A) cyclically unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) frictionally unemployed.
D) discouraged workers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the adult population is 6 million, the number of employed is 3.8 million, and the labor-force participation rate is 70%. What is the unemployment rate?
A) 6.7%
B) 9.5%
C) 10.5%
D) 28%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of efficiency wages provides a possible explanation as to why
A) workers form unions.
B) firms should try to reduce surpluses of labor.
C) firms may be inclined to keep their workers' wages above the equilibrium level.
D) firms may be inclined to keep their workers' wages below the equilibrium level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If all workers and all jobs were the same such that all workers were equally well suited for all jobs, then job search would not be a problem.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics computes labor-force participation rates for the entire adult population and for more narrowly defined groups.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If all workers and all jobs were the same such that all workers were equally well suited for all jobs, then there would be no frictional unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the number of people unemployed rose but the number of people employed and the adult population stayed the same, then the labor force participation rate would rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported in 2005 that there were 28.19 million people over age 25 who had no high school degree or its equivalent, 11.73 million of whom were employed and 1.04 million of whom were unemployed. What were the labor-force participation rate and the unemployment rate for this group?
A) 45.3% and 3.7%
B) 45.3% and 8.1%
C) 41.6% and 3.7%
D) 41.6% and 8.1%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics' U-5 measure of joblessness is the official unemployment rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Caitlin is an unpaid worker in her family's bakery. The Bureau of Labor Statistics counts Caitlin as
A) unemployed and in the labor force.
B) unemployed and not in the labor force.
C) employed and in the labor force.
D) employed and not in the labor force.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 10-4
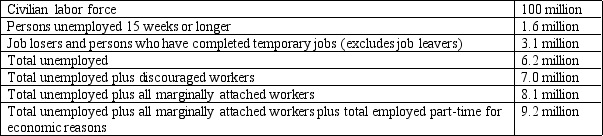 -Refer to Table 10-4. What is the U-5 measure of labor underutilization?
-Refer to Table 10-4. What is the U-5 measure of labor underutilization?
A) 7.5 percent
B) 7.9 percent
C) 8.1 percent
D) 26 percent
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
More generous unemployment insurance would
A) raise structural unemployment.
B) raise frictional unemployment.
C) lower structural unemployment.
D) lower frictional unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an unemployed person quits looking for work, then, eventually the unemployment rate
A) decreases and the labor-force participation rate is unaffected.
B) and the labor-force participation rate both decrease.
C) is unaffected and the labor-force participation rate decreases.
D) and the labor-force participation rate are both unaffected.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who is included in the labor force by the Bureau of Labor Statistics?
A) Chris, an unpaid homemaker not looking for other work
B) Marcus, a full-time student not looking for work
C) Gabe, who does not have a job, but is looking for work
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A firm might offer efficiency wages in order to attract a better pool of applicants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were told that someone you knew nothing else about had just become unemployed, your best guess would be
A) that they would be unemployed for a long time, and that most of the unemployed they've joined have been unemployed for a long time.
B) that they would be unemployed for a long time, even though most of the unemployed they've joined have been unemployed for a short time.
C) that they would be unemployed for a short time, even though most of the unemployed they've joined have been unemployed for a long time.
D) that they will be unemployed for a short time, and that most of the unemployed they've joined have been unemployed for a short time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unemployment insurance
A) may improve the ability of the economy to match workers with appropriate jobs.
B) reduces the job search efforts of the unemployed.
C) increases the amount of frictional unemployment in the economy.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bob is looking for work after school, but everywhere he fills out an application, the managers say they always have a lot more applications than open positions. Tom has a law degree. Several firms have made him offers, but he thinks he might be able to find a firm where his talents could be put to better use.
A) Bob and Tom are both frictionally unemployed.
B) Bob and Tom are both structurally unemployed.
C) Bob is frictionally unemployed, and Tom is structurally unemployed.
D) Bob is structurally unemployed, and Tom is frictionally unemployed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the theory of efficiency wages, if a firm stops paying efficiency wages it is likely to see
A) an increase in the number of job applicants and an increase in how long workers stay on the job
B) an increase in the number of job applicants and a decrease in how long workers stay on the job
C) a decrease in the number of job applicants and an increase in how long workers stay on the job
D) a decrease in the number of job applicants and a decrease in how long workers stay on the job
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The adult population must equal the sum of the employed, the unemployed, and those not in the labor force.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 541 - 560 of 562
Related Exams