A) an aggregate supply shock.
B) an aggregate demand shock.
C) a recession.
D) a depression.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the classical model, a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve will, in the long run,
A) increase real GDP and the price level.
B) increase real GDP and will not change the price level.
C) decrease real GDP and will not change the price level.
D) not change real GDP and will increase the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There is a distinction between the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve and the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve. In the long run
A) technology is fixed, but not in the short run.
B) the price level is constant in the long run, but fluctuates in the short run.
C) the aggregate supply curve is horizontal, while in the short run it is upward sloping.
D) all adjustments to changes in the price level have been made, but in the short run all changes in the price level do not occur.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the above figure. Suppose the current aggregate demand is represented by AD2. If aggregate demand falls to line AD3, then
A) the new equilibrium will be at j.
B) the new equilibrium will be at k.
C) the new equilibrium real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) will be x.
D) a new price level will be established at a.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrating force in the credit market in the classical model is
A) the interest rate.
B) the price level.
C) full employment.
D) fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an economic downturn, sticky wages and prices reduce the economy's speed of adjustment because
A) businesses are unable to adjust quickly to changes in aggregate demand.
B) they cause deflation.
C) hyperinflation will likely occur.
D) union workers would likely quit and look for work elsewhere.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A temporary increase in the price of oil would
A) increase both short-run and long-run aggregate supply.
B) increase short-run aggregate supply and decrease long-run aggregate supply.
C) decrease short-run aggregate supply and leave long-run aggregate supply unchanged.
D) decrease both short-run and long-run aggregate supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Keynes, the "stickiness" of wage rates could best be explained by
A) minimum wage laws.
B) unions and long-term labor contracts.
C) short-term labor contracts.
D) government interference.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Individuals will increase their saving as
A) the interest rate falls.
B) business investment falls.
C) the rate of inflation increases.
D) the interest rate increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the classical theory, the aggregate supply curve is
A) downward sloping.
B) horizontal.
C) upward sloping.
D) vertical.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in tastes for U.S. produced goods will
A) shift both the aggregate demand curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve.
C) shift the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) shift the long-run aggregate supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to classical economists, the credit market reaches an equilibrium when
A) planned investment equals government expenditures.
B) desired investment equals planned investment.
C) desired investment equals planned changes in aggregate supply.
D) desired investment equals desired saving.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Say's law explains
A) how long-term real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) stability is achieved in the classical model.
B) how long-run real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) stability is achieved in the Keynesian model.
C) how the economy can go into recession.
D) why economies experience business cycles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the above figure. Which point or points represent(s) a short-run equilibrium?
A) A only
B) B only
C) C only
D) both A and B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the classical model,
A) unemployment will never exist since workers will be willing to accept lower wages and will then be able to find work.
B) unemployment will never exist because employers will be willing to pay the wage rate demanded by the workers.
C) wages will go up but never go down.
D) full employment will never be reached.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the classical model, desired saving is
A) a function of real GDP.
B) equal to desired investment.
C) identical to the demand for saving at each level of real GDP.
D) affected by the money illusion at low income levels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If equilibrium level of real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is greater than the full-employment real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) consistent with the position of the economy's long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve, then the difference between full-employment real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and current equilibrium real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is
A) an aggregate demand shock.
B) the level of output consistent with natural unemployment.
C) a recessionary gap.
D) an inflationary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A short-lived increase in oil prices caused by destruction of oil-producing and oil-refining facilities by a large hurricane will
A) shift the SRAS curve to the right.
B) shift the LRAS curve to the right.
C) shift the SRAS curve to the left.
D) shift the AD curve to the right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a reason why real GDP can be expanded beyond a level consistent with its long-run growth path in modern Keynesian analysis?
A) In the short run, existing workers can work more hours.
B) Prices and wages are flexible, allowing for needed adjustments.
C) The existing capital stock can be used more intensively.
D) Higher prices induce firms to hire more workers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
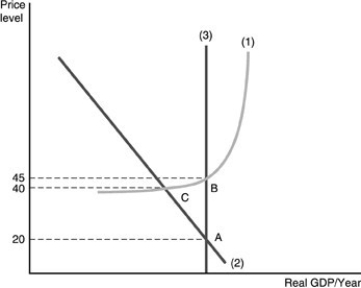 -The three curves in the above figure are
-The three curves in the above figure are
A) (1) the long-run aggregate supply curve, (2) the aggregate demand curve, and (3) the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) (1) the long-run aggregate supply curve, (2) the short-run aggregate supply curve, and (3) the aggregate demand curve.
C) (1) the short-run aggregate supply curve, (2) the aggregate demand curve, and (3) the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) (1) the aggregate supply curve, (2) the short-run aggregate demand curve, and (3) the long-run aggregate demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 321 - 340 of 368
Related Exams