A) cause the membrane to hyperpolarize and then depolarize.
B) can undergo temporal and spatial summation.
C) are triggered by a depolarization that reaches threshold.
D) move at the same speed along all axons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Figure 37.1, the minimum graded depolarization needed to operate the voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels is indicated by the label
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) E.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a simple synapse, neurotransmitter chemicals are released by
A) the dendritic membrane.
B) the presynaptic membrane.
C) axon hillocks.
D) cell bodies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chemical that affects neuronal function but is not stored in presynaptic vesicles is
A) acetylcholine.
B) epinephrine.
C) endorphin.
D) nitric oxide.
E) GABA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cation that is more abundant as a solute in the cytosol of a neuron than it is in the interstitial fluid outside the neuron is
A) HCO3-.
B) Cl-.
C) Ca2+.
D) Na+.
E) K+.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Self-propagation and refractory periods are typical of
A) action potentials.
B) graded hyperpolarizations.
C) excitatory postsynaptic potentials.
D) inhibitory postsynaptic potentials.
E) resting potentials.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ATP hydrolysis directly powers the movement of
A) K+ out of cells.
B) Na+ out of cells.
C) Na+ into cells.
D) Ca2+ into cells.
E) Cl- into cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The point of connection between two communicating neurons is called the
A) axon hillock.
B) dendrite.
C) synapse.
D) cell body.
E) axon.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A graded hyperpolarization of a membrane can be induced by
A) increasing its membrane's permeability to Na+.
B) decreasing its membrane's permeability to H+.
C) decreasing its membrane's permeability to Cl-.
D) increasing its membrane's permeability to Ca2+.
E) increasing its membrane's permeability to K+.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptors for neurotransmitters are of primary functional importance in assuring one-way synaptic transmission because they are mostly found on the
A) axonal membrane.
B) axon hillock.
C) postsynaptic dendritic membrane.
D) presynaptic membrane.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The botulinum toxin inhibits the synaptic release of
A) acetylcholine.
B) epinephrine.
C) endorphin.
D) nitric oxide.
E) GABA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a particular neurotransmitter causes an IPSP in postsynaptic cell X and an EPSP in postsynaptic cell Y. A likely explanation is that
A) the threshold value in the postsynaptic membrane is different for cell X and cell Y.
B) the axon of cell X is myelinated, but that of cell Y is not.
C) only cell Y produces an enzyme that terminates the activity of the neurotransmitter.
D) cells X and Y express different receptor molecules for this particular neurotransmitter.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Researchers injected bark scorpion venom in mouse neurons (both a common house mouse and the southern grasshopper mouse) and measured how many action potentials were generated after the venom was introduced. Their data is shown below. 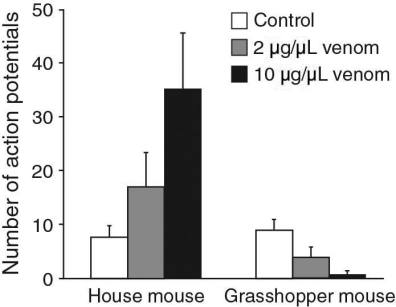 Based on these data, what effect do you think the venom is having on the grasshopper mouse?
Based on these data, what effect do you think the venom is having on the grasshopper mouse?
A) The venom is blocking voltage-gated sodium channels.
B) The venom is blocking voltage-gated potassium channels.
C) The venom is opening voltage-gated sodium channels.
D) The venom is opening voltage-gated potassium channels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The operation of the sodium-potassium "pump" moves
A) sodium and potassium ions into the cell.
B) sodium and potassium ions out of the cell.
C) sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out of the cell.
D) sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell.
E) sodium and potassium ions into the mitochondria.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nucleus and most of the organelles in a neuron are located in the
A) dendrites.
B) axon hillock.
C) axon.
D) cell body.
E) axon terminals.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following steps refer to various stages in transmission at a chemical synapse. 1) Neurotransmitters bind with receptors associated with the postsynaptic membrane. 2) Calcium ions rush into the neuron's cytoplasm. 3) An action potential depolarizes the membrane of the axon terminal. 4) The ligand-gated ion channels open. 5) The synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. Which sequence of events is correct?
A) 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5
B) 2 → 3 → 5 → 4 → 1
C) 3 → 2 → 5 → 1 → 4
D) 4 → 3 → 1 → 2 → 5
E) 5 → 1 → 2 → 4 → 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Functionally, which cellular location is the neuron's "decision-making site" as to whether or not an action potential will be initiated?
A) axonal membrane
B) axon hillock
C) dendritic membrane
D) presynaptic membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When several excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) arrive at the axon hillock from different dendritic locations and then depolarize the postsynaptic cell to threshold for an action potential, this is an example of
A) temporal summation.
B) spatial summation.
C) a normal action potential.
D) an action potential with an abnormally high peak of depolarization.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that excessive consumption of ethanol increases the influx of negative chloride ions into "commonsense" neurons whose action potentials are needed for you to act appropriately and not harm yourself or others. Thus, any resulting poor decisions associated with ethanol ingestion are likely due to
A) increased membrane depolarization of "commonsense" neurons.
B) increased membrane hyperpolarization of "commonsense" neurons.
C) more action potentials in your "commonsense" neurons.
D) more EPSPs in your "commonsense" neurons.
E) fewer IPSPs in your "commonsense" neurons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An amino acid that operates at inhibitory synapses in the brain is
A) acetylcholine.
B) epinephrine.
C) endorphin.
D) nitric oxide.
E) GABA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 76
Related Exams