A) 12
B) 11
C) 10
D) 9
E) 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Polysaccharides, triacylglycerides, and proteins are similar in that they
A) are synthesized from monomers by the process of hydrolysis.
B) are synthesized from subunits by dehydration reactions.
C) are synthesized as a result of peptide bond formation between monomers.
D) are decomposed into their subunits by dehydration reactions.
E) all contain nitrogen in their monomer building blocks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Figure 3.12 to answer the following questions.
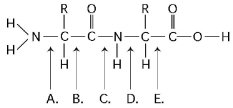 Figure 3.12
-At which bond would water need to be added to achieve hydrolysis of the peptide, back to its component amino acids?
Figure 3.12
-At which bond would water need to be added to achieve hydrolysis of the peptide, back to its component amino acids?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
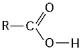 Figure 3.2
-What is the name of the functional group shown in Figure 3.2?
Figure 3.2
-What is the name of the functional group shown in Figure 3.2?
A) carbonyl
B) ketone
C) aldehyde
D) carboxyl
E) hydroxyl
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The tertiary structure of a protein is the
A) bonding together of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds.
B) order in which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain.
C) unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide.
D) organization of a polypeptide chain into an α helix or β pleated sheet.
E) overall protein structure resulting from the aggregation of two or more polypeptide subunits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
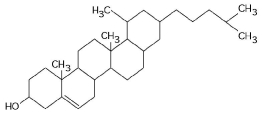 Figure 3.10
-What is the structure shown in Figure 3.10?
Figure 3.10
-What is the structure shown in Figure 3.10?
A) pentose molecule
B) fatty acid molecule
C) steroid molecule
D) oligosaccharide molecule
E) phospholipid molecule
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
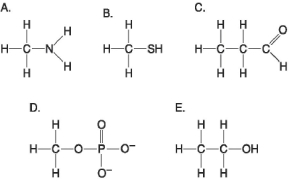 Figure 3.6
-Which molecule shown in Figure 3.6 contains a functional group that cells use to transfer energy between organic molecules?
Figure 3.6
-Which molecule shown in Figure 3.6 contains a functional group that cells use to transfer energy between organic molecules?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A carbon atom is most likely to form which of the following bonds with other atoms?
A) ionic bond
B) hydrogen bond
C) covalent bond
D) covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds
E) ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What maintains the secondary structure of a protein?
A) peptide bonds
B) hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one peptide bond and the carboxyl group of another peptide bond
C) disulfide bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) hydrogen bonds between the R groups
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula for a molecule made by linking three glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions?
A) C18H36O18
B) C18H32O16
C) C6H10O5
D) C18H10O15
E) C3H6O3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are 20 different amino acids. What makes one amino acid different from another?
A) different side chains (R groups) attached to a carboxyl carbon
B) different side chains (R groups) attached to the amino groups
C) different side chains (R groups) attached to an α carbon
D) different structural and optical isomers
E) different asymmetric carbons
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true for the class of biological molecules known as lipids?
A) They are insoluble in water.
B) They are made from glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphate.
C) They contain less energy than proteins and carbohydrates.
D) They are made by dehydration reactions.
E) They contain nitrogen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following hydrocarbons has a double bond in its carbon skeleton?
A) C3H8
B) C2H6
C) CH4
D) C2H4
E) C2H2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of both starch and cellulose?
A) They are both polymers of glucose.
B) They are cis-trans isomers of each other.
C) They can both be digested by humans.
D) They are both used for energy storage in plants.
E) They are both structural components of the plant cell wall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires
A) the release of a water molecule.
B) the release of a carbon dioxide molecule.
C) the addition of a nitrogen atom.
D) the addition of a water molecule.
E) the release of a nitrous oxide molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
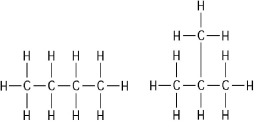 Figure 3.1
-The two molecules shown in Figure 3.1 are best described as
Figure 3.1
-The two molecules shown in Figure 3.1 are best described as
A) optical isomers.
B) enantiomers.
C) structural isomers.
D) cis-trans isomers.
E) chain length isomers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNAase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides together. What would first happen to DNA molecules treated with DNAase?
A) The two strands of the double helix would separate.
B) The phosphodiester bonds between deoxyribose sugars would be broken.
C) The purines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
D) The pyrimidines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
E) All bases would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 3.6
-Which molecule shown in Figure 3.6 contains an amino functional group, but is not an amino acid?
Figure 3.6
-Which molecule shown in Figure 3.6 contains an amino functional group, but is not an amino acid?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are polysaccharides except
A) lactose.
B) glycogen.
C) chitin.
D) cellulose.
E) amylopectin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of covalent bond between amino acid side chains (R groups) functions in maintaining a polypeptide's specific three-dimensional shape?
A) ionic bond
B) hydrophobic interaction
C) van der Waals interaction
D) disulfide bond
E) hydrogen bond
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 121
Related Exams