A) RNA nucleotides are more unstable than DNA nucleotides.
B) Replication of their genomes does not involve proofreading.
C) RNA viruses replicate faster.
D) RNA viruses can incorporate a variety of nonstandard bases.
E) RNA viruses are more sensitive to mutagens.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Viral envelopes can best be analyzed with which of the following techniques?
A) use of 15N to label specific nucleotides
B) antibodies against specific proteins not found in the host membranes
C) DNA staining and visualization with the light microscope
D) use of plaque assays for quantitative measurement of viral titer
E) immunofluorescent tagging of capsid proteins
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the few questions. The herpesviruses are very important enveloped DNA viruses that cause disease in all vertebrate species and in some invertebrates such as oysters. Some of the human ones are herpes simplex virus (HSV) types I and II, causing facial and genital lesions, and the varicella zoster virus (VSV) , causing chicken pox and shingles. Each of these three actively infects nervous tissue. Primary infections are fairly mild, but the virus is not then cleared from the host; rather, viral genomes are maintained in cells in a latent phase. The virus can then reactivate, replicate again, and be infectious to others. -If scientists are trying to use what they know about HSV to devise a means of protecting other people from being infected, which of the following would have the best chance of lowering the number of new cases of infection?
A) vaccination of all persons with preexisting cases
B) interference with new viral replication in preexisting cases
C) treatment of the HSV lesions to shorten the breakout
D) medication that destroys surface HSV before it gets to neurons
E) education about avoiding sources of infection
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
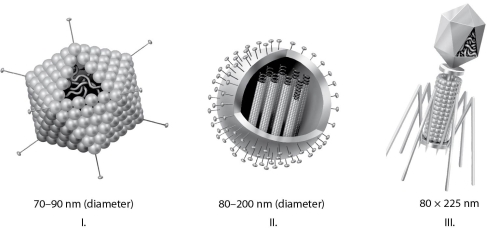 Figure 17.1
-Which of the three types of viruses shown in Figure 17.1 would you expect to include glycoproteins?
Figure 17.1
-Which of the three types of viruses shown in Figure 17.1 would you expect to include glycoproteins?
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) all three
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the best predictor of how much damage a virus causes?
A) ability of the infected cell to undergo normal cell division
B) ability of the infected cell to carry on translation
C) whether the infected cell produces viral protein
D) whether the viral mRNA can be transcribed
E) how much toxin the virus produces
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
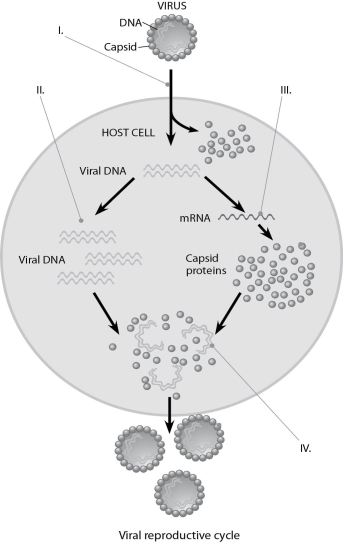 Figure 17.2
-In Figure 17.2, at the arrow marked II, what enzyme(s) are being utilized?
Figure 17.2
-In Figure 17.2, at the arrow marked II, what enzyme(s) are being utilized?
A) reverse transcriptase
B) viral DNA polymerase
C) host cell DNA polymerase
D) host cell RNA polymerase
E) host cell DNA and RNA polymerases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes the lysogenic cycle of lambda (λ) phage?
A) After infection, the viral genes immediately turn the host cell into a lambda-producing factory, and the host cell then lyses.
B) Most of the prophage genes are activated by the product of a particular prophage gene.
C) The phage genome replicates along with the host genome.
D) Certain environmental triggers can cause the phage to exit the host genome, switching from the lytic to the lysogenic.
E) The phage DNA is incorporated by crossing over into any nonspecific site on the host cell's DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 17.2
-In Figure 17.2, when new viruses are being assembled (IV) , what mediates the assembly?
Figure 17.2
-In Figure 17.2, when new viruses are being assembled (IV) , what mediates the assembly?
A) host cell chaperones
B) assembly proteins coded for by the host nucleus
C) assembly proteins coded for by the viral genes
D) viral RNA intermediates
E) nothing; they self-assemble
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below. Some viruses can be crystallized and their structures analyzed. One such virus is yellow mottle virus, which infects beans. This virus has a single-stranded RNA genome containing about 6,300 nucleotides. Its capsid is 25-30 nm in diameter and contains 180 identical capsomeres. -If the yellow mottle virus capsid has 20 facets, how many proteins form each facet?
A) 1
B) 5
C) 9
D) 20
E) 180
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most molecular biologists think that viruses originated from fragments of cellular nucleic acid. Which of the following observations supports this theory?
A) Viruses contain either DNA or RNA.
B) Viruses are enclosed in protein capsids rather than plasma membranes.
C) Viruses can reproduce only inside host cells.
D) Viruses can infect both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
E) Viral genomes are usually similar to the genome of the host cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes plant virus infections?
A) They can be controlled by the use of antibiotics.
B) They are spread via the plasmodesmata.
C) They have little effect on plant growth.
D) They are seldom spread by insects.
E) They can never be passed vertically.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which viruses have single-stranded RNA that acts as a template for DNA synthesis?
A) lytic phages
B) proviruses
C) viroids
D) bacteriophages
E) retroviruses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the few questions. The herpesviruses are very important enveloped DNA viruses that cause disease in all vertebrate species and in some invertebrates such as oysters. Some of the human ones are herpes simplex virus (HSV) types I and II, causing facial and genital lesions, and the varicella zoster virus (VSV) , causing chicken pox and shingles. Each of these three actively infects nervous tissue. Primary infections are fairly mild, but the virus is not then cleared from the host; rather, viral genomes are maintained in cells in a latent phase. The virus can then reactivate, replicate again, and be infectious to others. -In electron micrographs of HSV infection, it can be seen that the intact virus initially reacts with cell-surface proteoglycans, then with specific receptors. This is later followed by viral capsids docking with nuclear pores. Afterward, the capsids go from being full to being "empty." Which of the following best fits these observations?
A) Viral capsids are needed for the cell to become infected; only the capsids enter the nucleus.
B) The viral envelope is not required for infectivity, since the envelope does not enter the nucleus.
C) Only the genetic material of the virus is involved in the cell's infectivity, and is injected like the genome of a phage.
D) The viral envelope mediates entry into the cell, the capsid enters into the nuclear membrane, and the genome is all that enters the nucleus.
E) The viral capsid mediates entry into the cell, and only the genomic DNA enters the nucleus, where it may or may not replicate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between vertical and horizontal transmission of plant viruses is that
A) vertical transmission is transmission of a virus from a parent plant to its progeny, and horizontal transmission is one plant spreading the virus to another plant.
B) vertical transmission is the spread of viruses from the upper leaves to the lower leaves of the plant, and horizontal transmission is the spread of a virus among leaves at the same general level.
C) vertical transmission is the spread of viruses from trees and tall plants to bushes and other smaller plants, and horizontal transmission is the spread of viruses among plants of similar size.
D) vertical transmission is the transfer of DNA from one type of plant virus to another, and horizontal transmission is the exchange of DNA between two plant viruses of the same type.
E) vertical transmission is the transfer of DNA from a plant of one species to a plant of a different species, and horizontal transmission is the spread of viruses among plants of the same species.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the treatments listed below to answer the following questions. You isolate an infectious substance that is capable of causing disease in plants, but you do not know whether the infectious agent is a bacterium, virus, viroid, or prion. You have four methods at your disposal that you can use to analyze the substance in order to determine the nature of the infectious agent. I. treating the substance with nucleases that destroy all nucleic acids and then determining whether it is still infectious II. filtering the substance to remove all elements smaller than what can be easily seen under a light microscope III. culturing the substance by itself on nutritive medium, away from any plant cells IV. treating the sample with proteases that digest all proteins and then determining whether it is still infectious -If you already knew that the infectious agent was either a viroid or a prion, which treatment would allow you to distinguish between these two possibilities?
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) IV only
E) either I or IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 35 of 35
Related Exams