A) negative market feedback occurs.
B) positive market feedback occurs.
C) the tit-for-tat strategy will begin.
D) the network effect will increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A situation in which one firm's actions with respect to price, quality, advertising and related changes may be strategically countered by the reactions of one or more other firms in the industry is known as
A) strategic dependence.
B) economies of scale.
C) the concentration ratio.
D) barriers to entry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When there is a tendency for a particular product to come into favor with additional consumers because other consumers have chosen to purchase the product
A) negative market feedback occurs.
B) positive market feedback occurs.
C) there is no dominant strategy.
D) a price war must result.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When managers in oligopolistic firms make decisions that affect output or price, they must
A) also be sure they erect barriers to entry to prevent new entrants from affecting their plans.
B) anticipate the reactions of their rivals and plan accordingly.
C) register with the Antitrust Division of the Department of Justice.
D) inform the regulators of their industry about their plans.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over the past several decades, U.S. firms have faced more competition from overseas firms. Does this have any impact on the market power of U.S. oligopoly firms?
A) no, because domestic firms in oligopoly markets are always so dominant that overseas producers have little or no impact on those markets
B) no, because the United States government has effectively blocked all imports that might compete with domestic firms in oligopoly industries
C) Yes, competition from overseas firms can substantially limit domestic firms' market power.
D) There is no way to know.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After participating members of a cartel form an agreement on common prices and output quotas, then an individual firm can increase its own profits by
A) decreasing production.
B) decreasing prices.
C) advertising.
D) paying its employees higher wages.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The combining of First Union National Bank and The National Bank of Memphis is an example of
A) a vertical merger.
B) a horizontal merger.
C) a downstream formation.
D) a conglomerate merger.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an industry with network effects and differentiated products, it is possible for the industry to become an oligopoly if
A) they engage in a zero-sum game.
B) they use a price-leadership model.
C) they use a kinked demand curve model.
D) a few firms reap most of the sales gains resulting from positive market feedback.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Managers in oligopoly firms must
A) eliminate any barriers to entry if they hope to make short-run profits.
B) advertise heavily in order to differentiate their product.
C) anticipate the reaction of rival firms.
D) establish many varieties of their products to cover the spectrum of consumer tastes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A local utility is an example of
A) perfect competition.
B) oligopoly.
C) monopoly.
D) monopolistic competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The success of a cartel rests upon
A) inducing all members to limit their combined output and charge the same price.
B) inducing all members to differentiate their products and charge different prices.
C) making exit from the cartel as nearly costless as possible.
D) discouraging some firms in the market from joining.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The payoff matrix shows all of the following EXCEPT 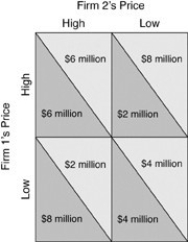
A) if both oligopolists choose a high price, each makes $6 million.
B) if they both choose a low price, each makes $4 million.
C) if one chooses a low price and the other doesn't, the low priced firm will make $8 million.
D) if one oligopolist chooses a high price and the other doesn't, the high-priced firm makes $8 million.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The manner in which one oligopolist reacts to a change in price, output, or quantity on the part of another oligopolist in the industry is known as
A) a positive-sum game.
B) the reaction function.
C) a noncooperative game.
D) a zero-sum game.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The joining of firms that are producing or selling a similar product is known as
A) a conglomerate merger.
B) a horizontal merger.
C) a vertical merger.
D) economies to scale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When U.S. Steel, a steel producer, bought control of iron ore companies at the beginning of the 20th century, the company was initiating
A) a horizontal merger.
B) a vertical merger.
C) a cartel.
D) an expropriation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the four-firm concentration ratio for an industry is 84 percent, then
A) each of the firms account for 21 percent of total sales.
B) the four largest firms in the industry account for 16 percent of the total sales.
C) the four largest firms in the industry account for 84 percent of the total sales.
D) the remaining firms in the industry accounts for 84 percent of the total sales.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, horizontal mergers will
A) increase the number of firms in an industry.
B) decrease the number of firms in an industry.
C) increase competition in an industry.
D) reduce economic profits in an industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of a positive market feedback is
A) installation of a phone app.
B) routine maintenance on a car.
C) the declining use of land-line telephones for long distance calls.
D) the use of telegraph services in the twenty-first century.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of a zero-sum game is
A) exchange.
B) a consumer purchasing a used car from a used car dealer.
C) the prisoners' dilemma.
D) poker.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The college textbooks market is an example of
A) perfect competition.
B) oligopoly.
C) monopoly.
D) monopolistic competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 308
Related Exams