parts of plants is called ________.
A) hydration
B) high heat of vaporization
C) respiration
D) gas exchange
E) transpiration
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct sequence from the growing tip of a primary root back towards its base?
A) Root cap Zone of cellular elongation Apical meristem Zone of cellular division Zone of cellular maturation
B) Zone of cellular division Apical meristem Root cap Zone of cellular elongation Zone of cellular maturation
C) Zone of cellular elongation Zone of cellular maturation Root cap Apical meristem Zone of cellular division
D) Apical meristem Zone of cellular elongation Zone of cellular division Root cap Zone of cellular maturation
E) Root cap Apical meristem Zone of cellular division Zone of cellular elongation Zone of cellular maturation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following arise, directly or indirectly, from meristematic activity?
A) secondary xylem
B) leaves
C) dermal tissue
D) tubers
E) secondary xylem, leaves, dermal tissue, and tubers
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose George Washington completely removed the bark from around the base of a cherry tree but was stopped by his father before cutting the tree down. The leaves retained their normal appearance for several weeks, but the tree eventually died. The tissue(s) that George left functional was/were the ________.
A) phloem
B) xylem
C) cork cambium
D) cortex
E) companion and sieve-tube members
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the drawings of root or stem cross sections shown in the accompanying figure. 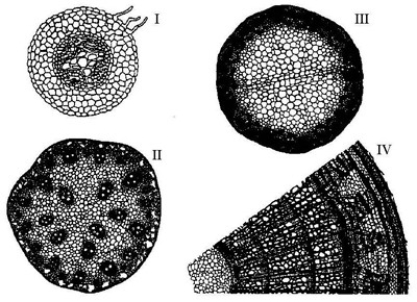 Refer to the figure. A monocot stem is represented by ________.
Refer to the figure. A monocot stem is represented by ________.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) IV only
E) I and III
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A student examining leaf cross sections under a microscope finds many loosely packed cells with relatively thin cell walls. The cells have numerous chloroplasts. What type of cells are they?
A) parenchyma
B) xylem
C) endodermis
D) collenchyma
E) sclerenchyma
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carbon dioxide enters the inner spaces of the leaf through the ________.
A) cuticle
B) epidermal trichomes
C) stoma
D) phloem
E) walls of guard cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pines have needlelike leaves, with the adaptive advantage of ________.
A) increased surface area, increasing photosynthesis
B) increased surface area, increasing gas exchange
C) decreased surface area, reducing gas exchange
D) decreased surface area, reducing water loss
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Heartwood and sapwood consist of ________.
A) bark
B) periderm
C) secondary xylem
D) secondary phloem
E) cork
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the drawings of root or stem cross sections shown in the accompanying figure. 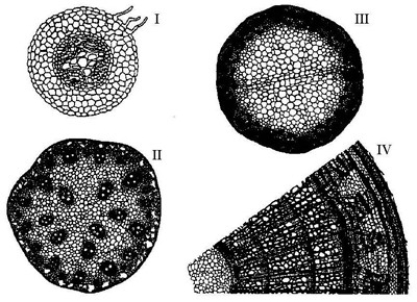 -Refer to the figure. A woody eudicot is represented by ________.
-Refer to the figure. A woody eudicot is represented by ________.
A) II only
B) III only
C) IV only
D) I and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some botanists argue that the entire plant should be considered as a single unit rather than a composite of many individual cells. Which of the following cellular structures best supports this view?
A) cell wall
B) cell membrane
C) cytosol
D) vacuole
E) plasmodesmata
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cells primarily transport sugars over long distances?
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) tracheids and vessel elements
E) sieve-tube elements
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A potato is a type of ________ known as a ________.
A) modified root; pneumatophore
B) root; lateral root
C) modified stem; stolon
D) modified stem; tuber
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While walking a cornfield, you notice roots emerging from the corn stalks themselves, and you suspect that these roots are helping to hold the plants upright. These roots belong to a category of roots known as ________.
A) taproots
B) fibrous roots
C) adventitious roots
D) root hairs
E) special roots
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is derived from the ground tissue system?
A) root hair
B) cuticle
C) xylem
D) pith
E) phloem
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following have unevenly thickened primary walls that support young, growing parts of the plant?
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) tracheids and vessel elements
E) sieve-tube elements
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correctly paired with its structure and function?
A) sclerenchyma-supporting cells with thick secondary walls
B) ground meristem-protective coat of woody stems and roots
C) guard cells-waterproof ring of cells surrounding the central stele in roots
D) parenchyma-supporting cells with unevenly thickened primary cell walls
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 46
Related Exams