A) meiosis II
B) meiosis I
C) mitosis
D) mitosis and meiosis II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sister chromatids separate from each other during ________.
A) mitosis only
B) meiosis I only
C) meiosis II only
D) mitosis and meiosis I
E) mitosis and meiosis II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the snail Pomacea patula catemacensis, n = 13. What is the diploid number for this organism?
A) 13
B) 26
C) 52
D) 7
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An advantage of asexual reproduction is that it ________.
A) allows the species to endure long periods of unstable environmental conditions
B) enhances genetic variability in the species
C) enables the species to rapidly colonize habitats that are favorable to that species
D) produces offspring that respond effectively to new pathogens
E) allows a species to easily rid itself of harmful mutations
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
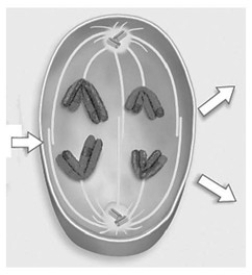 What phase of meiosis is seen in the accompanying figure?
What phase of meiosis is seen in the accompanying figure?
A) metaphase I
B) metaphase II
C) anaphase I
D) anaphase II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Independent assortment of chromosomes is a result of ________.
A) the random way each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I
B) the random combinations of eggs and sperm during fertilization
C) the random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II
D) the relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y chromosomes
E) the diverse combination of alleles that may be found within any given chromosome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a major difference between meiosis II and mitosis in a diploid animal?
A) Homologs align on the metaphase plate in meiosis II.
B) Sister chromatids separate in mitosis, and homologs separate in meiosis II.
C) Meiosis II occurs in a haploid cell, and mitosis occurs in diploid cells.
D) Crossover takes place in meiosis II.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the duration of meiosis I, each chromosome ________.
A) is paired with a homologous chromosome
B) consists of two sister chromatids joined by a centromere
C) consists of a single strand of DNA
D) is joined with its homologous pair to form a synaptonemal complex
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements is correct?
A) In humans, each of the 23 maternal autosomes has a homologous paternal chromosome.
B) In humans, the twenty-second pair, the sex chromosomes, determines whether the person is female (XY) or male (XX) .
C) Single, haploid (2n) sets of chromosomes in ovum and sperm unite during fertilization, forming a diploid (4n) , single-celled zygote.
D) At sexual maturity, ovaries and testes produce haploid gametes by meiosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diploid number of a roundworm species is 4. Assuming there is no crossover, and random segregation of homologs during meiosis, how many different possible combinations of chromosomes might there be in the offspring?
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 64
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Somatic cells of roundworms have four individual chromosomes per cell. How many chromosomes would you expect to find in an ovum from a roundworm?
A) four
B) two
C) eight
D) a diploid number
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a TRUE statement about sexual versus asexual reproduction?
A) Asexual reproduction, but not sexual reproduction, is characteristic of plants and fungi.
B) In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit half of their nuclear genes to each of their offspring.
C) In asexual reproduction, offspring are produced by fertilization without meiosis.
D) Sexual reproduction requires that parents be diploid.
E) Asexual reproduction produces only haploid offspring.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Asexual reproduction occurs during ________.
A) meiosis
B) mitosis
C) fertilization
D) chromosome exchange between organisms of different species
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All individuals of a particular species of whiptail lizards are females. Their reproductive efforts depend on ________.
A) fertilization of their eggs by males of other lizard species
B) gonadal structures that only undergo mitosis
C) meiosis followed by a doubling of the chromosomes in eggs
D) budding prior to the development of a sexual phenotype
E) fragmentation via autolysis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a cell has completed meiosis I and is just beginning meiosis II, which of the following is an appropriate description of its contents?
A) It has half the amount of DNA as the cell that began meiosis.
B) It has the same number of chromosomes, but each of them has different alleles than another cell from the same meiosis.
C) It has half the chromosomes but twice the DNA of the originating cell.
D) It has one-fourth the DNA and one-half the chromosomes as the originating cell.
E) It is identical in content to another cell formed from the same meiosis I event.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a major difference between mitosis and meiosis I in a diploid organism?
A) Sister chromatids separate in mitosis; homologous pairs of chromosomes separate in meiosis I.
B) Sister chromatids separate in mitosis; homologous pairs of chromosomes separate in meiosis II.
C) DNA replication takes place prior to mitosis, but not before meiosis I.
D) Only meiosis I results in daughter cells that contain identical genetic information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A couple has a child with Down syndrome. The mother is 39 years old at the time of delivery. Which of the following is the most probable cause of the child's condition?
A) The woman inherited this tendency from her parents.
B) The mother had a chromosomal duplication.
C) One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in somatic cell production.
D) The mother most likely underwent nondisjunction during gamete production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information and associated figure to answer the following question(s) . -A female with a paternal set of one orange and one long gene chromosome and a maternal set comprised of one blue and one short gene chromosome is expected to produce which of the following types of eggs after meiosis?
A) All eggs will have maternal types of gene combinations.
B) All eggs will have paternal types of gene combinations.
C) Half the eggs will have maternal and half will have paternal combinations.
D) Each egg has a one-fourth chance of having either blue long, blue short, orange long, or orange short combinations.
E) Each egg has a three-fourths chance of having blue long, one-fourth blue short, three-fourths orange long, or one-fourth orange short combinations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If meiosis produces haploid cells, how is the diploid number restored for those organisms that spend most of their life cycle in the diploid state?
A) DNA replication
B) reverse transcription
C) synapsis
D) fertilization
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There is a group of invertebrate animals called rotifers, among which a particular group of species reproduces, as far as is known, only asexually. These rotifers, however, have survived a long evolutionary history without evidence of having been overcome by excessive mutations. Since the rotifers develop from eggs, but asexually, what can you predict?
A) The eggs and the zygotes are all haploid.
B) The animals are all hermaphrodites.
C) While asexual, both males and females are found in nature.
D) All males can produce eggs.
E) No fertile males can be found.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 63
Related Exams